Antiseptics — these are chemical agents applied to the skin to reduce the number of microorganisms and reduce the risk of infections. The use of antiseptics dates back to the mid-1800s, when Ignace Semmelweis noted a dramatic decrease in the incidence of sepsis using appropriate handwashing methods. Commonly used antiseptic agents include chlorhexidine, povidone-iodine, isopropyl alcohol, benzalkonium chloride and ethyl alcohol.
On estet-portal.com read about the main types of antiseptic preparations and their properties.
- What determines the choice of antiseptic
- Chlorhexidine: the ideal broad spectrum antiseptic
- Povidone-iodine to fight bacteria and viruses
- Isopropyl alcohol for decontamination
- Benzalkonium chloride: effective against bacteria, not effective against viruses
- Side effects antiseptics
What determines the choice of antiseptic
Each antiseptic has a specific mechanism of action and a target microbial spectrum as well as a side effect profile that must be carefully weighed before selecting a remedy.
For the skin, the most common pathogens are Staphylococcus aureus, followed by other gram-positive organisms including coagulase-negative Staphylococcus, Enterococcus and group A streptococci and gram-negative rods, especially Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas.
Read also: US COVID-19 research
Broad-spectrum antiseptics typically cover more pathogens and subsequently are among the most popular.
Chlorhexidine: the ideal broad-spectrum antiseptic
Chlorhexidine is positive
a charged bisbiguanide that, at physiological pH, binds to negatively charged bacterial cell walls, causing destruction of microbial cell membranes and precipitation of cell contents.
At low concentrations, chlorhexidine is bacteriostatic, but at higher concentrations it is bactericidal.
Chlorhexidine has a broad spectrum of activity, including gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, fungi and viruses.
Read also: Disinfection in cosmetology: patient safety first
include:
broad spectrum of activity;- quick start of action;
- excellent sustained/residual activity after being wiped off the field.
- Chlorhexidine can be used to
.
Subscribe to our page onFacebook! Italian studies have shown that chlorhexidine 1%, as well as 70% ethanol, very quickly (less than 2 minutes)
damagescapsid virus, and he cannot reproduce. Povidone-iodine to fight bacteria and viruses
is a complex of povidone, hydrogen iodide and elemental iodine. It is thought to act via iodination (a form of halogenation) to oxidize cell membrane lipids and form salts with microbial proteins. povidone-iodine — broad-spectrum antiseptic with microbicidal activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria (including spores and M. tuberculosis), fungi, viruses and protozoa.
In addition, this antimicrobialacts quickly
after application to the skin, but unlike chlorhexidine, it has minimal residual activity. Another disadvantage of this drug as a hand sanitizer —
skin dyeing. Isopropyl alcohol for decontamination
Isopropyl alcohol— it is a hydrophilic alcohol that is likely to cause damage to membrane and denature proteins essential for microbial metabolism and growth.
Read the latest articles inTelegram! Isopropyl alcohol is usually
mixed with waterbecause microbial activity is greatest in a 60 to 90% solution, rather than pure or at lower concentrations. Alcohol solutions are generally considered to be more active against Gram-positive bacteria (bactericidal), but may have little activity against some viruses and fungi.
While isopropyl alcohol is one of the weakest cleansers with minimal residual activity, it has themost
fast onset. Benzalkonium chloride: effective against bacteria, not effective against viruses
is a quaternary ammonium detergent (also called a cationic surfactant) that acts by irreversibly binding to phospholipids and membrane proteins,
destroying the cell membrane. It acts as a bactericidal agent against many Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, but has an inconsistent coverage against fungi, viruses, and mycobacteria. Therefore, this antiseptic substance cannot be used to effectively fight viruses.
Read also:
Skin disinfection before injection procedures
The advantages of benzalkonium are its stability and the possibility of using it with alow incidence of irritant
Side effects of antiseptics While antiseptics are generally well tolerated, the side effects of antiseptics must be carefully weighed before selecting them:
Chlorhexidine can cause keratitis, conjunctivitis, and sensorineural deafness. Chlorhexidine is fortunately reported to be a rare contact allergen.
Povidone-iodine can stain skin, hair and clothing. Severe irritant contact dermatitis may occur with prolonged exposure to povidone-iodine on the skin;
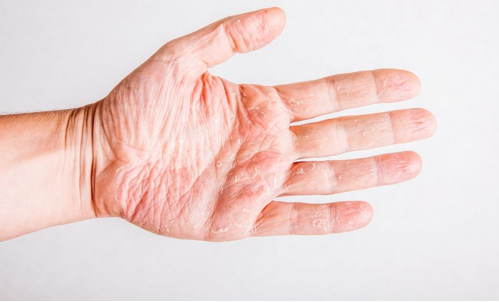
Isopropyl alcohol may cause irritant contact dermatitis.- Benzalkonium chloride may cause allergic contact dermatitis with prolonged skin exposure.
 coronavirus.
coronavirus.
against coronavirus . WHO also notes that thorough
washing of hands with soapis effective against coronaviruses, as viruses are effectively washed off the skin mechanically. More useful information on our YouTube
-






Add a comment