– These are cyclic fluctuations in the intensity of physiological processes associated with the change of day and night. It is also known that each organ has its own physiology and internal rhythm of work. Given that many chronic dermatological diseases are associated with impaired tolerance of the immune system or a failure in a certain part of it, scientists have conducted clinical studies that describe the dependence of circadian rhythms and the strength of the immune system response.
Such studies can significantly increase the effectiveness of the treatment of chronic dermatoses and allergies, as well as improve modern treatment regimens. Read about the results of the study at estet-portal.com
Circadian rhythms of the immune response
In a review article presented in Trends in Immunology, researchers from the Biomedical Center of the Ludwig-Maximilian University of Munich and the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Geneva, brought up for discussion the question of the features of the mechanisms of daily control of the body's immune response.
Follow us onInstagram! In their work, the authors collected and analyzed a number of studies, as well as clinical observations, in which the relationship between the circadian rhythm and immune responses was studied.
In particular, there is strong evidence that adaptive immune responses, which are mediated by the activity of highly specialized immune cells and develop over several weeks, are controlled by circadian rhythms.
The researchers believe that such findings should be carefully considered not only in the field of dermatology, immunology and allergology, but also in clinical medicine in general, including their undoubted importance in a wide range of clinical situations − from transplantation to vaccination.
Clinical studies on the effectiveness of intermittent fasting The body responds to various stimuli, including changing light conditions and fluctuations in hormonal levels, which makes it possible to predict the frequency of sleep rhythms, metabolism, and a whole range of physiological processes. Both in humans and animals, the level of leukocytes in the blood is also determined by circadian rhythms.
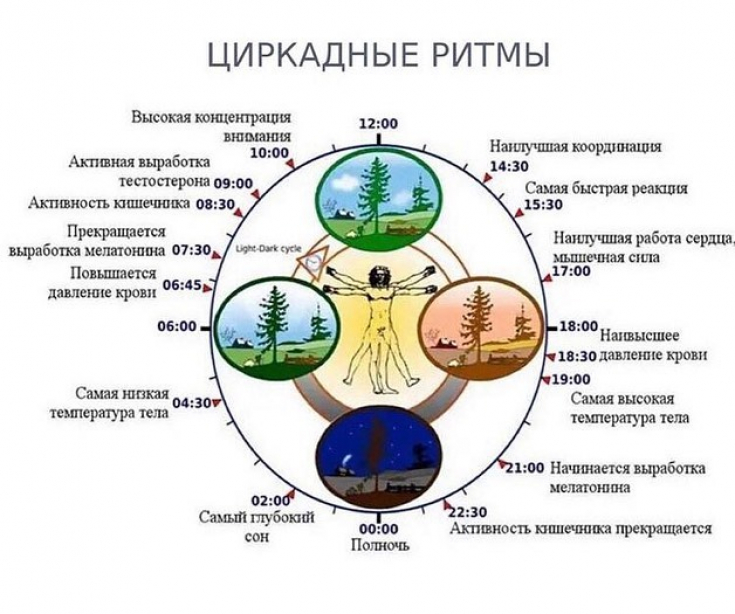
Immunity Circadian Rhythm Research Perspectives
In separate studies, the rhythms of the daily activity of immune cells were compared: under normal physiological conditions, with an inflammatory response and in certain diseases.
How lack of sleep affects the skin
Based on the analyzed data, the authors formulated a number of conclusions about circadian rhythms and the activity of the immune response:1. Despite the known data that the majority of heart attacks occur in the morning hours, it has been found that the clinical course of morning attacks is more severe than at night.
At the same time, in parallel with monocyte activity, animal studies have shown that the level of monocytes in the blood gradually increases during the day.
This allows for effective correction of diseases that are associated with pathological activity or defects in the work of monocytes.
2. Also, among the conclusions of the study, it was noted that the ability of immunocytes to be involved in counteraction processes may depend on CCR2 − a chemokine protein that regulates the body's inflammatory response cascade. During the day, CCR2 levels reach a maximum in the morning, and judging by its effect on immune cells, changes in leukocyte activity have been traced in a number of studies. Previously, the role of this protein in the development of chronic dermatoses, eczema, atopic dermatitis and chronic urticaria has been studied.

3. It has also been proven that the manifestations of allergic symptoms are rhythmic and dependent on circadian rhythms. They intensify between midnight and morning hours (4-6 am). Thus, the molecular biological clock controls the physiological activity of immune cells, and therefore − and consequences of a wide range of allergic diseases.
Skin Circadian Rhythms: Living on a Schedule is Now Fashionable Clinical conclusion on the influence of circadian rhythms on the physiology of the immune system
In conclusion, the authors of the review pointed out that a detailed study of the circadian regulation of innate and adaptive immunity is a powerful tool for fundamental understanding of the physiology of the interaction and sequence of events of immune responses that depend on the time of day.
Biological aging: modern possibilities of non-hormonal "replacement" therapy







Add a comment