The neglect of proper feeding of domestic dogs, as well as a poor culture of slaughter and inspection of livestock, can have bad consequences for patients. In this article on estet-portal.com, we will look at diseases that are caused by specific cestodes that parasitize canines and are known collectively as "echinococci".
For more information about what echinococcosis is, as well as what types of echinococci a doctor can meet in his practice, how to diagnose them in a timely manner and treat them correctly, read on estet-portal.com this article.
Echinococcosis as a consequence of infection from eating contaminated food
Cystic echinococcosis, also known as hydatid disease, is caused by the worm Echinococcus granulosus, and alveolar echinococcosis – worm Echinococcus multilocularis. In addition, there are six other, less common varieties of worms.
Follow us on Instagram!
Canines and other canines (raccoon dogs, wolves, foxes) act as the ultimate carriers of echinococci, with the eggs of these worms developing in the faeces of these animals.
The main route of human infection with echinococcus – food.
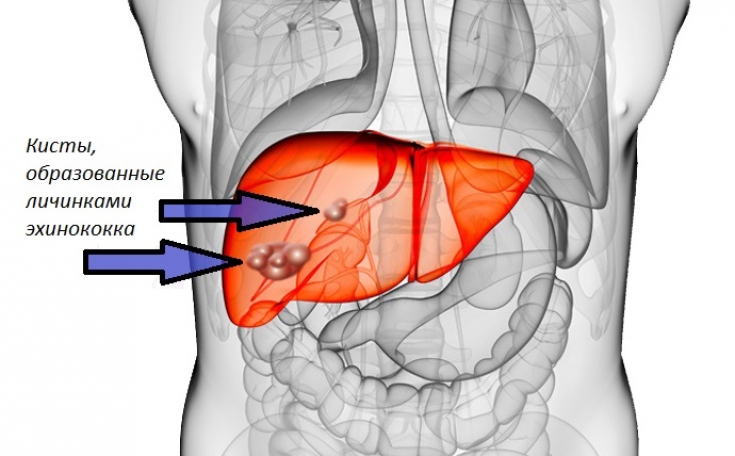
Intermediate vectors (sheep, deer, elk, small rodents, and humans as incidental vectors) become infected through food that has been contaminated with the faeces of the original host. Worm larvae are usually carried through the intestines to the liver or lungs, where they form a hydatid cyst. Over several years, the cyst can reach a diameter of several centimeters.
The meat of intermediate vectors (eg deer, elk) does not infect humans. Dogs and other canines can become infected by eating contaminated meat, including offal from infected animals.
You may be interested in: Are Dirty Hands to Blame: A Modern Perspective on Hepatitis A?
Echinococcosis: epidemiology and features of the clinical picture of the disease
Cystic echinococcosis occurs worldwide, especially in areas where offal is fed to dogs. Alveolar echinococcosis is common in the northern hemisphere, with foxes being the most common carriers, although other canines may also be carriers.
In many Central European countries, alveolar echinococcosis is the most common tissue parasitic disease. In Scandinavia, this disease is rare in animals, although sporadic cases are known in Sweden.
The following should be said about the clinical picture of cystic echinococcosis:
- cysts may not cause any symptoms for a long time and are often discovered by chance, for example during liver ultrasound;
- a cyst can reach 10 cm in diameter;
- cysts can cause "symptoms of compression" depending on their location, most often in the liver or lungs, but also in the central nervous system, bones, etc.;
- rupture of the cyst can lead to an anaphylactic reaction or hemoptysis (with a pulmonary cyst).
Symptoms of alveolar echinococcosis:
- in humans, the disease caused by Echinococcus multilocularis progresses faster and is more difficult to treat compared to cystic echinococcosis;
- cysts,
Modern methods for diagnosing cystic and alveolar echinococcosis
Diagnosis of the disease is based on identification of a typical cyst using imaging techniques (ultrasound, chest X-ray, CT or MRI). It is also important to make a differential diagnosis with other more common cystic diseases.
The presence of Echinococcus antibodies confirms the diagnosis, but a negative result does not necessarily indicate the absence of infection. Cyst specimens obtained by surgery or aspiration should be examined in a parasitological laboratory.
Faecal specimen analysis for parasites is not informative.
Tick-Demodex: is the parasite as terrible as they say
Optimal treatment options for echinococcosis and disease preventionThe choice of therapeutic approach is based on the size, location, and structure of the cyst. There are several treatment options for cystic echinococcosis:
1. Follow-up without treatment;
2. Chemotherapy with albendazole;
3. PAIR D procedure (ultrasound-guided puncture and aspiration of the cyst with albendazole, hypertonic saline filling and respiration);
4. Aspiration through a catheter (using albendazole);
5. Surgical removal of an intact cyst using albendazole (care must be taken to ensure that the cyst does not rupture during the operation).
If alveolar echinococcus is detected at an early stage, surgical removal is the only effective treatment option.
In the early stages of alveolar echinococcosis, surgical removal of lesions is the only treatment option. There are no alternatives.
Avoiding the spread of infections in canines (eg, avoiding offal feeding to dogs) and proper food hygiene, as well as a high culture of slaughtering and meat inspection of livestock are key methods for preventing echinococcosis.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dermatology" section. You may also be interested in:
Cat Scratch Disease: Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Felinosis
Adapted from EBM Guidelines "Echinococcosis"







Add a comment