Practitioners are well aware that the correction of the zygomatic area and nasolacrimal sulci is necessary for rejuvenation of the middle third of the face. This approach helps patients with complaints of tired appearance and age-related changes in this area.
At the same time, Dr. Pierre-Jacques Ackermann (Pierre Jacques Ackermann) believes that in some cases, harmonization of the face may be more appropriate than the correction of a specific zone.
Thus, injections of botulinum toxin into the masticatory muscle allow narrowing the lower part of the face and emphasizing the volume of the cheeks, thereby providing beautification of the middle third of the face.
Peculiarities of aging of the middle third of the face
Aging in this area is associated with changes in 4 anatomical structures:
1. Loss of elasticity and sagging skin.
2. Decrease in tone and weakening of muscles under the influence of gravity.
3. Shift of deep and superficial fat along the vertical axis, especially in the zygomatic zone.
4. Bone tissue degeneration.
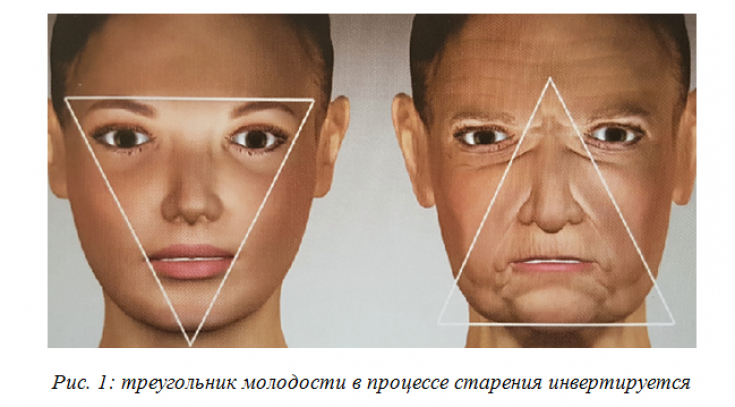

Age-related structural changes affect predominantly the periorbital and central zygomatic zones, including the superomedial and inferolateral parts of the orbit, the medial suborbital and piriform part of the maxilla, and the premaxillary region.
Follow us on Instagram!
This aging is called skeletalization of the face, in which there is sagging of the lower third and the formation of irregularities in the lower part of the oval of the face (most often after 50 years). In most cases, the practitioner can perform correction with HA-based dermal fillers, biostimulants, or lipofilling.
Botulinum Toxin Type A Injections into Masticatory Muscles: Aesthetic Masseters Concept
What if a patient seeks a mid-face correction, but there is no loss of volume in this area (Fig. 2)?
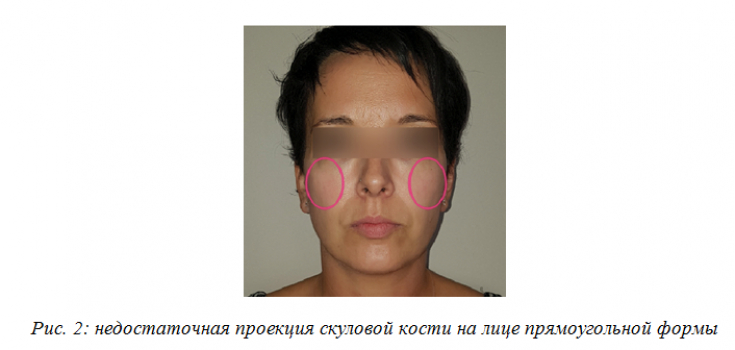
In this case, the author proposes not to restore the middle third of the face, but to emphasize it. This is possible if the patient has a sufficient volume of the zygomatic bone, but the features of the middle third of the face are "lost"; against the general background of a rectangular face. In order to harmonize, only the mandibular zone is corrected by injecting botulinum toxin type A into the masticatory muscles – the so-called Aesthetic Masseters concept.
The Aesthetic Masseters concept is relevant for masseter hypertrophy, and also suitable for patients with a rectangular or square face shape with insufficient projection of the zygomatic bone.

To propose such a procedure, the practitioner must conduct a detailed analysis of the face, considering the middle and lower thirds of the face as a whole, rather than in isolation. It is also necessary to first perform a correction in the area of the cheekbones and the nasolacrimal sulcus, and only then proceed to work with the nasopharyngeal folds.
Injection of botulinum toxin type A into the masticatory muscle does not affect the thickness of the subcutaneous tissues from the surface of the skin to the masseter muscle, the drug only affects the thickness of the muscle.
Beautification of the middle third of the face with botulinum toxin injections
Based on his own observations, the author concluded that the correction of the medial third, part of the face, consisting mainly of the zygomatic bone and the nasolacrimal groove – necessary step for facial rejuvenation.
However, in many cases the results did not meet the author's expectations and, worse, despite proper lateralization and projection of the zygomatic bone, the patients were dissatisfied. Moreover, due to volition, the face of such patients seemed excessively large.
The solution to the problem was found when the author began using botulinum toxin type A to treat bruxism or masseter hypertrophy.
In masticatory muscle hypertrophy, the distance between the two angles of the mandible is greater than the distance between the two zygomatic eminences, which is the definition of the inverted triangle of youth (inverted V).
Injections of botulinum toxin type A into masticatory muscles reduce their volume by about 30% and allow you to restore the lower third in accordance with modern standards of femininity. Thus, harmony is achieved between the middle and lower thirds of the rectangular face.

The author took into account 3 main criteria:
1. Two lines:
• two vertical lines, on the right and on the left, between the zygomatic eminence and the angle of the lower jaw are completely or almost parallel;
• the author also added a second line from the ear to the mandibular angle, however the results were not satisfactory.
2. The curvature of the zygomatic bone.
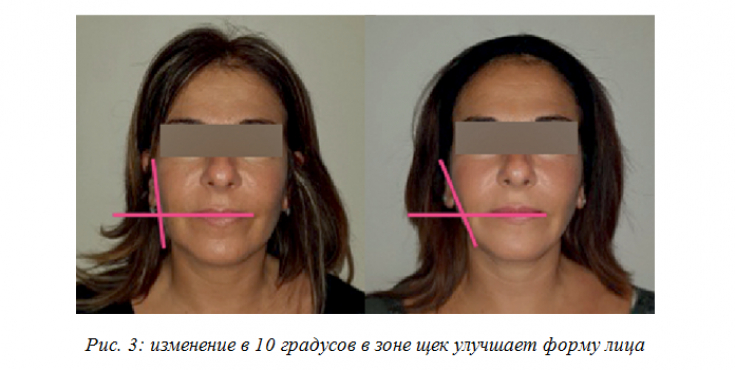
3. The angle formed by a vertical line running from the zygomatic eminence to the mandibular angle and a horizontal line that crosses the lips. This angle in the cases described below is equal to 90 & ndash; 95 degrees.
The third of the above criteria, according to the author, is most suitable for evaluating the result of the correction.
Satisfactory result – increase the angle by 10 degrees (Fig. 3).
Correction of the middle third of the face and complications after injections After injection of botulinum toxin into the masticatory muscles, the results were in line with the author's expectations: after reducing the width of the lower third of the face, the middle third seemed more voluminous and clear. It is important to remember that before this, the middle third of the face was uniform, had a good projection, but at the same time it was “lost”; in general against the background of a rectangular face.
With the help of this procedure, it was possible to create the necessary shape and make the zygomatic elevation more pronounced. Patients were satisfied with the results (Figure 4).
Patients and MethodsIn the course of the study at the author's clinic, 4 cases (8 masticatory muscles) were examined for the period from October to December 2017.
The group of patients consisted of 4 women (35-50 years old, mean 41 years old). Previously, patients did not receive injections of botulinum toxin type A in this area, which excludes its effect on the masticatory muscle.
Clinical evaluation was performed by inspection and palpation of the masseter muscle during jaw clenching and at rest. MRI was used to measure masseter muscle thickness in three dimensions before and 3 months after injection of botulinum toxin type A.
Read also:Anatomy of botulinum therapy: aesthetic correction of the lower third of the face
Procedure descriptionAll patients were injected with 25 units of botulinum toxin type A on each side of the face.
The drug was injected at five points, inserting the needle perpendicular to the skin to full depth. In 20% of cases, ultrasound showed that a longer needle had to be used to insert into the muscle (Figures 5 and 6).
For three months, patients were contacted by phone every two weeks and every month the patients came for follow-up examinations. Purpose of observation – do not evaluate the duration of the effect, but confirm the reduction in masseter muscle volumes using MRI.
At each visit, patients were photographed and warned to report any side effects.
The midface beautification procedure described above is characterized by a high level of patient satisfaction and safety, as well as a minimal complication rate.
ResultsThe degree of reduction in masticatory muscle volume varied in different patients and on different parts of the face. The author notes that the reported number of cases is not sufficient to draw definitive conclusions about the effectiveness of botulinum toxin type A. However, the author claims that the reduction in masticatory muscle volume is approximately 30%.
The midface beautification procedure described above is characterized by a high level of patient satisfaction and safety, as well as a minimal complication rate.
According to Prime magazine







Add a comment