In the salivary glands, cysts can occur, which are tumor-like formations. There are cysts of the minor salivary glands, parotid gland, sublingual and submandibular. Cysts of the salivary glands can form as a result of an injury to the gland, after which an inflammatory process has developed, as a result of obstruction of the salivary gland by a stone, and the cyst may also be congenital. Such cysts form from duct diverticula. When the gland is obturated, the cyst does not form, since it atrophies.
Small salivary gland cysts
Cysts of the minor salivary glands are usually localized in the area of the lower lip. The cyst is a formation with a thin capsule and contains a viscous yellow liquid. Such a formation appears after an injury to the lower lip, looks like a swelling of an elastic consistency, which eventually begins to interfere with talking and eating. A cyst of a minor salivary gland can break through, after which it temporarily disappears, then reappears. When cysts of the salivary glands are detected in the small glands, planned treatment is carried out, which consists in surgical excision. Excision of the cyst membrane is performed carefully because of its thinness. After that, hypertrophied lobules of small salivary glands remain in the wound, which must be removed to prevent recurrence of the salivary gland cyst.
Cysts of the salivary glands of the sublingual region. What is ranula?
This type of salivary gland cyst develops from the lobule of the sublingual gland. A cyst in the sublingual salivary gland is called a ranula. As it becomes large, the cyst resembles a sac-like formation at the bottom of the mouth.
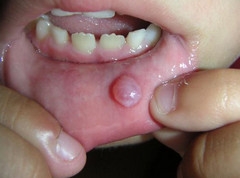 On examination, there is a bulge that is covered with a bluish-pink mucosa. When puncturing such cysts of the salivary glands, a mucous viscous liquid is obtained. Sometimes the ranula grows into the maxillofacial muscle and ends up in the submandibular region, where it appears as a swelling. Ranula quite often breaks into the oral cavity, the contents are released from it, and later the cyst forms again.
On examination, there is a bulge that is covered with a bluish-pink mucosa. When puncturing such cysts of the salivary glands, a mucous viscous liquid is obtained. Sometimes the ranula grows into the maxillofacial muscle and ends up in the submandibular region, where it appears as a swelling. Ranula quite often breaks into the oral cavity, the contents are released from it, and later the cyst forms again.
Differential diagnosis of salivary gland cysts is carried out with dermoid, epidermoid and other cysts. The final diagnosis is made on the basis of X-ray and morphological examination.
Treatment of a cyst of the sublingual region is only operative and consists of the following stages:
- excision of the ranula consists in removing the upper wall of the cyst in the place of its largest diameter,
- further, the cyst shell is sutured with the mucous membrane of the sublingual region.
Cyst of the salivary glands of the parotid and submandibular region
Such cysts are rare. Symptoms begin to appear with the formation of a painless swelling, which gradually increases, reaching a large size. The cyst of the submandibular and parotid region significantly disrupts the configuration of the face. Fluctuation is felt on palpation. After the puncture, the cyst disappears, then forms again.
For the treatment of salivary gland cysts of this nature, the contents of the cyst are aspirated, after which a hypertonic solution is injected into it. Then the solution is evacuated and a pressure bandage is applied.
Thus, the presence of a cyst of the salivary glands is only fraught with inconvenience and defects in appearance in some cases. Salivary gland cysts are excised to prevent the outflow of their contents into the oral cavity. Cysts do not pose any danger, therefore, having diagnosed a salivary gland cyst, it is worth explaining to the patient that it does not pose a big threat.






Add a comment