Hair loss is one of those cosmetic problems that worries patients very much, but does not prompt an immediate visit to the clinic. Usually, domestic causes are first attributed to hair loss and they try & nbsp; deal with the problem at home. As a result, the time needed to treat the disease that caused baldness is often missed. It is especially important to respond in a timely manner to those diseases that provoke the development of scar tissue instead of hair follicles. For what reasons such a substitution is possible and whether it can be recognized, read on estet-portal.com.
When scar tissue develops to replace hair follicles
Scarring alopecia causes hair loss in approximately 3% of men and women worldwide.
Scarring alopecia develops in a number of diseases and conditions accompanied by irreversible destruction of the hair follicle.
So, among the causes of cicatricial alopecia can be burns, frostbite, head injuries, exposure to acids and alkalis. Some fungal infections, staphylococcal lesions of the scalp, as well as some diseases can contribute to the destruction of the hair follicle:
- shingles and lichen planus,
- late syphilis,
- discoid lupus,
- sarcoidosis,
- scleroderma.
Scarring alopecia can manifest itself in different forms – for example, exfoliating panniculitis, Broca's pseudopelade, various types of folliculitis. In any case, the hair follicles are irreversibly destroyed and replaced scar tissue, after which the hair on the affected & nbsp; plots are never restored.
How does the development of scar tissue on the head manifest itself
Most often, scarring alopecia begins to manifest itself in the fact that small areas devoid of hair form on the scalp. Further, these areas gradually increase without causing any special symptoms – the hair falls out for quite a long time almost unnoticed by the patient, since the collapsing hair follicles lie deep under the skin. But it also happens that alopecia develops and progresses quickly, & nbsp; accompanied by itching and burning in places of hair loss.
Outwardly, the areas of the skin on the head affected by cicatricial alopecia are distinguished by a rough edging, but in themselves they are smooth and clean, although sometimes they can turn red and peel off. It happens during the formation of scar tissue, the appearance of pigmentation on the skin of the affected areas of the head, and sometimes even purulent blisters.
After some time, the inflammatory process subsides, the development of cicatricial alopecia stops. Pain disappears, hairless areas no longer grow.
Studies of bald areas of the skin with cicatricial alopecia show the complete absence of hair follicles in them.
The hair follicles are replaced by scar tissue. Sometimes, along the edges of the affected areas of the skin, there are a few dilapidated follicles that are able to recover over time.
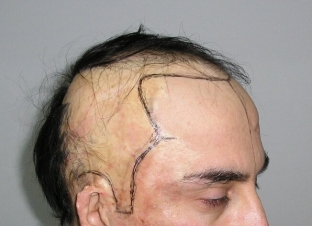
Diagnostics and treatment of the scalp in scarring alopecia
A skin biopsy will help confirm the diagnosis of cicatricial alopecia – a small element taken from the affected area. The taken sample is examined under a microscope, while the destruction of the hair follicles and foci of inflammation next to them, the formation of scar tissue deep in the skin.
Scarring alopecia is treated quite aggressively and quickly to prevent significant damage to the hair follicles. Depending on the form of the disease, therapy is prescribed: with an increased level of lymphocytes, corticosteroids are recommended topically and by injection into the affected areas of the skin, with increased neutrophils – antibiotics and isotretinoin are required.
A few years after the final attenuation of the inflammatory process, when the hair no longer falls out, follicles from other scalp plots can be transplanted into areas with scar tissue.







Add a comment