Blood in the urine or hematuria – this is one of the most alarming symptoms in urology, forcing patients to urgently seek medical help. Such a condition is not always accompanied by any other clinical symptoms, but in a large percentage of cases it signals the development of a dangerous disease of the urinary system. Depending on the characteristics of the clinical picture and anamnestic data, the doctor may suspect a certain pathology, and diagnostic measures will be aimed at clarifying the diagnosis and excluding the malignant process.
Interstitial cystitis is one of the common urological pathologies, which is accompanied by the appearance of blood in the urine.
Effective methods of diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis is a non-specific inflammatory process of the bladder of a non-infectious nature, which occurs as a result of a deficiency of glycosaminoglycans lining the transitional epithelium of the bladder. Against the background of insufficiency, components of normal urine can penetrate the wall of the bladder and cause damage to all its layers. Interstitial cystitis develops predominantly in women, somewhat less frequently in men, and very rarely in the elderly and children. The disease has a characteristic clinical picture, on the basis of which it is possible to suspect this particular pathology.
Interstitial cystitis:
- characteristic clinical symptoms of interstitial cystitis;
- diagnosis of interstitial cystitis: cystoscopy;
- effective treatments for interstitial cystitis.
Characteristic clinical symptoms of interstitial cystitis
The clinical picture of interstitial cystitis is very similar to the symptoms of ordinary cystitis, but it has some characteristic features. The main symptoms of interstitial cystitis are:
- frequent appearance of blood in the urine, mainly gross hematuria;
- bladder pain;
- frequent and painful urination;
- dysuria and nocturia due to a decrease in bladder volume.
Interstitial cystitis is characterized by a long course with alternating periods of exacerbations and relapses. The disease affects the general condition of the patient, worsens the quality of his life, reduces his ability to work.
Diagnosis of interstitial cystitis: cystoscopy
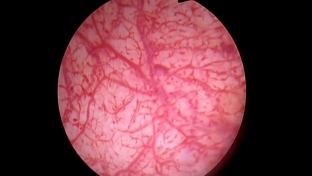
The main method for diagnosing interstitial cystitis is cystoscopy, which is indicated when blood appears in the urine. In the early stages of the disease, during cystoscopy, on the wall of a reduced bladder, more often in the apex area, against the background of a pale mucous membrane, areas of hyperemia, a petechial rash and superficial linear ulcers of irregular shape are determined.
In the late stage of the disease, a small orange-pink mucosal defect with smooth edges is determined on the wall of the bladder, around which swelling of the mucosa is observed – this is a simple bladder ulcer or Hanner's ulcer, which is the characteristic sign of interstitial cystitis.
Effective treatments for interstitial cystitis
Treatment of interstitial cystitis includes conservative and surgical therapies. Conservative treatment is aimed at eliminating the symptomatic manifestations of the disease and includes the appointment of heparin therapy and instillation of drugs into the bladder, such as silver solutions. A good therapeutic effect is also given by phonophoresis, electrophoresis and laser therapy. If conservative therapy does not give the desired effect and the disease progresses, and symptoms of damage to the upper urinary tract appear, surgical treatment of interstitial cystitis is indicated. Endovesical electrocoagulation of the edges of the ulcer or transurethral electroresection of the ulcer with electrocoagulation of the mucous membrane and submucosal layer is performed, which allows achieving remission in almost half of the patients.







Add a comment