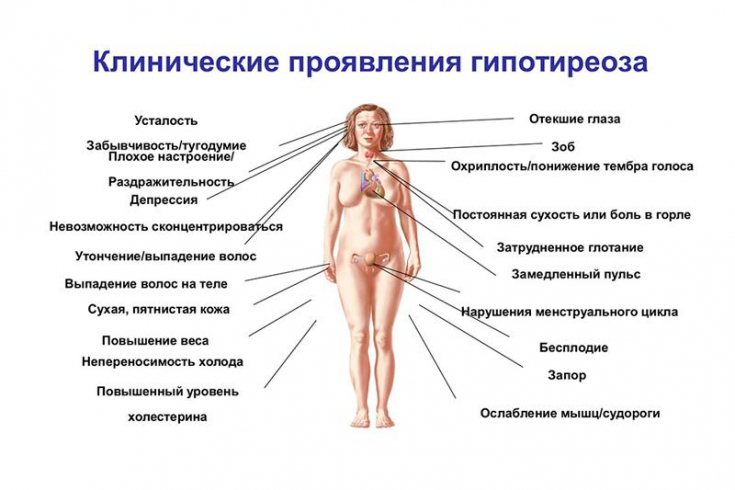
Thyroid dysfunction is a common disorder that affects 3 to 21% of the population, with a higher prevalence among women and the elderly. The clinical picture of thyroid dysfunction is non-specific and in most cases slowly progresses.
Learn in the article on estet-portal.com about modern approaches to the diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction and the main effects of thyroid hormones in the body.
Regulation of thyroid hormones in blood serum
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) has a complex feedback relationship with thyroid hormones − thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Accordingly, overt hypothyroidism is defined as a serum thyroid stimulating hormone concentration above reference levels with low free T4 levels, while subclinical hypothyroidism is diagnosed when TSH levels are high and circulating free T4 remains normal.
Follow us on Instagram!
The relationship between TSH and thyroid hormones is influenced by a number of factors, including age, smoking, and the amount of thyroid peroxidase antibodies.
Recent research data suggest that serum levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone increase in the elderly.
In this regard, scientists in the UK analyzed the results of various studies of patients with hypothyroidism, in order to establish the optimal hormone replacement therapy in older people.
Thyrotoxicosis is dangerous due to atherosclerotic complications
Age-related variability in thyroid hormone concentrations
Study shows that blood TSH levels increase with age in women over 45, but this phenomenon is not seen in men. The use of thyroid-stimulating hormone reference values for all age groups in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III (NHANES) resulted in approximately 70% of older people with slightly elevated serum TSH levels being incorrectly classified as having subclinical hypothyroidism, and the researchers noticed that the level of TSH gradually shifts towards higher concentrations with age.
The prevalence of TSH elevation can be greatly overestimated if age-specific ranges are not used.
Thyroid function test
Laboratory examination of thyroid function in the form of determination of circulating TSH and thyroid hormones in the blood serum is essential for establishing a diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction. Current testing methods have the ability to detect very low levels (<0.1 IU/L), and in general TSH testing should now be the first line test to assess thyroid status in most patients with suspected thyroid disease.
How to Boost Your Metabolism: The Secret to a Boosted Metabolism
However, it is important to remember that serum TSH measurements are only reliable for diagnosing thyroid disorders, provided that patients do not have pituitary disease and are not receiving drugs that affect TSH secretion.
Several studies show significant differences in repeated TSH measurements over time in the same individuals, suggesting that TSH levels increase with age when measured over many years.
Thus, the upper end of the serum TSH range in the elderly does not reflect age-related changes and leads to overdiagnosis of hypothyroidism and, as a result, possible inappropriate treatment of thyroid hormones in people in this age group.
Cardiovascular disease and thyroid hormones
The cardiovascular system is the main target of thyroid hormone action and is sensitive to even small changes in thyroid hormone concentrations. A number of observations have shown that even a slight decrease in the level of thyroid hormones is associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Analysis of participants in the Rotterdam study found that the risk of sudden cardiac death is higher in individuals with high T4 levels. In an age-stratified analysis, the risk of sudden cardiac death was found to be significantly higher in older individuals (> 65 years) with high T4 levels or low TSH levels.
Attention to the face: signs of possible thyrotoxicosis in the patient
Influence of thyroid hormones on cognitive functions
The relationship between overt hypothyroidism and cognitive impairment, depression and other psychiatric manifestations has long been studied. The term "myxedematous madness" was coined to describe the constellation of conditions with manifestations such as confusion, disorientation, and psychosis that accompanied profound hypothyroidism. While hypothyroidism has been described as the cause of "reversible dementia", there is insufficient evidence to confirm that there is a complete recovery of neurocognitive deficits after treatment for hypothyroidism.
Surgical treatment of parathyroid hyperfunction

PAQUID surveys of individuals aged 65 years and older have shown that elevated TSH levels are significantly associated with the presence of depression. Two large randomized controlled trials, one of which involved 94 patients over 65 years of age, found no improvement in cognitive function with thyroid replacement therapy for subclinical hypothyroidism.
Research in the field of thyroid pathology is quite relevant and the function of hormones has not yet been thoroughly studied, since the spectrum of their action is quite extensive. Follow our articles on estet-portal.com to keep up to date with the latest medical discoveries.
Therapeutic Strategies for the Development of Insulin Analogs







Add a comment