Among the severe hereditary pathologies, there is a rare disease, which is characterized by thickening of the bones of the skeleton, which leads to a decrease in the bone marrow space. This is marble disease. Synonyms of the name – congenital osteosclerosis, hyperostotic dysplasia, Alberts disease – Schoenberg. Pathology is transmitted by autosomal – recessive type. The detection rate averages 1 case per 200-300 thousand newborns. In different genetic groups, this number varies. Find out the causes and clinical manifestations of marble disease.
The main causes of the development of marble disease
Violation of the bone structure in marble disease develops against the background of profound changes in phosphorus – calcium metabolism, as well as imbalance & nbsp; between the destruction of old bone tissue and the formation of a new one. At the same time, the cortical layer of the bone becomes thicker, and the space of the bone marrow gradually narrows up to its complete disappearance.
Osteosclerosis progresses, as a result of which the bones become dense, and at the same time fragile. How this affects the state of other organs, read further on estet-portal.com. The closure of the medullary canal is accompanied by the development of hypoplastic anemia and compensatory enlargement of the lymph nodes, spleen and liver.
Due to the growth of bone tissue, the skull is enlarged and deformed. Cranial exit hole – brain nerves are also narrowed, which contributes to the development of hearing loss and visual impairment in marble disease.
Clinical symptoms and diagnosis of marble disease
Although symptoms usually appear in early childhood, the disease can be detected at any age. Sometimes hardening of the bone canal is an incidental finding on x-ray.
The earlier marble disease begins to appear, the worse the prognosis and the more pronounced clinical symptoms. In the first years of life, hydrocephalus appears in children. Such children start walking late, lag behind their peers in growth, and their teeth erupt later.
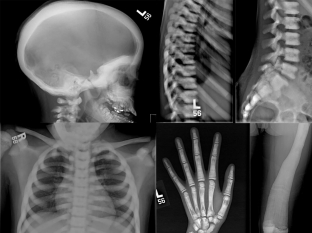
With the progression of marble disease, patients come to the doctor with complaints of pain and fatigue in the limbs when walking. Fractures often occur with marble disease, especially of the femur. Bone fusion occurs at a normal time, but the likelihood of developing osteomyelitis is increased. To clarify the diagnosis, an X-ray examination of flat and tubular bones is carried out, which reveals a sharp compaction of the bone tissue.
Appearance of patients with marbled disease:
- pale;
- weakened;
- get tired quickly;
- enlarged liver, spleen and lymph nodes.
Aspects of treatment and prognosis of marble disease
There is no etiotropic and pathogenetic treatment of marble disease.
Therapy of marble disease consists in symptomatic treatment, which is aimed at strengthening the nervous and skeletal – muscular system.
Fortified nutrition, massage, exercise therapy and spa treatment are recommended. For pathological fractures, standard fracture-specific treatment is performed.
With timely and adequate treatment, the prognosis for marble disease is favorable. The exception is malignant forms of the disease, which are accompanied by damage to myelogenic tissue. Possible death from marble disease against the background of anemia and septicopyemia in osteomyelitis.







Add a comment