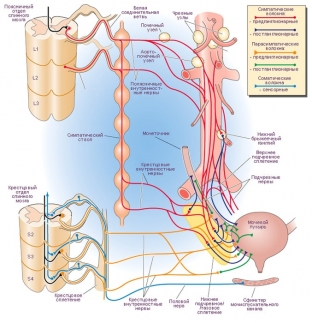
Much in the functioning of an organ depends on its innervation. In case of violation of innervation, the organ may have either an excessive number of impulses, or very little, on which its ability to perform its actions directly depends. Against the background of these disorders, there are many nosologies of diseases. Among them is a neurogenic bladder.
Neurogenic bladder implies a whole range of disorders that are associated with dysfunction of the urinary system. A disease such as a neurogenic bladder develops against the background of acquired or congenital pathologies of the nerves that are responsible for the process of voluntary urination. This damage to the nervous system makes the urinary system inactive or, conversely, overactive.
Causes of neurogenic bladder development
The normal functioning of the bladder is regulated by a large number of nerve plexuses at several levels. Starting from congenital defects of the terminal spine and spinal cord to dysfunction of the nervous regulation of the sphincter, all these disorders can provoke the appearance of symptoms of a neurogenic bladder. These disorders may be the consequences of trauma and be explained by other pathological processes in the brain, such as:
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Stroke
- Discirculatory encephalopathy.
- Alzheimer's disease.
- Parkinsonism.
Spinal cord lesions such as spondylarthrosis, osteochondrosis, Schmorl's hernia, and trauma can also cause the development of a neurogenic bladder.
Main symptoms of neurogenic bladder
In the presence of neurogenic bladder dysfunction, the ability to voluntarily control the process of urination is lost.
Manifestations of neurogenic bladder are of 2 types: hypertonic or hyperactive type, hypoactive (hypotonic) type.
Hypertonic type of neurogenic bladder
This type appears when the function of the part of the nervous system that is located above the pons of the brain is impaired. At the same time, the activity and strength of the muscles of the urinary system becomes much greater. This is called detrusor hyperreflexia. With this type of innervation disorder of the bladder, the process of urination can begin at any time, and often this happens in an inconvenient place for the person, which leads to serious social and psychological problems.
Having an overactive detrusor eliminates the possibility of urine accumulating in the bladder, so people feel the need to go to the toilet very often. Patients with hypertonic type of neurogenic bladder feel the following symptoms:
- Stranguria - pain in the urethra.
- Nycturia - frequent urination at night.
- Compulsory urinary incontinence - rapid flow with strong urge.
- Severe tension in the pelvic floor muscles, which sometimes provokes a reverse flow of urine through the ureter.
- Frequent urge to urinate with little urine.
Hypoactive type of neurogenic bladder
The hypotonic type develops when the area of the brain below the pons of the brain is damaged, most often these are lesions in the sacral region. Such defects of the nervous system are characterized by insufficient contractions of the muscles of the lower urinary tract or the complete absence of contractions, which is called detrusor areflexia.
In a hypotonic neurogenic bladder, there is no physiologically normal urination, even with sufficient urine in the bladder. People feel these symptoms:
- Feeling of inadequate bladder emptying, ending with a feeling of fullness.
- No urge to urinate.
- Very sluggish urine stream.
- Pain along the urethra.
- Bladder sphincter incontinence.
Disturbance of innervation at any level can cause trophic disturbances.
Influence of innervation disorders on the urinary tract
With improper innervation, the blood supply to the organs of the urinary tract is disturbed. So, with a neurogenic bladder, cystitis often accompanies, which can cause microcysts.
A microcyst is a reduction in the size of the bladder due to chronic inflammation. With a microcyst, the function of the bladder is significantly impaired. A microcyst is one of the most difficult complications of chronic cystitis and neurogenic bladder.
If urine remains in the bladder, the risk of inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract increases. If the neurogenic bladder is complicated by cystitis, then this is a health hazard and sometimes requires surgical intervention.
Diagnosis and treatment of neurogenic bladder and its type
After collecting a detailed history, it is important to take urine and blood tests to exclude the inflammatory nature of the disease. Indeed, often the symptoms of inflammatory processes are very similar to the manifestation of a neurogenic bladder.
It is also worth examining the patient for the presence of anatomical anomalies in the structure of the urinary tract. To do this, radiography, urethrocystography, ultrasound, cystoscopy, MRI, pyelography and urography are performed. Ultrasound gives the most complete and clear picture.
After ruling out all causes, neurological examinations should be performed. For this purpose, EEG, CT, MRI are performed and various methods are used.
Neurogenic bladder is treatable. For this, anticholinergics, adrenoblockers, means to improve blood supply, and, if necessary, antibiotics are used. Therapeutic exercise, rest and rational nutrition will help to overcome the process faster.






Add a comment