Pregnancy is accompanied by a change in hormonal levels, which is manifested by physiological skin features. However, during pregnancy, dermatological problems and exacerbation of pre-existing skin conditions may occur.
In their treatment, it should be noted that some drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy. It should also be borne in mind that skin manifestations can be a symptom of a serious pathology that requires immediate diagnosis and the appointment of an acceptable treatment strategy for pregnant women.
For example, if a pregnant woman is itchy, ALT and bile acid levels should be checked to rule out hepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Read about this and other pathologies that lead to skin changes in pregnant women, as well as the tactics of their treatment in this article on the website estet-portal.com.
Physiological changes in the skin during pregnancy
Under the influence of hormonal levels during pregnancy, a woman's skin undergoes physiological changes:
1. Physiological itching (pruritus gravidarum).
Occurs during the 1st or 2nd trimester of pregnancy. Most often of moderate intensity, diffuse nature, mainly on the trunk. Probably related to dry skin.
Follow us on Telegram
2. For most women, skin becomes less oily and may be dry.
4. Stretches (striae gravidarum).
Stretch marks usually appear in the abdomen, buttocks, chest and mammary glands.
Linear hyperpigmentation in the midline of the abdomen (linea nigra), nipples and genital area is a physiological phenomenon.
Telangiectasias, small hemangiomas, edema of the lower extremities due to impaired venous outflow, occurrence of varicose veins of the lower extremities, constant erythema on the palms.
About 3 months after childbirth, increased hair loss often occurs.
The appearance of dark longitudinal lines on the nail plate, delamination of the nail is typical.
The most common pathological skin changes during pregnancy
1. Atopic eczema.
Skin changes are typical for the clinical picture of atopic eczema, usually in history, the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis precedes pregnancy.
Atopic eczema is characterized by exudative and lichenoid eruptions, elevated serum IgE levels, and hypersensitivity to irritants. It has a clear seasonal dependence.
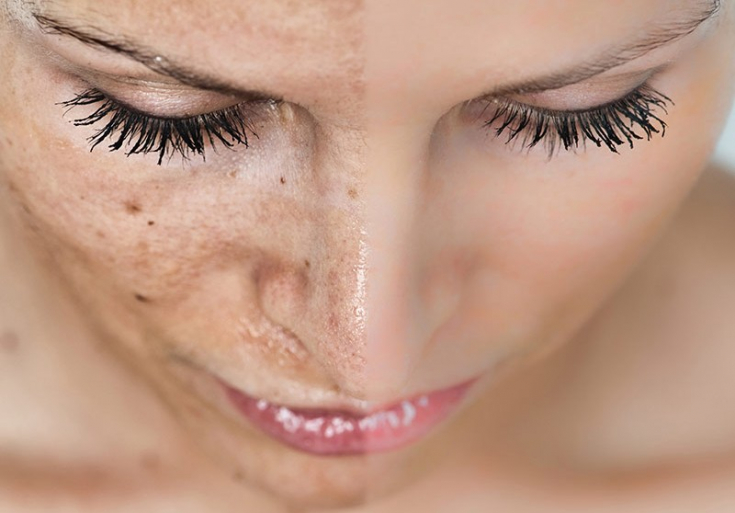
2. Chloasma and melasma.Melasma – This is a benign hyperpigmentation of the skin due to increased production of melanin in the form of yellow-brown spots of a non-inflammatory nature. It usually appears on the face and around the eyes. May be prevented with sun protection during pregnancy.
What is the danger of obesity for the skin 3. Acne.
May worsen or occur for the first time during pregnancy. In this case, the drugs of the first line are benzoyl peroxide and ointments with azelaic acid. For topical dot application to inflamed elements, an emulsion or solution of clindamycin can be used. Topical vitamin A preparations or oral tetracycline are not recommended for use during pregnancy.
5. Eczema in the genital area.
More rare skin problems in pregnancy
It is a variant of allergic vasculitis, characterized by the appearance of bluish-red nodules along the vessels on both legs. The surface of the skin in the places of formations slightly swells, becomes reddish and smooth. Possible hyperthermia.
May appear for the first time or worsen during pregnancy. Topical use of medium to high potency glucocorticoids may be acceptable intermittently, for example for 2-3 weeks. Keratolytic ointments (containing urea) can be used to soften and remove thick scales. Moisturizing ointments usually reduce the need for glucocorticoid ointments and reduce the duration of an exacerbation.
Skin problems associated with this pathology include erythematous scaly patches on the eyebrows, nasolabial folds, face, scalp, and ears.
Accompanied by a typical clinical picture.
May occur for the first time or worsen during pregnancy. In the systemic form of the disease, the patient has general symptoms, in forms limited to the skin there is a scaly, patchy eczema, aggravated by sunlight, usually localized on the face and upper trunk.
7. Atopic dermatitis
8. Bullous Gestational Pemphigoid
Acne treatment: efficacy and safety of topical antibacterial agents
 9. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (hepatosis)
9. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (hepatosis)
The mother should be admitted to the maternity hospital for observation because hepatic cholestasis of pregnancy is associated with a risk of preterm delivery and an extremely low (<1%) risk of fetal death.
10. Pyogenic granulomaA rapidly growing, erythematous tumor that bleeds easily. It is a lobular capillary hemangioma. It is usually found on the distal extremities. The problem worries every 20th pregnant woman. Etiological factor – bacterial and traumatic. A biopsy is needed to confirm the diagnosis. Recommended methods for removing granuloma – tangential excision and electrodesiccation.
To make a correct diagnosis and select a rational therapy, it is necessary to carefully examine a pregnant woman with skin problems. Determine if the problem is acute or chronic? Were these changes before pregnancy? Does the patient have any congenital feature such as atopic eczema? Does the patient have systemic symptoms related to the skin problem, such as fever and malaise?
Examine all skin for additional manifestations. Give preference to non-pharmacological methods of treatment. The safest drugs are antihistamines and topical application of ointments containing antibiotics and glucocorticoids in acceptable concentrations. It should be borne in mind that chronic diseases often worsen during pregnancy, but taking previously effective drugs can be dangerous for the fetus.
Read more about acceptable medicines for use in pregnancy in the article on our website in the Gynecology section: Evidence-Based Acceptable Pharmacotherapy for Expectant Mothers.
According to the Evidence-Based Medicine Guidelines







Add a comment