Before treating synechiae, it is necessary to accurately diagnose the type and location of adhesions. Synechia is diagnosed by an otolaryngologist, and only anterior synechia is revealed during examination. Middle and posterior synechia are detected during rhinoscopy. Probing with a bellied probe makes it possible to establish the nature of the synechia tissue. To clarify concomitant diseases, laryngoscopy, pharyngoscopy, otoscopy are performed, the patency of the auditory tube is checked, and the paranasal sinuses are examined. The etiology of the identified inflammatory diseases helps to establish a bacterial study of smears from the nose and throat. Treatment of synechiae is only surgical.
What methods of surgical treatment of synechiae are used?
Synechiae are removed surgically. Indications for surgical treatment of synechia are significant violations of nasal breathing, since any surgical intervention in the nasal cavity can do more harm than good. An indication for urgent surgical intervention in the nasal cavity in the presence of synechia is their detection in newborns, when synechia is life-threatening, causing respiratory failure.
Synechiae are removed by excision with a scalpel. Bone synechiae are removed using a chisel, and cartilaginous ones are excised using a conchotomy. Synechia removal operations may be accompanied by the removal of the inferior turbinate if necessary. The endoscopic method for the treatment of synechia is more gentle. It is performed under local anesthesia and is characterized by a shorter postoperative period.
In the postoperative period, in order to prevent the recurrence of synechiae, glove rubber, celluloid or special foil is introduced into the nasal cavity. Also for this purpose, a skin flap on a leg is used, which is fixed with tampons or hair sutures.
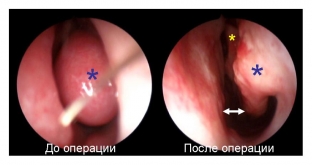
Prevention of the formation of synechiae. Prognosis after treatment of synechia
Synechia in the nasal cavity have a high degree of recurrence. Their excision by surgery can further aggravate the situation, making the process of nasal breathing even more difficult. Therefore, the otolaryngologist must individually approach each specific case and determine the feasibility of surgical treatment of synechia.
In order to prevent synechia in the nasal cavity, it is important to treat inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses and upper respiratory tract in a timely manner, to require highly qualified assistance for any nasal injuries. When performing surgical intervention, it is important to do everything in the postoperative period to prevent recurrence of synechia. At the first sign of a breathing disorder, a change in the sense of smell or a change in the tone of the voice, you should contact the otolaryngologist for a consultation, after which the specialist will make a conclusion about the need for surgical treatment of synechia.







Add a comment