− one of the most common herpesvirus infections in the world. In most cases, infectious mononucleosis resolves spontaneously and has a favorable prognosis, but sometimes acute complications occur, such as splenic rupture, hepatitis, and severe tonsil enlargement with airway obstruction. Find out in the article on estet-portal.com what serious complications threaten infectious mononucleosis and what are the current approaches to the treatment of this disease.
Early complications of infectious mononucleosis
Liver parenchymal damage occurs in approximately 75% of patients who also report elevated ALT levels during the acute phase of infectious mononucleosis, with ALT levels returning to normal after 3 weeks.
Follow us onInstagram! Cholestatic and chronic hepatitis, which are provoked by the Epstein-Barr virus, are rare complications, but it is advisable to prescribe an analysis for "liver tests" when establishing the diagnosis and during monitoring of patients with severe infectious mononucleosis.
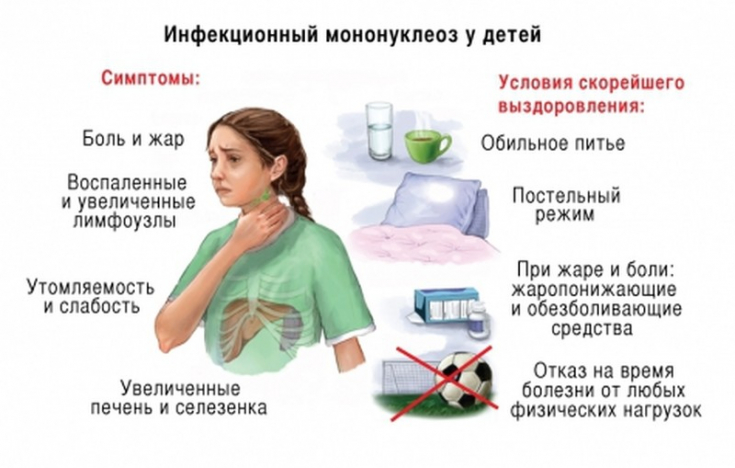
Swollen cervical lymph nodes: correct diagnosis Rupture of the spleen as a result of splenomegaly and altered structure of the organ is the most dangerous and acute complication of infectious mononucleosis. It is, however, a very rare complication with an incidence of 0.1 to 0.5%, with most cases occurring within the first 3 weeks of diagnosis. Peak enlargement of the spleen in infectious mononucleosis is confirmed about 12 days after the onset of symptoms by ultrasound.
Athletes are at high risk of ruptured spleens and should refrain from competing during the first 3 weeks of illness.
Cervical lymphadenopathy is the hallmark of infectious mononucleosis and involves the nasopharynx and palatine tonsils. Epstein-Barr virus edema is estimated to cause airway obstruction in 1-3.5% of cases of infectious mononucleosis and is more common in young children.
Late complications of Epstein-Barr virus
Lymphoproliferative disorders are the most common late complication of infectious mononucleosis and have been investigated in several different cohorts since the 1970s. However, infection with the Epstein-Barr virus does not affect the tactics of treatment, remission is observed in > 85% of cases.
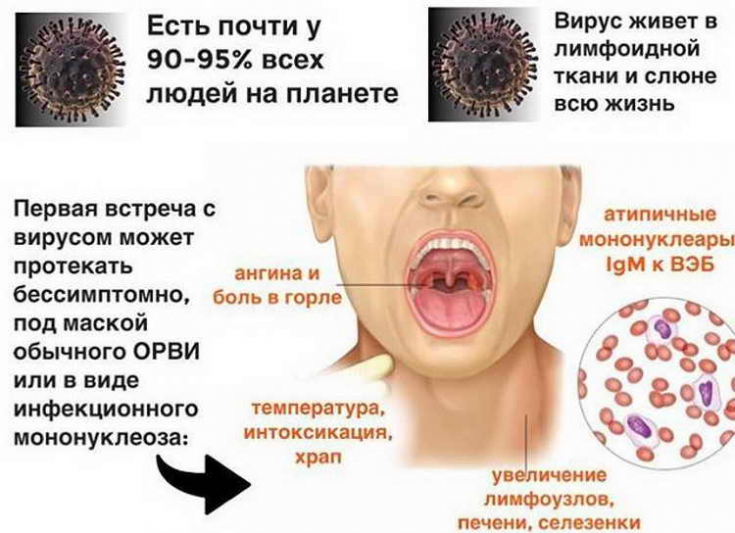
Infectious mononucleosis: modern methods of diagnosing the disease The risk of developing multiple sclerosis is 2.3 times higher in individuals with a history of Epstein-Barr virus infection and infectious mononucleosis in adulthood than in EBV-positive individuals without infectious mononucleosis in the past. The study also showed that the highest incidence is observed in people aged 25-30 years and decreases to almost zero in people 60 years old.
If there really is a causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis, then this supports the notion that EBV vaccination may have the potential to reverse the development of multiple sclerosis.
Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection is a rare condition and is geographically mostly restricted to Japan and East Asia, but has attracted international attention due to an increase in cases worldwide.
Vaccination as the only way to avoid infectious mononucleosis
After initial evaluation of a patient with symptoms suggestive of infectious mononucleosis, a diagnosis is recommended. Treatment should focus on symptomatic relief of general condition and rest. Hospitalization may be required in severe cases of dehydration and risk of airway obstruction.
Ganciclovir in the treatment of cytomegalovirus infection Hepatitis is a common and early complication of infectious mononucleosis that is more likely to resolve spontaneously and should be monitored by liver function test results. Splenic rupture is rare and may occur spontaneously, although most cases occur 3 weeks after diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis, and ultrasound of the spleen provides the best risk assessment.
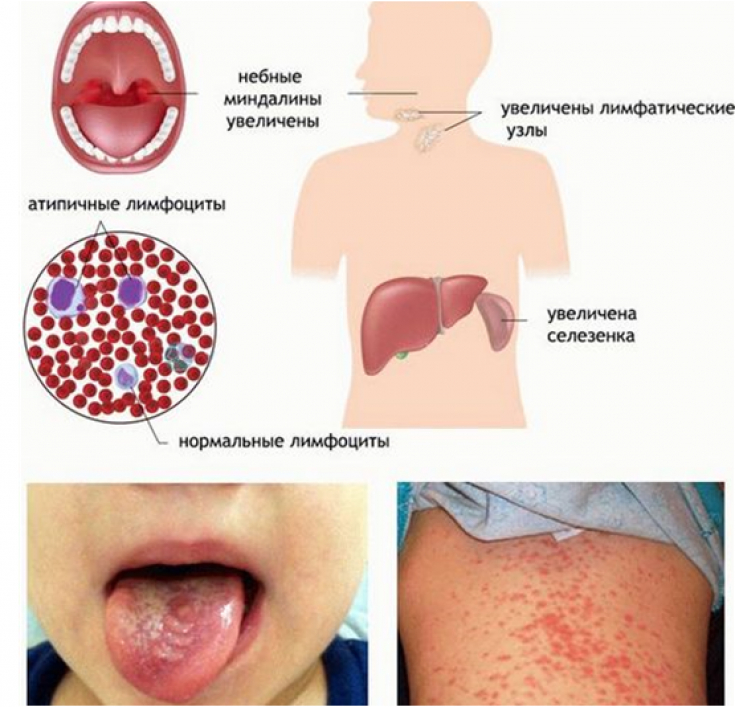
Due to the high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus-infected people worldwide, preventive measures should be prioritized to prevent complications, ideally through vaccination. Modern studies of vaccination have shown success, because in 78% of cases, vaccination prevents the development of infectious mononucleosis.
Fever of Unexplained Origin: Correct Diagnostic Algorithm







Add a comment