The endocrinological status of a person is unthinkable without the function of the thymus gland. The gland in Latin is thymus, so it is also called by another name - & nbsp; thymus. The thymus gland is located in the upper part of the chest cavity behind the body of the sternum. The gland consists of two lobes. The body of the gland expands from below and is adjacent to the heart, pericardium and large vessels.
The thymus gland in embryogenesis develops in the region of the 3rd pharyngeal pocket in the form of an outgrowth and is a derivative of the prechordial plate. All its derivatives are very similar to the epidermis of the skin.
Age-related changes in the thymus gland. Gland involution
With age, the size of the thymus changes, which is the norm. After birth, the thymus begins to grow rapidly and increase in size.
The process of growth and differentiation of the thymus lasts up to 15 years, after which age-related involution occurs. The process of involution is characterized by a decrease in the mass of the thymus gland.
The elements are replaced by connective tissue, while the silhouette of the gland is preserved. Atrophy of the lateral parts of the gland. In cases where the thymus does not decrease with age, and in adolescence the thymus gland is larger than that of peers, we are talking about thymomegaly.
The thymus gland secretes the following substances into the bloodstream:
- thymalin;
- thymosin;
- thymopoietin;
- insulin-like growth factor – 1;
- thymic humoral factor, which has a direct effect on T – lymphocytes.
Anatomical structure and functions of the thymus gland
The thymus is covered from above with a capsule, from which the septa extend inside the gland, dividing it into lobules. Each lobule contains cortex and medulla. Thymocytes are found in the cortex. The medulla is characterized by compacted and keratinized cells.
The thymus gland provides the T-lymphocytes that have entered it with protective properties. Epithelial cells in thymus lobules secrete a hormone that regulates the conversion of lymphocytes in the thymus gland. In adulthood, a violation of immunological processes in the thymus often develops, which is called thymico – lymphatic status. What are the dangers of such a condition, read further on estet-portal.com.
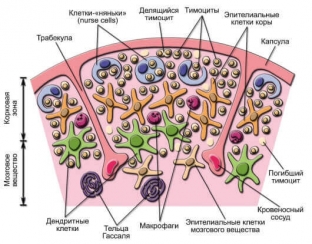
Violation of the structure or function of the thymus gland leads to inferiority of the reactivity of the body and the entire immune system. This condition can cause death during surgery using anesthesia.
Thymus, turning stem cells into T – lymphocytes, controls cellular immunity. The thymus gland is supplied with blood by arteries that originate from the thoracic trunk. The gland has a large network of lymphatic vessels and nodes.
Thus, the thymus gland is the central organ of the immune system. You can learn more about such a pathology as thymomegaly in our next article.







Add a comment