Among the various injection methods from the arsenal of a modern cosmetologist, one of the leading places today is occupied by biorevitalization. This procedure involves the intradermal injection of hyaluronic acid, and its optimal concentration in preparations for biorevitalization continues to cause discussion among specialists.
 Vladimir Nikolaevich Khabarov
Vladimir Nikolaevich Khabarov
PhD in Chemistry,
Director of ANO "Research Center for Hyaluronic Acid", Moscow
According to the already classic definition, biorevitalization is considered as "....a method of intradermal injections of unmodified hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan), which allows to restore the physiological environment and normalize metabolic processes in the dermis."
More than 10 years of experience in the use of native hyaluronic acid for biorevitalization allows us to determine the main characteristics of such preparations. This is especially important in modern conditions, when dozens of biorevitalizants are presented on the market of injectables for aesthetic medicine, differing in concentration, molecular weight, and source of origin of hyaluronic acid.
Reasons for using hyaluronic acid for biorevitalization
Aesthetic medicine offers anti-age programs not only to correct existing disorders, but also to stimulate and optimize the skin's own capabilities. Of course, one of the main methods of solving these problems is biorevitalization. The main purpose of applying this technique is to replenish the hydration reserve of tissues and recreate favorable natural conditions in the skin for the functioning of cells, and hence to activate the synthesis of endogenous hyaluronic acid and other components of the intercellular matrix of the dermis.
The extracellular matrix is a dynamic system. Its structures are continuously updated at different speeds - they are destroyed and simultaneously restored. The constancy of the cellular structures of the dermis, as, indeed, of the whole organism, is based on the consistency of the processes of catabolism and anabolism. The presence of a perfect system of interconnections, regulation and coordination of these processes ensures the maintenance of the internal parameters of the matrix within the normal range. A necessary condition for maintaining the stationary state of the cell is the material and energy exchange. And most importantly, a deficiency of substrates or an excess of metabolites, such as hyaluronic acid, are stress factors and can cause dysregulation of metabolism and regeneration of the cellular structures of the dermis. In particular,
How to determine the optimal amount of hyaluronic acid?
Considering the above, it becomes clear that the amount of hyaluronic acid injected into the skin is an extremely important parameter in anti-aging procedures. In this regard, at the Research Institute of General Pathology and Pathophysiology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences under the guidance of Candidate of Medical Sciences A.A. Moskovtsev, work was carried out to study the effect of hyaluronan concentration on the viability of fibroblasts.
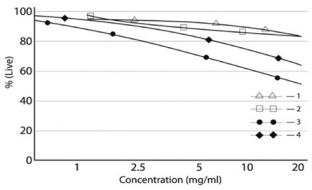
Fig. Fig. 1. Metabolic activity of EA.hy926 endotheliocytes (curves 1 and 2) and foreskin fibroblasts (curves 3 and 4) during 24- and 48-hour (respectively) exposure to hyaluronic acid preparations with different initial concentrations
How to correctly calculate the optimal amount of hyaluronic acid for the procedure?
It is quite obvious that a decrease in the metabolic activity of cellular structures can lead to a mismatch between the processes of catabolism and anabolism. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid an unwanted overdose of the drug, and for this you need to know exactly how much biorevitalizant will be safe for the patient when the drug is injected. Let us estimate how much hyaluronan can be administered to a patient once. If the injection zone has an approximate size of 20x20 cm (400 cm2), then with an average dermis thickness of 4 mm, the volume of the dermal layer will be 160 cm3. The physiological concentration of hyaluronic acid in the dermis is 0.05 wt% (0.5 mg/ml). Thus, the physiological amount of hyaluronan in the area of the intended injection is 160 cm2 x 0.5 mg/cm3 = 80 mg.
Numerous studies show that the age-related decrease in the content of endogenous hyaluronic acid in the skin of patients becomes noticeable only after the age of 60, and the main fluctuations in its amount are associated with the seasonal factor (in particular, the decrease in its content in the skin in the summer occurs mainly exposed to UV light). As a rule, these fluctuations amount to 15–20% of its physiological content. It follows that the maximum biorevitalizing effect can be achieved with the introduction of 2-2.5 ml of 0.5% or 1-1.5 ml of 1% hyaluronan hydrogel.
It should be noted that a 1% (10 mg / ml) solution of hyaluronic acid is the concentration limit for a biorevitalizant. Let's dwell on this in more detail.
The property of hyaluronan macromolecules, even at relatively low concentrations (of the order of 0.05-0.1 wt %), to form viscous hydrogel structures in aqueous solutions is well known. A hyaluronic acid molecule with a molecular weight of 1-1.5 million Da is capable of absorbing at least 100 times more water than it weighs. Thus, in a 1% solution of hyaluronan, all water is in a bound state. Its macromolecules in such a solution exhibit significant conformational variability, but, as a rule, acquire the structure of an average statistical semirigid coil. Forming a more or less rigid coil, the polysaccharide molecules capture a huge amount of water and form very large domains.
Why is too much hyaluronic acid bad?
As shown by hydrodynamic studies, the actual density of hyaluronan chains within the molecular domain is low (about 0.1-0.5 wt %), but depends on its molecular weight. When such a gel is injected into the skin, divalent calcium and magnesium ions from the intercellular matrix of the dermis bind to the molecules of the introduced hyaluronic acid and form cross-links of ionic polymer chains. With an increase in the density of cross-links, the gel acquires a sparingly soluble bulk structure. At the same time, the size of its pores decreases, which makes it difficult for such a structure to be permeable to cleavage enzymes (hyaluronidases). As a result, both the distribution of the gel in the intercellular space of the dermis and the catabolism of hyaluronic acid slow down.
With an increase in the concentration of hyaluronic acid in the gel, especially when the value exceeds 1 wt%, a dense intermolecular network is formed, which leads to a significant increase in its viscosity. In concentrated hydrogels, hyaluronic acid can no longer exist as an "independent body" and acquire various spatial structures. Only such conformations are possible in which each disaccharide unit of each macromolecule occupies only that place in space that is not occupied by neighboring macromolecules. Therefore, in concentrated solutions, molecular coils are significantly intertwined with each other and in some places form regions with a low water content. In these areas, hyaluronic acid is, as it were, underdissolved and is a kind of compressed sponge. When such hydrogels enter the aquatic environment, and the dermis is 70-80% water, the hyaluronic acid coils straighten out, taking on the most energetically favorable conformation, and begin to "pull" water from the intercellular (interstitial) space of the dermis. (The same thing happens when the compressed sponge is released from deforming stresses.) Thus, highly concentrated hyaluronan gels, when injected intradermally, lead, paradoxically, not to growth, but, on the contrary, to a decrease in the level of hydration of the dermis. This is confirmed by the results of clinical trials conducted in 2008 at the Institute of Plastic Surgery and Cosmetology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation under the direction of V.G. Zmazova.
water from the intercellular (interstitial) space of the dermis. (The same thing happens when the compressed sponge is released from deforming stresses.) Thus, highly concentrated hyaluronan gels, when injected intradermally, lead, paradoxically, not to growth, but, on the contrary, to a decrease in the level of hydration of the dermis. This is confirmed by the results of clinical trials conducted in 2008 at the Institute of Plastic Surgery and Cosmetology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation under the direction of V.G. Zmazova.
water from the intercellular (interstitial) space of the dermis. (The same thing happens when the compressed sponge is released from deforming stresses.) Thus, highly concentrated hyaluronan gels, when injected intradermally, lead, paradoxically, not to growth, but, on the contrary, to a decrease in the level of hydration of the dermis. This is confirmed by the results of clinical trials conducted in 2008 at the Institute of Plastic Surgery and Cosmetology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation under the direction of V.G. Zmazova.to a decrease in the level of hydration of the dermis. This is confirmed by the results of clinical trials conducted in 2008 at the Institute of Plastic Surgery and Cosmetology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation under the direction of V.G. Zmazova.
to a decrease in the level of hydration of the dermis. This is confirmed by the results of clinical trials conducted in 2008 at the Institute of Plastic Surgery and Cosmetology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation under the direction of V.G. Zmazova.
How can excess hyaluronic acid harm?
Avicenna's well-known saying "Everything is medicine and everything is poison" just means that the physiological effect of various chemical compounds and physical factors is, as a rule, dose-dependent. The redistribution of interstitial water of the intercellular matrix with the introduction of significant amounts of hyaluronic acid, of course, is a stress factor for the dermis. Instead of "... achieving the effect of revitalizing the skin and increasing its adaptive capabilities by recreating a high-quality intercellular matrix and increasing the proliferative activity of fibroblasts within genetically programmed limits", as they say in articles on biorevitalization, injections of large amounts of hyaluronic preparations, on the contrary, lead to destabilization of tissue and cellular homeostasis.
Loss of moisture by fibroblasts and other structural elements of the dermis leads to a change in pH, ionic composition and ionic strength of the intercellular medium, which can disrupt the normal functioning and activity of matrix proteins due to changes in their structure or their partial denaturation. Hydrophobic amino acids - tryptophan, tyrosine, phenylalanine, which in the three-dimensional structure of proteins are usually located inside the macromolecule, come to the surface of protein aggregates. These amino acids actively absorb UV radiation at a wavelength of 280 nm, and proteins become more sensitive to this part of the spectrum. As a result, an unstable conformation of proteins occurs, leading to their aggregation and the formation of deposits (amyloids). Besides, as a result of energy transfer processes excited by UV radiation, hydrophobic amino acids can participate in the formation of singlet oxygen, an active form of oxygen involved in oxidative stress processes. Singlet oxygen, being a precursor of the hydroxyl radical, promotes the appearance of intermolecular crosslinks in the proteins of the intercellular matrix of the dermis. This is an extremely undesirable process that leads to a deterioration in the physicochemical properties of collagen, a decrease in its elasticity and swelling ability, the development of resistance to collagenase and the likelihood of collagenosis.
promotes the appearance of intermolecular crosslinks in the proteins of the intercellular matrix of the dermis. This is an extremely undesirable process that leads to a deterioration in the physicochemical properties of collagen, a decrease in its elasticity and swelling ability, the development of resistance to collagenase and the likelihood of collagenosis.promotes the appearance of intermolecular crosslinks in the proteins of the intercellular matrix of the dermis. This is an extremely undesirable process that leads to a deterioration in the physicochemical properties of collagen, a decrease in its elasticity and swelling ability, the development of resistance to collagenase and the likelihood of collagenosis.
The data presented in the article convincingly indicate the importance of taking into account such a parameter as the concentration of hyaluronan in preparations for biorevitalization during aesthetic procedures. In practice, it is possible to determine whether an overdose of a biorevitalizant has occurred by the duration of the existence of papules after injections. Papules at injection points that do not resolve within a day directly indicate an excess amount of injected hyaluronic acid.
Human skin is the organ that first takes on the action of many external negative factors. It has a high adaptive and regenerative potential. Therefore, a one-time excess of the administered dose of hyaluronan, of course, will not have a significant detrimental effect. But we must not forget that biorevitalization courses usually include 3-5 injection procedures and are carried out at intervals of 2-3 times a year. Such “rejuvenating” injections of a biorevitalizant with an excess of the permissible water dose of hyaluronic acid can significantly worsen the patient's skin condition over several years of use. Our task is to draw the attention of cosmetologists, and the patients themselves, to the possible consequences of such procedures.
> It must be remembered that the presence of papules that do not resolve for a long time after the introduction of a biorevitalizant is not just a cosmetic defect, but a serious reason to refuse to use such a drug. In the light of the topic raised, a completely logical question may arise - is a similar situation possible with fillers based on hyaluronic acid, since the concentration of polysaccharide in them is 2% or more? When using fillers, these problems are unlikely, because. the sorption capacity of cross-linked hyaluronic acid is several times less than that of unmodified one. According to http://www.beauty-face.ru/





Add a comment