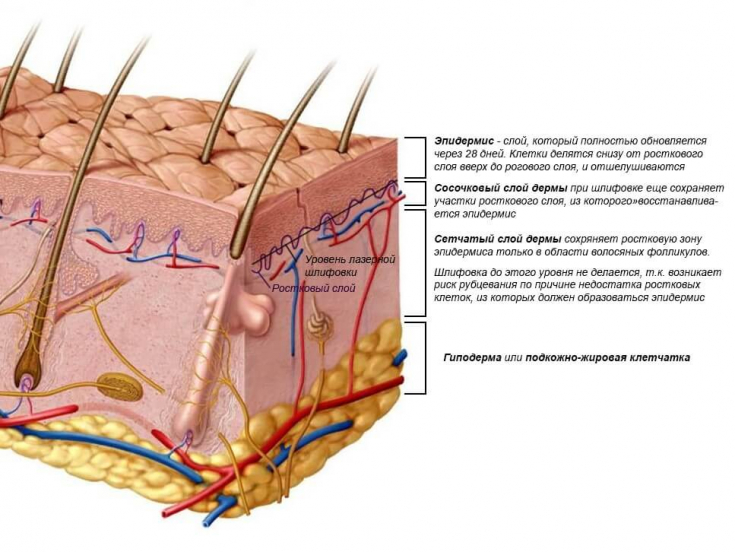
Perhaps there is no other organ that would attract as much attention as the skin. The skin is the largest organ of the human body and at the same time the largest organ that is attractive to others. It is known that the skin consists of the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue (hypoderm).
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com what skin functions should be taken into account during various procedures, as well as morphological features of the skin as an organ.
- The structure and function of the layers of the skin
- Mechanical and sensory functions of the skin
- Function of fat cells in cosame
The structure and function of the layers of the skin
Epidermis − it is an epithelial layer of keratinocytes that also contains Langerhans cells, Merkel cells, and melanocytes. The thickness of the epidermis ranges from 0.04 mm on the eyelashes to 1.6 mm on the palms.
Follow us on Instagram!
The dermis has two layers:
- thin papillary layer, which is located just behind the epidermis;
- reticular (mesh) layer, which is located on the border with the hypodermis.
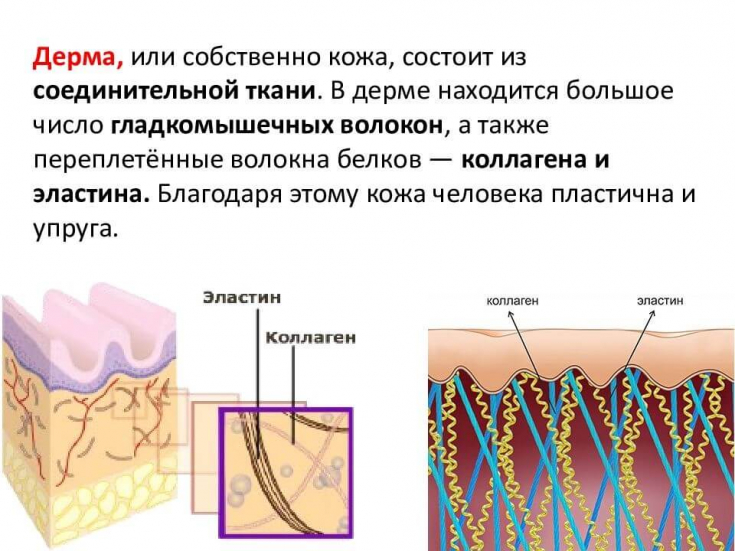
The dermis contains a basic substance composed predominantly of polysaccharides (glycosaminoglycans) as well as proteins and forms macromolecules known as proteoglycans.
In this framework are placed collagen and elastic fibers along with cellular elements such as fibroblasts, mast cells and other cell types, as well as nerve and vascular formations.
The thickness of the dermis ranges from 1 mm on the face to 4 mm on the back and thigh. The dermis represents the mechanical resistance of the epidermis.
Skin protects the body from negative influences and penetration of harmful substances, prevents fluid loss. Different sites have different degrees of transdermal absorption. It is known that the skin of the face is the most permeable, while the skin of the palms is resistant to many substances. Mechanical and sensory functions of the skin
The mechanical functions of the skin and its properties of stretching provide the fibers of the dermis.
The ability to stretchof the skin is not the same in different areas. The skin of the abdomen has an amazing ability to stretch, but to a certain extent, which is observed in
striae distensae in adolescents and striae gravidarum in pregnant women. First of all, in some women, genetic factors contribute to this.
The skin has sensory functions and also produces odorous substances. The smell is better in women than in men,
more pronounced during ovulationthan during the rest period of the menstrual cycle. The skin has certain characteristic properties, for example,
catabolizes steroids and produces active hormones. Skin appendages respond to the production of sex hormones. In the same way, such sexual characteristics as the density of hair on the face, in the axillary zones and on the bosom respond to androgenic stimulation.
How can vitamin C increase keratin synthesis and eliminate hyperpigmentation? The skin is a target for a wide range of influences. The response of the skin to hormonal influences varies between men and women.
For example, hair follicles and sebaceous glands are targets for androgenic steroids secreted by the gonads and adrenal cortex, while melanocytes are directly affected by polypeptide hormones produced by the pituitary gland. The effect of estrogens on the skin is not fully understood, although during menopause they can stimulate
epidermal mitosis.
are known to increase both dermal and bone collagen levels. There is no doubt that they inhibit the secretion of sebum and their effect precedes other stimulations.
Retinoids and antiaging: the possibilities of vitamin A derivatives in the fight against aging
Androgensaffect extremely specific areas: sebaceous glands, hair follicles, apocrine glands. Testosterone is metabolized to five-dihydrotestosterone by the enzyme − reductase in some tissues, including skin. In adults, the activity of the enzyme is higher in areas where sensitivity to testosterone is determined, so
them as zones of sebaceous activity, in women − in areas of hair growth in idiopathic hirsutism. The function of fat cells in the skin
The subcutaneous tissue consists of three layers of fat with connective tissue bridges between them. On the thighs of women, especially where the pinch test helps to establish the "mattress phenomenon", the superficial subcutaneous layer consists of fatty areas of average size 0.5 x 1.5 cm, separated from each other by a wall of connective tissue.
This lace resembles arches, with adipose papillae extending from fatty areas in the dermis. They separate in the reticular layer and around the hair follicle and blood vessels,
protecting these formations from pressure and cuts.
Lipofilling of various areas of the face for optimal rejuvenation and beautification The shape of the fatty areas may change under pressure. Meanwhile,
«mattress phenomenon»can only be on the skin of the thighs in women, when there is compression and protrusion of fat cells. In comparison, the subcutaneous tissue of the thighs in men is much thinner, and the crossed septa divide the fat areas into polygonal formations. In addition, the dermis of men is thicker than that of women.
See the latest news from the world of aesthetic medicine on our







Add a comment