Meningitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the meninges (leptomeninx): pia mater and arachnoidea. Mainly the pathological process develops in the pia mater.
In the practice of a doctor, meningitis of infectious etiology is most common, less often – toxic. In this case, most often inflammation of the meninges is caused by three pathogens: pneumococcus, meningococcus and Haemophilus influenzae.
In this article on estet-portal.com, we will consider the main clinical signs of meningitis that a doctor of any specialty should be aware of and remember.
Timely diagnosis of meningitis in a patient is the main condition for effective treatment, on which life can depend on meningitis.
Intense headache – leading clinical sign of meningitis
Headache is the main clinical sign of meningitis.
At the same time, it has some characteristic features:
1. Intensity: with meningitis, the headache is so pronounced that it occupies a leading place among all clinical symptoms. Patients with meningitis, even against the background of deep depression of consciousness, often groan, holding their heads;
2. Persistence: the headache may only get worse or worse intermittently, but it's there all the time;
3. Localization: more often diffuse, or in the temples and forehead. Never with meningitis, the headache is localized in the back of the head, it can also never have the character of hemicrania. These points should be taken into account when conducting differential diagnosis;
4. Accompanied by photophobia and hyperacusis, as well as other symptoms of meningitis.
Headache – leading clinical sign of meningitis of any etiology.
Together with symptoms such as fever and vomiting, headache belongs to the so-called meningeal triad.
Meningeal triad: headache, fever and vomiting.
Therefore, every physician, regardless of specialty, who deals with a patient complaining of intense headache, should rule out the diagnosis of meningitis in the first place.
Follow us on Telegram
Meningeal triad: other characteristic features of meningitis
In addition to headache, the meningeal triad also includes vomiting and fever.
Vomiting – an important clinical sign of meningitis, which in this case also has some features:
1. "Fountain" – abrupt, often without preceding nausea;
2. Occurs at the height of headache intensity;
3. Not accompanied by dyspeptic manifestations (abdominal pain, diarrhea) – an important sign of differential diagnosis of acute intestinal infections.
Botulinum toxin is effective in treating headaches
Because most cases of meningitis are infectious, fever is almost always present in this condition. But its nature depends on the characteristics of the etiological pathogen. It is incorrect to talk about any features of fever in meningitis at the level of syndromic diagnosis.
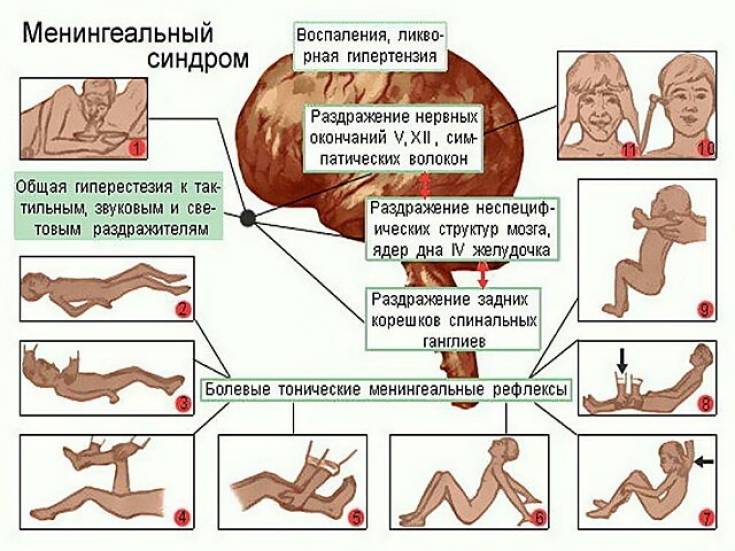
Meningeal symptoms: the most important clinical features of meningitis
If a doctor suspects that a patient has meningitis, he should check for meningeal symptoms. There are over a hundred different meningeal symptoms, but the most clinically significant are the following:
1. Neck stiffness – an attempt to passively bend the patient's head to his chest allows the doctor to catch the hypertension of the muscles of the back of the head that extend the head. In this case, the patient may complain of pain. Early and persistent sign of meningitis of any etiology;
2. Kernig's symptom: the procedure is as follows:
• Starting position: the patient lies on his back, the doctor passively bends the patient's leg in the hip and knee joint at an angle of 90 degrees;
• The doctor performs passive extension of the patient's leg in the knee joint;
• Evaluation of the result: the symptom is positive if the doctor cannot extend the patient's leg due to muscle stiffness.
3. Upper Brudzinski's symptom: when the patient's head is passively bent forward, the legs are bent at the hip and knee joints;
4. The average symptom of Brudzinsky: when the doctor presses the edge of the palm on the patient's bosom, the legs are bent at the hip and knee joints;
5. Inferior Brudzinski's sign: while checking for Kernig's sign, involuntary flexion occurs in the other leg.
Identification of meningeal symptoms is essential for the timely diagnosis of meningitis. Every doctor should know how to detect meningeal symptoms. In addition to meningitis, meningeal symptoms can also be a manifestation of meningism.
Infectious mononucleosis: modern methods of diagnosing the disease
Clinical signs of meningitis – indication for lumbar puncture
Meningitis – This is a condition that requires timely diagnosis and proper treatment. The earlier meningitis is diagnosed, the better the prognosis.
Every physician should be aware of the key signs of meningitis, as well as be able to identify meningeal symptoms.
The above signs of meningitis are quite simple to identify, but have a very high diagnostic value.
To make a definitive diagnosis of meningitis, or to exclude the condition of meningism, as well as to determine the etiology of the disease, it is necessary to perform a lumbar puncture followed by a laboratory assessment of cerebrospinal fluid.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Infectology" section. You may be interested in: Diarrhea and exanthema can be symptoms of an enterovirus infection







Add a comment