Subacute thyroiditis, also known as de Quervain's thyroiditis, or granulomatous thyroiditis, is an inflammatory disease, probably of viral origin. Susceptibility to the disease is associated with the appearance of certain types of human leukocyte antigens, which can influence the course of the disease. The prevalence of subacute thyroiditis is highest among middle-aged women, about 75-80% of cases of this disease are females.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com about the main symptoms and criteria for diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis.
- Clinical presentation of subacute thyroiditis
- Confirmation of the diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis
- Symptoms of subacute thyroiditisa
Clinical presentation of subacute thyroiditis
For several decades, the diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis has been based on the presence of pain when the thyroid gland is enlarged (usually the pain radiates to the ears, lower jaw, and upper chest area) or when the thyroid gland becomes more sensitive to palpation and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is significantly accelerated ( ESR), and these two parameters were considered as the main diagnostic criteria.
Follow us on Instagram!
In addition, cases of subacute thyroiditis with painless syndrome are increasingly being described. In some patients, the absence of pain does not exclude the diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis if other criteria support this disease.
Clinical efficacy of methods for diagnosing thyroid neoplasmss
Confirmation of the diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis
It is considered that two main criteria and any two additional criteria must be present to confirm the diagnosis. Additional criteria: decrease in iodine storage capacity, presence of transient thyrotoxicosis, fever, a typical picture for subacute thyroiditis during ultrasound (ultrasound) and fine needle aspiration puncture biopsy (FNA), low level of antithyroid antibodies in the blood.

But lately in> 25% of patients showed an increase in the level of antithyroid antibodies, so this criterion is controversial. But considering only these diagnostic criteria can lead to incorrect diagnosis and treatment.
However, the situation is much more dangerous when both the main criteria for subacute thyroiditis and two additional ones (except for TAPP) are taken into account, and a false diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis significantly delays the treatment of an oncological disease that can clinically mimic subacute thyroiditis.
The situation is extremely dangerous if the diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis is erroneously established on the basis of other criteria than the results of ultrasound and TAP, which leads to untimely diagnosis of malignant tumors with a poor prognosis. The main diagnostic criterion in such cases is not taken into account, because the diseases can be confirmed in the presence of multinucleated giant cells according to the results of tAPB.
Diagnosis of hypofunction of the parathyroid glands from the standpoint of evidence-based medicines
Symptoms of subacute thyroiditis
Typical symptoms of subacute thyroiditis are pain in the neck and tenderness on palpation of the thyroid gland, accompanied by a significant increase in the level of ESR. The affected part of the thyroid gland is usually enlarged and has a hard consistency. Inflammation of the thyroid gland causes destruction of the follicles and release of hormones into the blood, which in turn leads to an increase in the level of free thyroid hormones and a decrease in TSH levels.
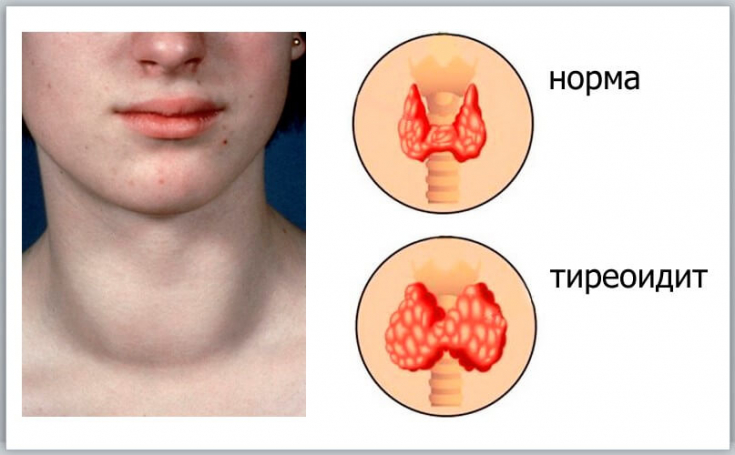
Given the above observations, the investigators propose the following criteria for diagnosing subacute thyroiditis:
- Increased blood ESR or CRP.
- Presence of a hypoechoic area with blurred borders and reduced vascularity on ultrasound.
- PTAB to confirm the diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis, or at least to rule out malignancy.
Clinical studies of hypothyroidism
Additional criteria include:
a) significant swelling in the thyroid gland;
b) pain in the thyroid gland;
c) increase in the level of T4 St. and a decrease in the level of TSH in the blood
d) decrease in iodine storage capacity.
Thyrotoxicosis is dangerous due to atherosclerotic complications
For a qualitative diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis, the results of the first three criteria and at least one of the additional ones should be taken into account. Ultrasound should be the mandatory method for examining every patient with suspected subacute thyroiditis. And the decisive diagnostic method should be PTAB, especially if there is doubt after ultrasound.

According to the researchers, the priority goal of the TAPT method is to exclude a malignant process that mimics the manifestations of subacute thyroiditis. It should always be remembered that the diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis should be established only after the exclusion of a malignant process in the thyroid gland. After all, only the correct diagnosis can prolong the life of a patient with a malignant tumor.
Attention to the face: signs of possible thyrotoxicosis in the patient







Add a comment