Genital herpes is caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or 2 and can present as a primary or recurrent infection.
This is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections.
Genital herpes can be suspected if the patient complains of:
- appearance of a rash in the genital area in the form of blisters that burst, leaving erosion;
- tingling, burning, itching of the genitals;
- pain when urinating;
- Vaginal discharge.
Read more about the clinical picture and methods for effective treatment of genital herpes at estet-portal.com in this article.
- Genital herpes: primary, recurrent, asymptomatic carriage
- Features of the treatment of genital herpesa
Genital herpes: primary, recurrent, asymptomatic carriage
- Primary genital herpes
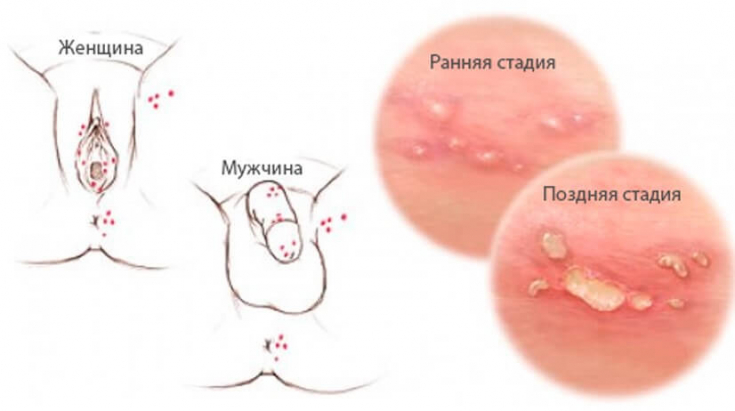
Classically, herpes begins with a macular or papular rash and mucosal lesions 4-7 days after sexual contact.
The rash then progresses to vesicles, pustules and ulcers which may persist for up to 3 weeks.
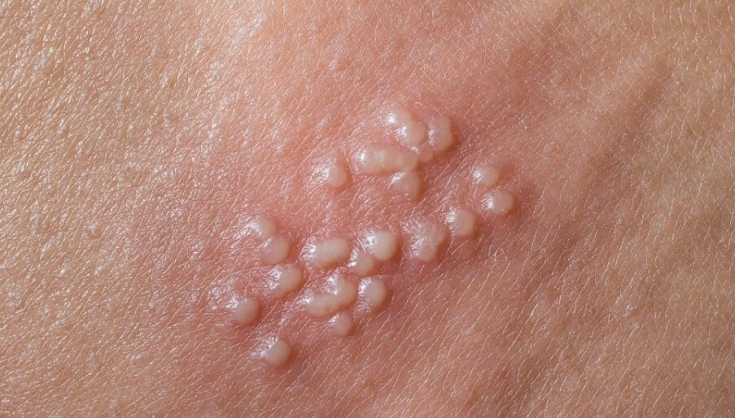
Typical symptoms also include burning pain and dysuria, especially in women.
Lymphadenopathy, fever and cervicitis (in women)/proctitis (in men) are relatively common associated symptoms.
Dangers of atypical presentation of genital herpes in women
- Recurrent genital herpes
After the primary infection, the virus becomes a lifelong companion of a person, periodically reminding of itself with exacerbations.
Numerous physiological and environmental factors such as fever, ultraviolet radiation, menstruation, stress, or trauma can be genital herpes triggers.
Relapses occur in almost every person suffering from primary genital herpes caused by HSV-2, in a third of patients this happens quite often (at least 6 times a year).
Recurrent genital infections HSV-1 are five times less common.
Compared to primary infection relapse symptoms are significantly less pronounced and the clinical course is shorter.
Patients with both symptomatic/obvious genital herpes and those with asymptomatic HSV can transmit the virus to their sexual partners.
- Asymptomatic carriage of the genital herpes virus
In most cases, endogenous viral reactivation is characterized by asymptomatic shedding of the genital herpes virus.
HSV-2 is most commonly shed in seropositive patients with HSV-2. In contrast, HSV-1 isolation is rare.
These data suggest, with a high degree of certainty, that HSV-2 seropositive patients should alwaysa be considered as potential carriers of the virus.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Peculiarities of treatment of genital herpes
Standard First line drugs include:
- acyclovir;
- valaciclovir;
- Famciclovir
Triphosphate nucleoside analogs inhibit and fix viral DNA polymerase when incorporated into the growing DNA strand as "false" enzyme substrates.
In the case of aciclovir/valaciclovir this leads to chain termination.
Aciclovir is the best therapeutic agent against HSV infections, including genital herpes. However, its bioavailability is only 15-30% when taken orally.
Infections of the skin and mucous membranes, including genital herpes, are treated orally.
Severe HSV infections, especially in immunocompromised patients, should be treated with intravenous administration aciclovir.
The dose of acyclovir for the treatment of genital herpes depends on the infection status, immune competence, and whether the patient is pregnant. If relapses occur at a frequency of more than four episodes per year, long-term treatment to suppress the virus should be considered.
Valacyclovir is a prodrug (L-valyl ester) of acyclovir suitable for oral administration. After oral administration, it is converted to acyclovir by the liver enzyme valacyclovir hydrolase.
Oral valaciclovir has a bioavailability of 54%, with an active ingredient concentration 3-4 times higher than that of oral aciclovir.
Valacyclovir is also the standard treatment for genital herpes in immunocompetent patients, and studies have shown it to be effective in suppressing viral activity and preventing recurrent genital herpes.
Famciclovir is an inactive prodrug of the diacetyl ester, the only local acyclic nucleotide analogue of penciclovir, which occurs after cleavage of two ester groups in the small intestine and liver.
The bioavailability of famciclovir is 77% after oral administration.
Famciclovir is also considered one of the standard therapeutic agents for the treatment of genital herpes, along with aciclovir and valaciclovir.
You may also be interested in: Aesthetic procedures and the herpes simplex virus: how to avoid complications







Add a comment