Pathology of the thyroid gland – quite common.
Thyroid hormones have a multidirectional effect, so the hyperfunction of this gland can manifest itself as a whole symptom complex.
In this publication on estet-portal.com we bring to your attention a guide to laboratory control and clinical observation of patients with hyperthyroidism, in particular with hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis.
- Hyperthyroidism in adults
- Peculiarities of treatment of hyperthyroidism in children
- Monitoring of prescription of drugs for hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism in adults It is recommended to prescribe therapy with radioactive iodine isotopes as the first line of choice for adults with secondary hyperthyroidism against the background of multiple nodular changes in the thyroid gland, except for clinical situations where this tactic is unacceptable, for example, there is a risk of compression, malignancy; during pregnancy, or if the birth of a child is expected within the next 4-6 months. Follow us on
!
To suggesttotal thyroidectomy or lifelong antithyroid drugs as first-line choice in adults with secondary hyperthyroidism associated with multiple nodular changes, only possible if treatment with radioactive iodine isotopes unacceptable. Therapy with radioactive iodine isotopes
orsurgery (hemithyroidectomy) as first line of choice for treatment of overactive thyroid in adults is indicated when there is a single nodule or lifelong antithyroid drugs are contraindicated, and also in case of resistant hyperthyroidismza.
Causes of pain in the thyroid gland Peculiarities of treatment of hyperthyroidism in children
Children and adolescents withGraves' disease or toxic nodular goiter are recommended to be given antithyroid drugs for at least 2 years and possibly long-term use
as the first line of choice for therapy in children and adolescents with Graves' disease.What is the danger of subacute thyroiditis Consider continuing or resuming antithyroid medication, and considering radioiodine therapy or surgery (total thyroidectomy) for children and adolescents with Graves' disease
who are on antithyroid medication only if ifrelapse of hyperthyroidism.
Children and adolescents with secondary hyperthyroidism against the background of single or multiple nodular changes should be prescribed antithyroid drugs in the carbimazole titration regimen, as well as the possibility of using
radioactive iodine isotopessurgical intervention 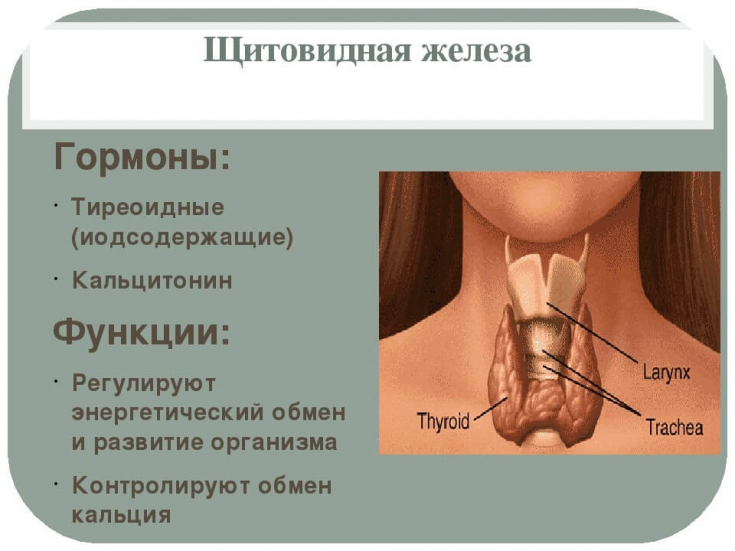 after consulting with allied experts.
after consulting with allied experts.
It is possible to cancel and not prescribe in the future thyrostatic drugs if the patient that agranulocytosis
.Monitoring the prescription of drugs for hyperthyroidism
For adults, children, and adolescents receiving thyrostatic drugs, tests for TSH, T4, and T3 every 6 weeks until TSH reaches the control range, and then − assessment of TSH levels every 3 months until the withdrawal of antithyroid drugs. Monitoring of general clinical blood counts and liver enzyme activity is not recommended in adults, children and adolescents who receive thyrostatic drugs to correct hyperthyroidism, if there is no evidence of the possible development of agranulocytosis or liver dysfunction.
For adults who have discontinued thyrostatic drugs, TSH levels should be assessed within 8 weeks of stopping the drug, then − TSH every 3 months for 1 year and then TSH once a year.
Monitoring of the condition of patients after surgical treatment includes prescribing
hormone replacement therapylevothyroxine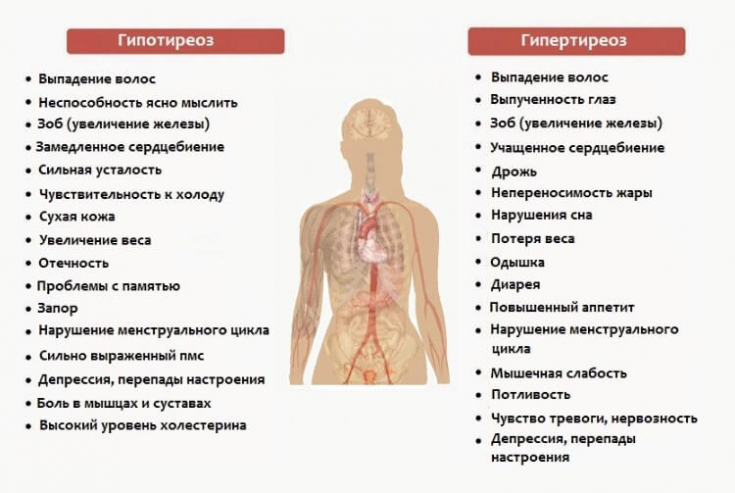 , taking into account recommendations for dosage and monitoring of hypothyroidism.
, taking into account recommendations for dosage and monitoring of hypothyroidism.
It is also important to assess the level of TSH and T4 2 and 6 months after surgery, and then − Once a year for adults, children and adolescents who have had a hemithyroidectomy.







Add a comment