Hair follicles of a person are constantly undergoing renewal: immediately after hair loss, the entire follicle begins to grow and develop again.
Scientists used to be sure that this process depends only on the work of stem cells, but recent studies have shown that regulatory T-cells play a significant role in the hair growth process.
Current evidence suggests that T-cell defects can directly cause alopecia areata and other types of alopecia, a common autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss. Read more about the scientific discovery on estet-portal.com in this article.
New research into the role of T cells
Scientists have recently discovered that regulatory T cells, which are normally responsible for controlling the inflammatory response, trigger stem cells in the skin to promote healthy hair growth. Thus, it became clear that these cells are absolutely indispensable in the activation of stem cells. This means that it is they that trigger the restoration of the hair follicle, and without them, alopecia develops.
Anti-inflammatory immune cells directly activate skin stem cells.
Regulatory T-cells also trigger stem cells to repair skin injuries, which makes them promising for use in regenerative medicine for wound healing.
Human stem cells for hair regeneration
The classic role of human skin T-cells
Normally, the T-regulators act as "peacekeepers", telling the entire immune system where the enemy is and where the friend is. When they do not perform their function properly, allergies or autoimmune diseases can develop.
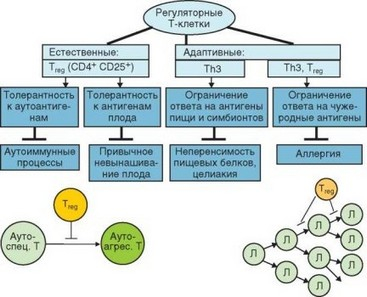
Most T-regulators circulate through the lymphatic system, but some reside in other tissues where they appear to have local anti-inflammatory effects.
For example, in the skin, T-regulators ensure the tolerance of the immune system to opportunistic flora.
Researchers tried to establish the effect of T-regulators on the skin, for which they artificially removed these cells from mice. But the result surprised them: when the animals were shaved off to observe the affected skin, the shaved hair never grew.
Read the latest articles in Telegram!
T-cell regulators – hair growth activators
Research has shown that T-regulators play a role in triggering hair follicle regeneration as they are closely linked to the stem cells that reside in hair follicles and allow them to regenerate. The number of active regulatory T cells around the follicle stem cells usually increases greatly as the hair enters the growth phase.
Stem cells only in combination with immune cells will enable the follicle to begin the regeneration process.
T-regulators are usually responsible for suppressing the inflammatory process in tissues, however, the mechanism of hair growth activation is not associated with this function. The fact is that T-cells stimulate stem cells through intercellular connections, by expressing specific signaling proteins.
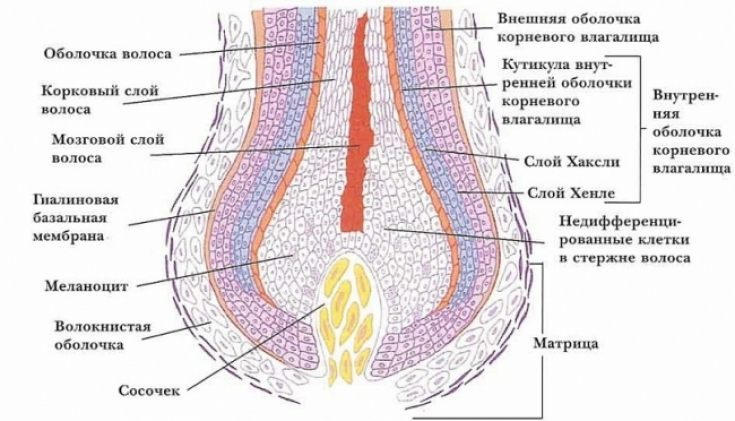
Scientists suggest that skin stem cells and T-regulators have co-evolved, so that T-cells not only protect stem cells from inflammation, but also take part in their regenerative work.
These results may have implications for the treatment of focal alopecia and other autoimmune diseases of the skin and the whole organism.
You may also be interested in: A new compound has been synthesized for the treatment of alopecia and skin inflammation







Add a comment