Among all the neoplasms of the oral cavity, cancer of the tongue is in second place in terms of frequency of occurrence. The highest frequency of its development occurs after the age of 40 years. Tongue cancer has become widespread in the countries of India and Asia, which is associated with the tradition of chewing in these countries tonic mixtures of betel leaves, tobacco, ash, spices and vegetable oils, which have a carcinogenic effect. In our country, tongue cancer is more common in heavy smokers. Why does tongue cancer develop? Who is more at risk of developing oral cancer?
Why does tongue cancer develop? The main causes of epithelial metaplasia
The first place among the provoking factors for the development of tongue cancer is rightfully given to carcinogens, which are formed during the combustion of tobacco.
Alcohol potentiates the effect of tobacco smoke. Therefore, drinking smokers have a very high risk of developing tongue cancer. In addition to bad habits, occupational hazards have a carcinogenic effect. These are asbestos, salts of heavy metals, petroleum products, perchlorethylene.
The second place in importance is occupied by permanent traumatization of the oral mucosa. This can occur against the background of incorrectly made dentures, insufficient processing of the filling, in the presence of a sharp tooth edge with a broken tooth, or biting the tongue in the same place.
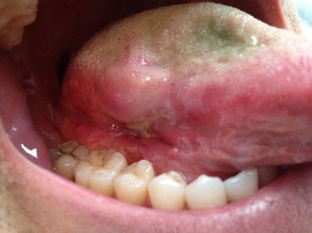
What is the role of viruses in the development of tongue cancer?
Studies in recent years have found a link between the occurrence of tongue cancer and chronic viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus or human papillomavirus. Read more about the effect of viruses on the epithelium on estet-portal.com. These viruses are able to block the influence of – tumor growth suppressors. Therefore, in patients who receive immunosuppressive therapy, a similar mechanism for the development of tongue cancer is observed.
All of the above factors provoke damage to the structure of the DNA of the cells of the epithelium of the tongue, the field of which develops hyperplasia or dysplasia of its mucous membrane. After some time, with further exposure to factors, changes in the mucous membrane are transformed into cancer.
Precancerous conditions of the tongue are:
- leukoplakia;
- chronic erosion of the tongue;
- pokingly – erosive or hyperkeratic form of systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Bowen's disease;
- lichen planus;
- benign neoplasms against the background of chronic trauma often degenerate into cancer of the tongue.
Classification of tongue cancer and measures to prevent dangerous pathology
Depending on the location of the damage to the cells of the tongue, cancer of the body of the tongue is distinguished, which is about 70% of cases, cancer of the lower surface of the tongue (10% of cases), and cancer of the root of the tongue. Cancer of the body of the tongue is more often localized in the middle of its lateral surface.
According to the microscopic characteristics of tongue cancer, such clinical forms are distinguished – exophytic (ulcerative or papillary) and endophytic (infiltrative – ulcerative, infiltrative). Cancer of the tongue in almost all cases is microscopically squamous.
Every person can prevent the development of tongue cancer by giving up bad habits - tobacco and alcohol use. It is important to increase immunity to fight chronic viral infections, which predisposes to neoplasms. When examining the oral cavity, the dentist should identify a possible cause of chronic trauma in the presence of damage to the oral mucosa. If tongue cancer affects the oral cavity, the process develops in several stages, which are characterized by certain symptoms. Find out the clinical manifestations of tongue cancer in our next article.







Add a comment