Diabetes mellitus – a pathological condition that is characterized by a violation of all types of metabolic metabolism: fat, protein, water-mineral and, to the greatest extent, carbohydrate. The concept of "diabetes mellitus" today includes not one, but a whole group of diseases, different in etiology, pathogenesis and clinical manifestations. Common to these endocrinopathies is the presence of chronic hyperglycemia.
The constant increase in blood glucose levels leads to the development of cardiological, surgical, neurological and other pathologies that significantly impair the quality of life. Carrying out glycemia control – a necessary condition for effective correction of diabetes mellitus and prevention of its complications.
About Key Parameter for Monitoring Diabetes Mellitus – glycosylated hemoglobin, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
- Glycosylated hemoglobin: what does this indicator represent
- Glycosylated hemoglobin as an indicator of carbohydrate metabolism disorders
- Glycosylated hemoglobin: a key parameter for diabetes monitoring
Glycosylated hemoglobin: what does this indicator show
Today, more than 400 million people around the world are diagnosed with diabetes. The World Health Organization predicts that by 2030 diabetes will be the seventh leading cause of death in the population.
Correction of chronic hyperglycemia – the main component of the treatment of diabetes mellitus, the effectiveness of which is determined by the degree of compensation of carbohydrate metabolism.
See also: What do skin rashes look like in diabetes
Glycosylated hemoglobin, also known as glycated hemoglobin, is a compound of glucose and red blood cell hemoglobin.
This lab value represents the blood sugar levels in the blood over the previous 120 days – erythrocyte lifespan.
There are several types of glycosylated hemoglobin fractions, but the most informative is HbA1c.
Glycosylated hemoglobin as an indicator of carbohydrate metabolism disorder
The scale and speed of the reactions of the non-enzymatic compound hemoglobin and glucose directly depend on the level of hyperglycemia: the more glucose in the blood, the faster it penetrates the erythrocyte membrane, and the higher the value of glycosylated hemoglobin will be.
Follow us on Instagram!
At the same time, the process of its formation is irreversible. Glycated hemoglobin is also formed in healthy people, but in small amounts: 4-6% among all hemoglobin. Exceeding its normal value indicates that over the past 90-120 days blood glucose has been high.

The level of glycosylated hemoglobin 5.7-6.4% indicates disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism and the presence of the state of "prediabetes", and a level of over 6.5% has been the criteria for diagnosing diabetes mellitus since 2011 according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization .
Glycosylated hemoglobin: a key parameter for diabetes monitoring
This indicator does not require special preparation and is quite stable: it is not related to food intake, does not depend on the time of day, physical or emotional stress. In this regard, it is widely used both for the diagnosis and follow-up of diabetes mellitus. With the help of glycosylated hemoglobin, prediabetes and diabetes are diagnosed, the degree of compensation of the disease is determined, and the effectiveness of the treatment regimen.
is evaluated.The recommended target for diabetes management is a glycated hemoglobin level of <7.0% for most adults and <7.5% for children.
Read also: Prediabetes: what blood glucose values indicate prediabetes and why
However, in each case, the target values for the compensation of the disease are determined by the doctor individually, depending on the medical history, age.
According to numerous studies, it has been found that a 1% increase in glycated hemoglobin corresponds to a change in glycemia, that is, blood sugar, on average by 2 mmol / l. The value of glycosylated hemoglobin directly correlates with the degree of compensation of diabetes mellitus.
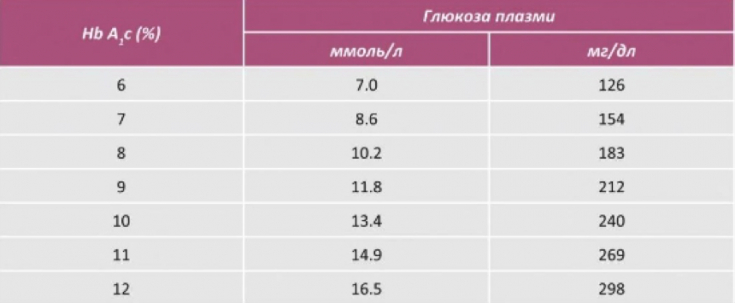
Fig.1 Correlation of HbA1c and blood glucose
Glycosylated hemoglobin is included in the list of mandatory screenings for diabetes mellitus. However, there are situations when this indicator is not objective. These include: the presence of sickle cell anemia, a history of blood loss or blood transfusion, hemodialysis, treatment with erythropoietin.
Follow updates on Facebook!
Also during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, for physiological reasons, the indicator HbA1c should be considered unreliable and for diagnosis, focus more on the level of glucose in blood plasma.
According to the level of glycated hemoglobin, one can judge:
- About having prediabetes:
According to the 2018 American Diabetes Association recommendations, glycated hemoglobin is the screening test for determining prediabetes: 5.7% - 6.4%.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus: the value of the indicator over 6.5%;
- Degrees of compensation for carbohydrate metabolism in diabetes mellitus:
- less than 7.0% – compensation;
- 7.1% – 7.5% – subcompensation;
- more than 7.5% – decompensation.
- Risk of complications from diabetes:
- less than 6.5% – low risk of angiopathy;
- more than 6.5% – risk of macroangiopathies;
- more than 7.5% – risk of microangiopathies.
According to international studies, the level of glycosylated hemoglobin of 7.0% or less significantly inhibits the development of micro- and macrovascular complications of diabetes mellitus.
Thus, glycosylated hemoglobin is the key parameter for monitoring the condition of people diagnosed with "diabetes mellitus". Optimal therapy requires regular testing of glycated hemoglobin levels at a frequency of 2-4 times a year. This approach enables timely correction of the diabetes treatment regimen and prevents the development of complications.
Read also: What kind of anemia can be with a normal hemoglobin level
Besides, effective therapy of complications of diabetes mellitus and other concomitant diseases is impossible without achieving an optimal level of glycemia.
More information on our YouTube-channel:







Add a comment