Among all pathologies, including hematological ones, anemia due to iron or vitamin B12 deficiency often fades and is considered a less severe disease. Anemia develops gradually, without any special clinical manifestations, and may not be diagnosed for a long time due to the mild severity of nonspecific symptoms. But with the development of the process and its long-term existence, the complications of anemia no longer seem to be harmless processes. What are the main signs of B12 deficiency anemia that will allow diagnosing the process and preventing the development of complications?
Appearance of a patient with B12 deficiency anemia
As mentioned above, the symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia develop gradually, slowly and are non-specific. When collecting an anamnesis, it turns out that the patient feels fatigue, dizziness, weakness, shortness of breath and palpitations for a long time. Objectively, patients have pale skin. On examination, one pathognomonic sign of B12-deficiency anemia can be detected – glossitis, in which the tongue looks even, smooth, shiny, acquiring the appearance of a "varnish tongue". The color of such a tongue with gloss is bright red or crimson. Such changes in the tongue are due to atrophy of the papillae.
What complication of B12-deficiency anemia should be feared?
The nervous system reacts to vitamin B12 deficiency by the development of funicular myelosis. Demyelination of nerve fibers is manifested by paresthesia in the extremities, symptoms of polyneuropathy, impaired sensitivity and increased tendon reflexes. Neurological symptoms should be feared, as they can make the patient "lying down".
Funicular myelosis significantly affects the well-being and quality of life. Gastrointestinal symptoms may include: – nausea, dyspepsia. From laboratory and instrumental studies, fibrogastroscopy is performed, in which atrophy of the mucous membrane is detected, and a blood test.
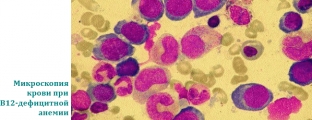
Anemia is detected in the blood test (decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells), the size of red blood cells is increased, which is why B12-deficiency anemia is called macrocytic, the color indicator is increased.
Thus, B12 deficiency anemia is characterized by the presence of a triad of symptoms:
- Blood damage.
- Gastrointestinal disorders.
- Nervous system damage.
Methods of treatment of B12 deficiency anemia. Prevention of anemia
If B12 deficiency anemia is detected, therapy is carried out taking into account the severity of the process, the presence of neurological disorders and depending on the cause of the disease.
If helminths have become the cause of anemia, it is necessary to deworm the body, and then prescribe vitamin B 12. In case of organic disorders of the digestive tract, it is advisable to use enzyme preparations together with the introduction of parenteral vitamin B12. If antibodies to gastromucoprotein or gastromucoprotein + B12 complex are detected, corticosteroid therapy is prescribed.
In case of a significant decrease in hemoglobin (less than 60 g / l) or in a coma, blood transfusion is recommended. The erythrocyte mass is injected in 250-300 ml (5-6 transfusions). In the presence of funicular myelosis, the dose of cyanocobalamin is 500 mcg daily, which is administered 1 or 2 times.
Criteria for the effectiveness of therapy for B12-deficiency anemia:
- After several blood transfusions, a sharp reticulocytosis is observed without fail.
- Restoration of blood counts occurs within 2 months, and before the disappearance of the symptoms of funicular myelosis, it may take about six months.
To prevent the development of B12 deficiency anemia, you just need to correctly and rationally eat. Vegetarians should include milk in their diet. A timely visit to a doctor with symptoms from the digestive tract can prevent the development of neurological symptoms, which for a long time reduces or eliminates the patient's ability to work and worsens the quality of life. It is recommended to take a general blood test every six months for early detection of pathological processes.







Add a comment