Donovanosis, or venereal granuloma, has been known to doctors since the beginning of the 20th century, when the Irish doctor C. Donovan first described the causative agent of the disease and the features of its transmission. This is a slowly progressive chronic disease, transmitted almost exclusively through sexual contact. The peculiarity of donovanosis is that the disease is manifested by granulomatous ulcerations of the skin, and therefore it is sometimes confused with inguinal lymphogranuloma. Most often, men are ill, and women are characterized by a latent carriage of the infection and severe complications after it. Read about the features of the manifestation of the disease and the principles of treatment of donovanosis at estet-portal.com.
How donovanosis spreads and why it is dangerous
Infection in the form of the so-called Donovan bodies penetrates the body through small defects in the skin and mucous membranes, causing an inflammatory process under the skin. The disease begins with a small papule or swelling, then an abscess forms, turning into an ulcer with abundant granulations.
Researchers believe that the individual susceptibility of the organism to this type of pathogen plays an important role in infection with donovanosis and the course of the disease.
The danger of donovanosis is that pseudo-elephantiasis of the genital organs may occur, narrowing of the urethra and anus may develop, which makes it difficult to defecate and urinate. Women may develop a narrowing of the vagina, men – phimosis and necrosis of the penis. Epidermoid carcinoma is very rarely observed. Women are more likely to suffer from complications of donovanosis.
Characteristic symptoms of donovanosis and their features of manifestation
The incubation period of Donovanosis can be 24 hours, sometimes its first symptoms appear three months after infection, but on average the disease is activated one month after infection. The duration of this period depends primarily on the state of the patient's immune system.
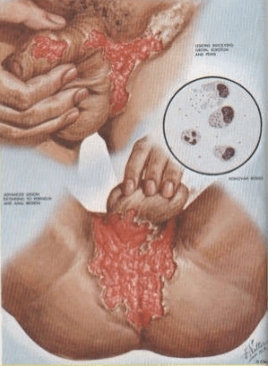 The first symptoms of donovanosis are small bright pink spots at the site of infection. Then the spots turn into red nodules, which grow and in two weeks can reach a diameter of 4 cm. Further, the nodule turns into an ulcer – soft, brown, painless, with a granular bottom and jagged edges, with an unpleasant odor. Such an ulcer can be both superficial and deep, up to the bone, gradually it grows in breadth. If there are several ulcers nearby, they merge.
The first symptoms of donovanosis are small bright pink spots at the site of infection. Then the spots turn into red nodules, which grow and in two weeks can reach a diameter of 4 cm. Further, the nodule turns into an ulcer – soft, brown, painless, with a granular bottom and jagged edges, with an unpleasant odor. Such an ulcer can be both superficial and deep, up to the bone, gradually it grows in breadth. If there are several ulcers nearby, they merge.
With donovanosis, the inguinal folds and the pubic area, perineum, skin around the anus, and inner thighs are affected. Often ulcers spread because the patient touches them with his hands and himself transfers the infection to healthy areas, and also because of the contact of skin surfaces with affected areas. Possible damage to the face, oral cavity. After some time, the ulcers heal, leaving behind rough scars. But this does not mean recovery – new skin lesions soon appear.
Despite severe ulcers, the general condition of the patient almost never worsens, and only in case of tissue necrosis does weakness and fever occur.
Why is it important to treat donovanosis in a timely and adequate manner
Like any venereal disease, donovanosis does not go away on its own, without proper treatment it threatens with unpleasant complications, and if the patient does not seek medical help for a long time, then the disease becomes chronic. Foci of infection may either disappear or reappear, and relapses of the disease are repeated after six months, and sometimes after several years.
The patient should be explained that the doctor selects the antibacterial treatment of donovanosis individually, taking into account the body's sensitivity to certain antibiotics, and therefore self-treatment is unacceptable.
Incomplete antibiotic therapy for donovanosis significantly worsens the prognosis of the disease, forms resistance to drugs and increases the frequency of relapses of the disease.
Donovanosis is recommended to be treated with sulfonamides, broad-spectrum antibiotics. The duration of the course of taking the drugs is approximately 3-4 weeks, depending on the patient's condition. If the disease proceeds without complications, then this course of treatment may be quite enough. In addition, you can prescribe immunomodulators (if necessary), vitamins.
Some time after the full course of Donovanosis therapy, the patient is scheduled for a follow-up examination to confirm the cure.







Add a comment