Most chronic processes develop as a complication or as a result of incomplete treatment of an acute process. But there are chronic pathologies that were not preceded by an acute course. So, odontogenic sinusitis, unlike other sinusitis, has a primary chronic course. When the maxillary sinus communicates with the oral cavity through the socket of the extracted tooth, symptoms of acute inflammation are often absent. How to identify the symptoms of chronic odontogenic sinusitis, knows estet-portal.com
What are the clinical manifestations of chronic odontogenic sinusitis
The main symptom, which indicates the presence of odontogenic sinusitis, is a purulent discharge from the corresponding half of the nose. Often these secretions have a very unpleasant odor. Headache in odontogenic sinusitis is intermittent, which is explained by the limitation of the process and the periodic release of exudate through the hole in the hole. If the outflow is difficult, the headache is intense and constant, the pain may radiate along the second branch of the trigeminal nerve.
The patient feels a feeling of heaviness in one half of the head on the side of the lesion. Sleep is disturbed, performance decreases, body temperature rises. If chronic odontogenic sinusitis is combined with perimaxillary phlegmon, they do not appear clinically during an exacerbation of the process. Already 1-3 days after the phlegmon opens in the upper jaw, the syndrome of mutual burdening decreases. Only then can the clinical symptoms of sinusitis make themselves felt.
What methods will help diagnose odontogenic sinusitis
Even the most thorough rhinoscopy can not always help to identify traces of purulent discharge in the nasal passage. This is due to the predominant development of a productive form of inflammation. The most informative method for diagnosing chronic odontogenic sinusitis, as well as cysts of the maxillary sinus, is a contrast X-ray examination. This study also allows you to determine the drainage function of the sinus.
But such a study is indicated to the patient only before the planned surgical intervention, since contrast radiography is not removed independently from the sinus, and causes more harm to the patient than good. As a contrast agent, iodolipol is used, which is heated to a temperature of 370C. After puncture of the maxillary sinus and removal of its contents, contrast is injected.
If the shadow of the contrast agent has uneven contours, forms filling defects, this indicates the presence of polyposis formations. Cysts of the maxillary sinus have a filling defect of a rounded shape, and tumors are visualized as separate islets and depressions.
Methods of treatment of chronic odontogenic sinusitis
Chronic odontogenic sinusitis is treated conservatively and surgically.
In the presence of a catarrhal form of sinusitis, the removal of the causative tooth is first shown, then vasoconstrictor drugs and physiotherapy procedures are prescribed – electrophoresis with 10% potassium iodide solution and UHF. If there is exudate in the sinus, it should be evacuated by puncture followed by washing with antiseptic solutions and enzymatic preparations. Washing is carried out daily to clean wash water. Antibiotics are prescribed according to indications. In some cases, a maxillary sinusectomy is performed.
Indications for sinusectomy in case of odontogenic sinusitis:
- lack of effectiveness of conservative treatment;
- presence of a tooth root in the maxillary sinus;
- presence of a proliferative form of sinusitis (polypous sinusitis);
- development of osteomyelitis in the alveolar process of the upper jaw with perforation of the floor of the maxillary sinus.
Method of sinusectomy . Prevention of odontogenic sinusitis
When performing a maxillary sinusectomy, the altered mucous membrane is removed, creating a wide fistula between the maxillary sinus and the lower nasal passage for the outflow of exudate. Currently, the Caldwell-Luke maxillary sinusotomy is the most common sinusotomy technique. Also, in some cases, sparing maxillary sinusectomy is used when there is a high risk of complications.
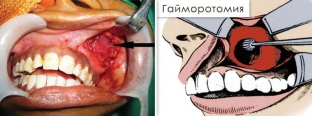
Prevention of chronic odontogenic sinusitis is the timely detection and treatment of dental caries. Special attention should be paid to elderly patients, since odontogenic sinusitis in them is often complicated by the development of cancer of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus.









Add a comment