Botulinum toxin has been used in ophthalmology since 1973 for the treatment of blepharospasm and strobism. Botulinum toxin is called "the deadliest poison" because it is the most poisonous substance known to mankind.
In medical practice, botulinum toxin type A is most often used. It is the most toxic, but its action is well studied. Less commonly, type B toxin is taken, the action of which is short-term − 1-2 months It is used in ophthalmology.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com, what are the differences between botulinum toxin preparations and their clinically proven effectiveness.
Mechanism of action of botulinum toxin
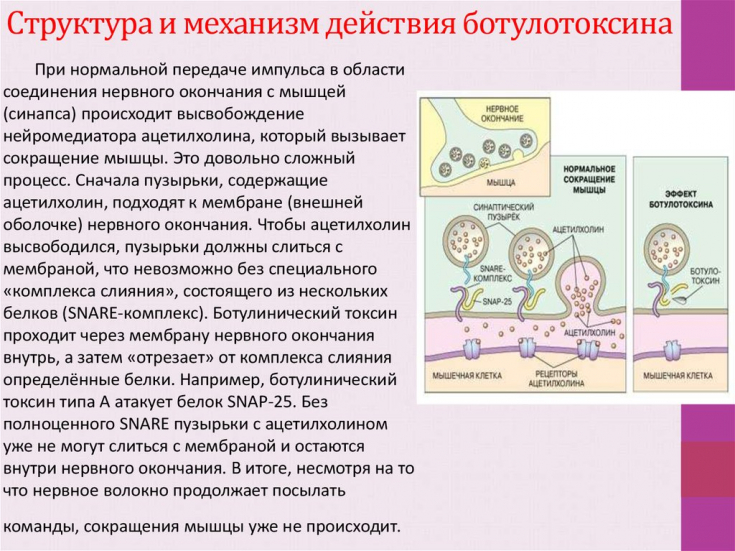
All botulinum toxins work by preventing the release of acetylcholine at the level of the neuromuscular junctions in the muscles, causing muscle paralysis. The action of the toxin on the presynaptic receptors of neurons is fast and specific. It is called chemical denervation.
Follow us on Instagram!
The first clinical manifestations can be observed after 24 hours, the maximum effect is achieved at the end of the second week. And although the process of chemical denervation is long, functions are restored in all treated neuromuscular synapses within 3-6 months. The toxin is available in lyophilized form in a vial containing 100 units of the toxin. The role of the stabilizer is performed by the amyloid complex. All drugs are diluted with saline.
Botulinum toxin is effective in treating headaches
Areas of application and side effects of botulinum toxin
Application areas:
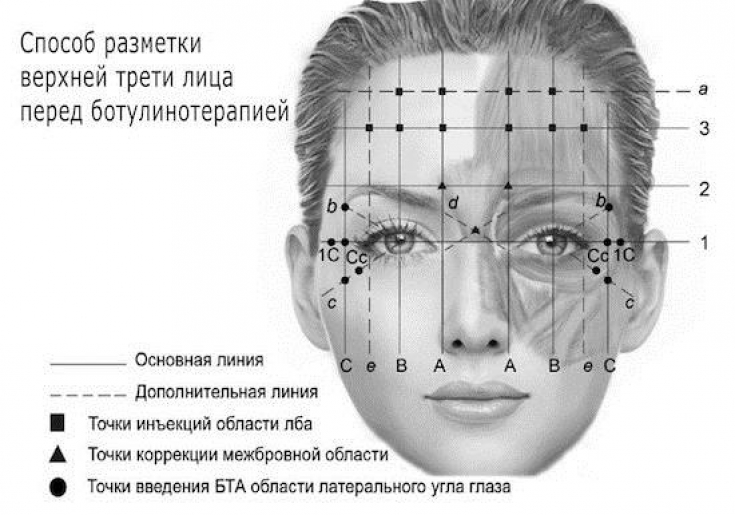
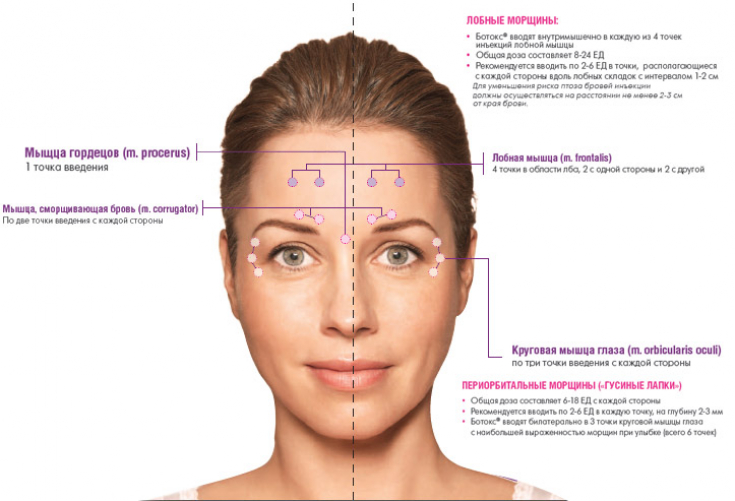
− glabella zone (eyebrow crease)
− horizontal forehead wrinkles;
− lateral corners of the eye cavity ("crow's feet");
− perioral area;
− nasolabial folds;
− neck and décolleté.
In addition to correcting age-related changes, botulinum toxin is also used to treat hyperhidrosis, this method allows you to block sweating in the groin area for up to 6 months. Disadvantages: short action - up to 6 months, the need for each next time to increase the dose. Botulinum toxin is considered a safe therapeutic drug, but occasionally side effects occur:
1) allergic reactions;
2) hematomas at the injection site;
3) ptosis of the upper eyelid or eyebrow.
In case of complications, it should be remembered that cephalosporins have an inhibitory effect on botulinum toxin. Also cholinesterase inhibitors and antihistamines.
Botulinum toxin: the hottest news in botulinum therapy
Clinical trials of botulinum toxin
The latest study on botulinum toxin was on the comparative efficacy of onabotulinumtoxin and incobotulinumtoxin. The experiment involved 30 people who underwent a comparative treatment of changes in the skin condition with two drugs.
Standard forehead photographs of patients were taken at baseline (before administration) and 2, 4, 6 and 8 weeks after botulinum toxin administration and weekly thereafter. Subjective and objective evaluations were carried out. The effectiveness of botulinum toxin preparations was evaluated by plastic surgeons and dermatologists. This panel used 4-point scales: Facial Winkling Grading (FWG) and Clinical Improvement Scale (CIS). The FWG scores were as follows: 0 = no wrinkling, 1 = slight wrinkling, 2 = moderate wrinkling, and 3 = severe wrinkling with full frontal muscle contraction.
CIS for each patient was calculated individually, including the FWG score at each subsequent visit. Subjective scores were assessed by each patient using a self-assessment questionnaire to assess satisfaction at each follow-up visit; scores ranged from 0 (not satisfied at all) to 3 (completely satisfied).
Of the 30 patients included in this study, 19 were male and 11 were female. The patients were aged 21 to 61 years (38.6 ± 10.0 years).
No patients exited due to side effects. All patients were followed up for an average of 24 weeks.
Results of the study of botulinum toxin preparations
Mean time to reappearance of forehead lines with Onabotulinumtoxin A was 8.3 weeks (range 6 to 10 weeks) compared to 10.1 weeks (range 8 to 12 weeks) with incobotulinum toxin A. Mean baseline FWG in patients was 2.6.
Forehead lines improved for both toxins at 2, 4 and 6 weeks, respectively. It was found that OnabotulinumtoxinA was less effective than IncobotulinumtoxinA for long-term wrinkle correction, with more significant (P<0.0.05) appearance of the forehead line after OnabotulinumtoxinA treatment.
The parts of the face that were injected with Incobotulinumtoxin A showed a more consistent mean improvement than the sides that were injected with OnabotulinumtoxinA, where performance scores declined more sharply from week 8 onwards. The mean FWG score also indicated that there were significantly more lines in the parts treated with OnabotulinumtoxinA from week 8 onwards. Conversely, there was a significant improvement in the parts of the face where Incobotulinumtoxin A was injected. Taken together, these results indicate a longer lasting outcome with IncobotulinumtoxinA.
Furthermore, subjectively, all patients in the interviews had indicators that coincided with the data of clinical studies. However, two patients developed mild drooping of the upper eyelid in the area where Incobotulinumtoxin A was injected. However, overall, the efficacy of Incobotulinumtoxin preparation was significantly higher than that of Onabotulinumtoxin.
The history of the world's most famous botulinum toxin drug
This is the first clinical study reporting a relevant clinical comparison of the efficacy and longevity of OnabotulinumtoxinA and IncobotulinumtoxinA non-reconstituted botulinum toxin vials. The comparatively better durability and efficacy of IncobotulinumtoxinA is due to its more stable chemical composition than that of Onabotulinumtoxin A.
It is also known that Incobotulinumtoxin A contains only 150 kDa of botulinum toxin, is cleared from fermentation and does not contain complexing proteins (hemagglutinins and non-toxic hemagglutinating proteins). Thus, it has a low foreign protein content, since any adverse reactions and deterioration in the effectiveness of the botulinum toxin may be associated with the injected foreign protein.
The use of high doses of botulinum toxin in the correction of glabellar wrinkles







Add a comment