Not the simplest ingredient name – "hyaluronic acid" - now almost anyone knows, even a little interested in the topic of cosmetology. The familiar abbreviations "hyaluronka" and "hyaluronochka" are found in online discussions and are heard in the conversations of girlfriends in cafes and fitness clubs.
Hyaluronic acid is drunk, injected, smeared on the skin, dreaming of preserving youth and beauty forever. How does this wonderful ingredient work and how to use it correctly? Is it really Makropoulos' magical remedy to get rid of wrinkles and keep youthful forever?
Tiina Orasmäe-Meder, Cosmetologist, developer of Meder Beauty Science
What is hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid, if we talk about it from the standpoint of chemistry, is an anionic non-sulfate polysaccharide glycosaminoglycan, which can also be called hyaluronan or hyaluronate (but not hyaluronic acid!). It is a polymer of disaccharides consisting of D-glucuronic acid and DN-acetylglucosamine molecules linked by glycosidic bonds.
In different tissues of the human body, polysaccharide chains can be of different lengths, include up to 25 thousand fragments and have a size from five thousand to 20 million daltons. The average size of synovial fluid hyaluronate is three to four million daltons, while in the umbilical cord HA is 3.14 million daltons.
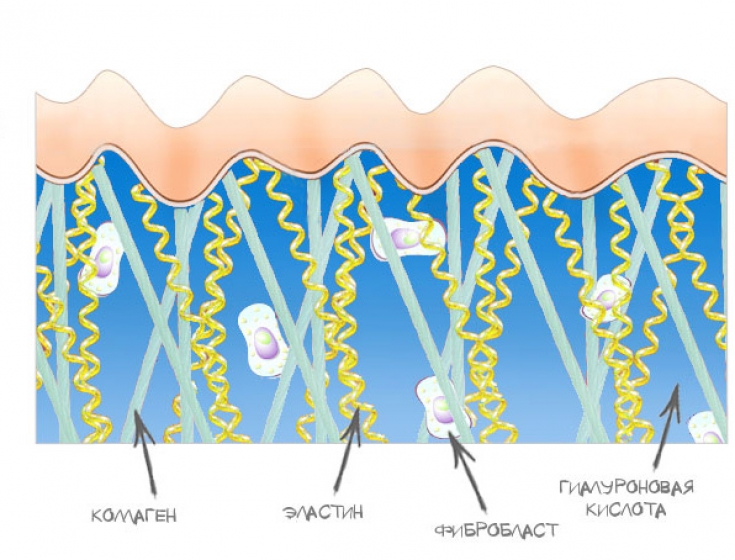
Hyaluronic acid is known to be one of the main components of the extracellular matrix of various tissues: it is found in the tissues of the nervous system, in connective and epithelial tissues, it is one of the components of the plasma membrane of the Golgi complex.
But it also plays a big role in the migration of malignant tumors and the spread of streptococcal infection: it all depends on the processes occurring in the body; deficiency or excess of hyaluronan can be both beneficial and harmful.

Several types of hyaluronic acid receptors have been found in the cells of the human body, which are activated by various processes.
The popularity of hyaluronic acid-based products in cosmetology has led many experts to mistakenly believe that hyaluronic acid is the actual basis of the dermis, and quite naively imagine that any introduction of hyaluronic acid implies some kind of "repair" effect of the dermis, which is described by a variety of commercial terms that have no physiological basis, such as "revitalization" or "redermalization".
In fact, there is not as much hyaluronic acid in the body as a cosmetologist might think.
The body of a woman weighing about 70 kilograms contains approximately 15 grams of pure hyaluronic acid, a third of which is destroyed and renewed daily.
In fact, a complete renewal of the entire pool of hyaluronic acid in a healthy middle-aged person takes about three to four days, and this implies degradation and new synthesis of hyaluronan in the tissues of the brain, joints, nerve trunks, all types of epithelium, blood vessels, eyes, skin and subcutaneous fat.
Synthesis of hyaluronic acid in the human body
The synthesis of hyaluronic acid can be accelerated and slowed down, its volumes can decrease and increase, and this is not always associated with age-related processes. We used to think that the amount of hyaluronic acid is a marker of skin aging; it is from this thesis that it is customary to proceed when prescribing hyaluronic acid preparations for cosmetic purposes.
Peculiarities of removing hyaluronic acid from the body: important information for specialists!
In fact, this is not always the case. The most important stimulus that accelerates the synthesis of hyaluronic acid in tissues is inflammation, including inflammation as a result of damage or injury.
Increased hyaluronic acid synthesis is part of a typical injury response and is an essential element in the early stages of inflammation.
Only after an increase in the amount of hyaluronic acid at the site of damage, cell migration and the synthesis of some important biological factors become possible.
Interestingly, hyaluronic acid plays a dual role in the inflammation process: it can both enhance and prolong the inflammatory response, and accelerate the healing process by accelerating granulation. In the skin, hyaluronate is actively involved in the processes associated with wound healing: it plays an important role in the process of hemostasis, inflammation, re-epithelialization and remodeling of the dermis.
The most dangerous complications from hyaluronic acid injections and how to avoid them?
How hyaluronic acid protects against free radicals
A very important feature of HA is its ability to protect cells from free radical damage.
Thanks to this, wound granulation is faster and more successful.
In the skin, hyaluronan is found in high concentration not only in the dermis, as we used to think, but primarily in the basal layer of the epidermis, where it plays a key role in the process of proliferation and migration of keratinocytes, that is, the actual renewal of the epidermis.
It is the characteristics of hyaluronic acid in the basal layer of the epidermis that largely determine the parameters of the stratum corneum of the skin and the ability of the epidermis to re-epithelialize.
With a decrease in the amount of hyaluronic acid in the basal layer, there is an activation of local inflammatory reactions, a weakening of the protective properties of the skin, a violation of the healing process, a decrease in the ability to retain moisture and a decrease in elasticity.
Hyaluronic acid in the body - not only beauty, but also health?
Cosmetologically, this looks like a sharp increase in skin sensitivity, the appearance of dryness, foci of peeling and irritation, and later on as the addition of fine wrinkles and a noticeable decrease in tone.







Add a comment