In a series of experiments in mice, researchers used a new experimental compound, D-threo-1-phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol (D-PDMP), to successfully reverse alopecia, the appearance of gray hair hair and skin inflammation associated with eating a diet rich in cholesterol and fats.
Researchers say the new compound stops the production of certain fats called glycosphingolipids (GSLs), which are major components of skin and other cell membranes.
Read in the estet-portal.com article which synthetic compound can treat alopecia, inflammation of the skin and stop the appearance of gray hair.
Induction of alopecia, graying of hair and skin inflammation with diet
Researchers fed one group of mice a high-fat, high-cholesterol Western diet and a second – standard food. All mice were fed prescribed diets from 12 weeks of age to 20 weeks of age.
Compared to those eating the standard diet, mice that ate the Western diet lost hair, suffered skin damage and hair lightening (75% of mice). These results were greater when the mice continued to eat the Western diet for 36 weeks.
Mice fed a diet high in fat and cholesterol are more likely to develop gray hair, alopecia, and skin inflammation.
Follow us on Instagram
Efficacy of D-PDMP for the treatment of alopecia and skin inflammation
Ranging from 20 to 36 weeks of age, mice in both groups were given varying amounts of D-PDMP, either in a capsule or as a topical liquid.
Mice given D-PDMP at 1mg/kg po capsule and 10mg/kg topically as a solution for weeks 20 to 36 on a Western diet showed hair color recovery, alopecia and skin inflammation reduction. Systemic (E) and local (F) application of the drug showed the same effectiveness.
• The research team then looked at the skin of the mice under a microscope and found that the skin of mice fed a Western diet was infiltrated with neutrophils, indicating inflammation in various areas of the skin.
D-PDMP significantly reduced the number of neutrophils, which meant a decrease in inflammation and skin alteration.
• Mass Spectrometric Analysis – method of identification and quantitative determination of the chemical composition – was used to determine the levels of GSLs such as ceramides, glucosylceramides and lactosylceramides in mice.

 After administering D-PDMP to mice at the above dosage, an increase in ceramide levels to normal levels was confirmed.
After administering D-PDMP to mice at the above dosage, an increase in ceramide levels to normal levels was confirmed.
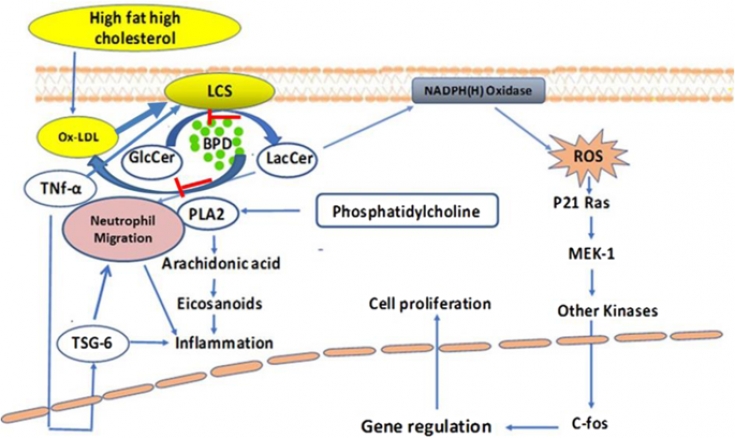
Let's consider the mechanism of action of lactosylceramide in inflammation and skin repair with D-PDMP. Feeding a Western diet increases levels of an oxidized phospholipid that activates lactosylceramide synthase (GalT-V) to synthesize lactosylceramide, which produces reactive oxygen species. Lactosylceramide also reacts with infiltrating neutrophils to activate phospholipase A-2, thereby releasing arachidonic acid, eicosanoids, and promoting inflammation.
This event loop can be broken by the judicious use of D-PDMP.
Perspective of using D-PDMP in the treatment of alopecia and hair bleaching
The results show that a Western diet high in fat and cholesterol causes alopecia, hair discoloration and skin inflammation in mice.
 You may be interested in an article on our website estet-portal.com in the "Trichology" section:
You may be interested in an article on our website estet-portal.com in the "Trichology" section:







Add a comment