Nails − special protective epidermal formations. Convex, transparent, closely adjacent to the back of the terminal phalanges of the fingers.
The pink color of the nails provides a highly vascularized nail bed.
Pathology of the nail plate is observed both in congenital anomalies and in generalized skin diseases, systemic diseases, non-infectious lesions of the nail folds, localized bacterial and fungal infections.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com about the most common congenital and acquired nail pathologies plates, the causes of their occurrence, as well as what skin changes are observed in these diseases.
- The most common pathologies of the nail plate
- Pachyonychia: congenital pathology of the nail plate
- Complex approach to managing patients with congenital pathologies of the nail plates
The most common pathologies of the nail plate
Anonychia − lack of nails – congenital pathology of the nail plate; it can be both isolated and accompany a congenital pathology of the development of the fingers.
Follow us on Instagram!
Leukonychia – pathology of the nail plate, which consists in discoloration: opaque white coloration of the nail plate.
May be spotted, banded, or diffuse.
Leukonychia of all nails is a component of a rare genetic disease that includes:
- epidermal cysts;
- diseases of the kidneys and urinary system;
- deafness.
Other manifestations of nail discoloration accompany a variety of serious childhood pathologies.
Leukonychia. What white spots on nails indicate
Onycholysis – pathology of the nail plate, which consists in its detachment from the nail bed, starting from its distal edge.
Bo Lines – pathology of the nail plate in the form of transverse linear depressions that occur as a result of damage to the growth zone of the nail, which appears near the nail root at the age of 1-1.5 months. and moves distally as it grows.
The disease reflects metabolic changes in the early postnatal period.
Dariaer's disease is characterized by red and white longitudinal stripes that cross the nail hole, sometimes complete leukonychia is observed.
Paronychia − inflammatory damage to the nail folds of staphylococcal or streptococcal etiology.
This pathology of the nail plate is characterized by all signs of inflammation and is treated with antibacterial drugs and symptomatic therapy.
Surgical drainage is sometimes necessary.
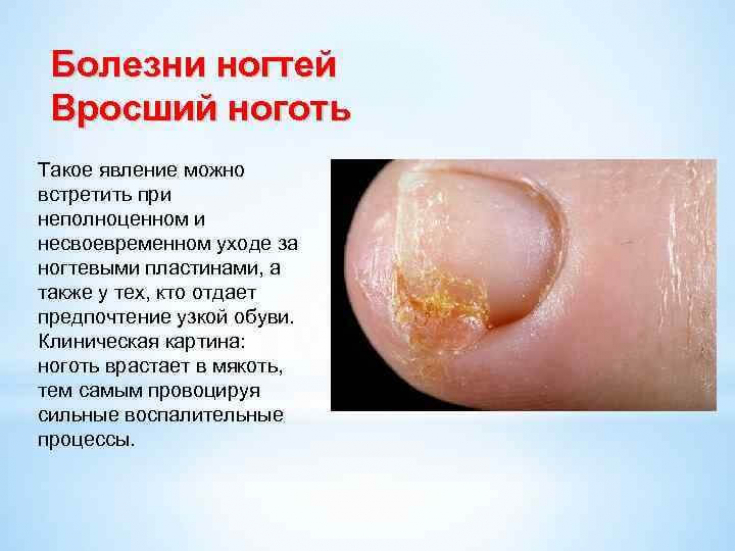
Ingrown toenail – acquired pathology of the nail plate, most often the big toe is damaged.
This is accompanied by pain, erythema and swelling.
Surgical treatment consists in removing the nail plate or its lateral part together with the nail matrix.
− hereditary disease of the fingers of the upper extremities, in which the size of the nails is 1/3-1/2 of the normal. Nail sockets triangular or pyramidal in shape.
The size of the patella is also small, so the knee joint is unstable.
There may be excessive mobility in other joints, flabbiness of the skin, hyperhidrosis, malformations of the kidneys
Treatment of the fungus from the inside: systemic therapy for onychomycosis Pachyonychia: congenital pathology of the nail plate
is present at birth or develops in the first months of life. A hereditary disease, the classic type of which (
Jadasson-Lewandowski syndrome) is manifested by nail dystrophy (thickened, convex). Accumulation of horny detritus is visible under the nail plate.
Almost always there is keratoderma and hyperhidrosis on the palms and soles.
Treatment not always effective, but
emollient ointments, keratolytics (urea, salicylic acid, lactic acid), oral retinoids (isotretinoin, acitretin, etretinate) ). It is important to remove the nail plates and nail matrix, as well as the keratinized mass after baths with sodium chloride solution.
The microbiome in protecting the skin: how bacteria help us live
Dystrophy of twenty nails (trachyonychia)is characterized by the presence of ridges and pits on all nail plates, while they are thin, brittle, cloudy. Sometimes accompanied by alopecia areata, but there are no skin or systemic diseases, and
Diseases of the appendages of the skin is a pathology that is difficult to diagnose and treat.
She demands:
unconditional observance of the sanitary and hygienic conditions of the patients' residence;
- optimum temperature;
- humidity of the environment;
- rational nutrition with a sufficient set of basic ingredients of food enriched with vitamins and microelements.
- It is also necessary to
of such children by a pediatrician, dermatologist, dentist and other related specialists, as well as timely correction of pathological abnormalities. Only under such conditions is it realistic to ensure a satisfactory quality of life for patients with these pathologies and provide them with the opportunity to socialize in an environment where they would be happy next to their parents and peers.







Add a comment