This disease is called allergic purpura or capillary toxicosis, it is noted that it is widespread in young people. Hemorrhagic vasculitis is a systemic inflammation of small blood vessels, capillaries, which affects the skin and joints. As a rule, patients complain of pain in the joints and rashes on the skin, sometimes gastrointestinal troubles. But sometimes hemorrhagic vasculitis takes a fulminant course, affecting the kidneys and causing cerebral hemorrhages. How to prevent severe complications, read on Estet-portal.com.
Why does hemorrhagic vasculitis develop and what provokes it
Specialists note that hemorrhagic vasculitis most often affects people who have a genetic predisposition to it. The essence of the problem is that, under certain conditions, immune complexes are formed in the patient's blood and begin to circulate. They settle on the walls of blood vessels and cause inflammation, which increases their permeability, and thrombotic masses form in the vessels themselves. As a result, microthrombosis of capillaries and venules develops, hemorrhagic syndrome develops.
The following are considered as provoking factors that trigger vascular inflammation and the development of hemorrhagic vasculitis:
- viral infections – flu, SARS, herpes;
- bacterial infections – staphylococci, streptococci;
- parasitic infections – worms, trichomonas;
- allergy to medicines and vaccines;
- severe hypothermia.
Forms of hemorrhagic vasculitis and main symptoms
Hemorrhagic vasculitis usually begins in an acute form, and then either the symptoms subside and recovery occurs, or the disease becomes a protracted or chronic form.
A simple form of hemorrhagic vasculitis manifests itself as mild rashes on the skin and slight arthralgia, sometimes a rise in temperature to febrile values \u200b\u200bis possible.
Rheumatoid the form is a manifestation of a moderate disease, when the patient complains of symptoms of arthritis and profuse skin rashes. Abdominal syndrome is often added.
A severe form of hemorrhagic vasculitis is characterized by necrosis of skin areas with profuse rashes, gastric bleeding, angioedema are possible.
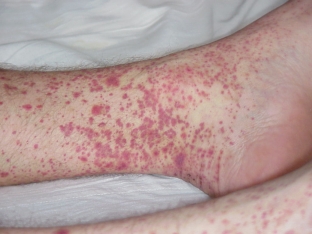
Key syndromes of manifestation of hemorrhagic vasculitis:
- dermal – small maculopapular hemorrhagic elements on the skin of the thighs and legs, less often the buttocks; in severe cases of the disease, ulcers and necrosis develop; after treatment, hyperpigmentation and peeling remain on the skin for a long time;
- articular – severe pain in large joints, their redness and swelling; may be volatile and never deforms joints;
- abdominal – it can appear even earlier than skin rashes, it is expressed by pain in the abdomen without precise localization, sometimes paroxysmal in the form of colic, sometimes moderate; nausea, vomiting, stool disturbance are often added; in severe form, blood may appear in the stool;
- renal – signs of glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome.
Complications of hemorrhagic vasculitis can be cerebral hemorrhage, myocarditis, hemorrhagic meningitis, severe renal syndrome with uremia.
Principles for the treatment of hemorrhagic vasculitis in a patient
In the treatment of hemorrhagic vasculitis, emphasis is placed on the use of heparin. Antibacterial drugs are excluded, since they can provoke an allergic response of the body, and other drugs that can cause allergies.
Corticosteroids can be used in severe hemorrhagic vasculitis, but their effectiveness is questionable by specialists, in the absence of an effect they are replaced by cytostatics. Plasmapheresis and hemosorption are shown. Pain in the joints is stopped by anti-inflammatory drugs, with a pronounced abdominal syndrome, enterosorbents are used. Patients are advised to follow a hypoallergenic diet and bed rest.







Add a comment