Every person during his life more than once faces such a problem as skin damage in the form of a burn. This is one of the most traumatic and unpleasant types of injuries, which is characterized by intense pain and a long period of rehabilitation. And it is dermatologists who should have the most knowledge about the nature and methods of treating burns. In today's article, estet-portal.com talks about a chemical burn of the face. For what reasons it can occur, and what methods of treatment are most effective in this case, read in this article.
Chemical burn of the face – a common phenomenon of our time
Burn – common occurrence in the daily life of every person. There are several main types of burns: thermal, electrical, radiation, and, finally, chemical. Sunburn or thermal injury to limbs on contact with a hot object or liquid – such situations are often found in everyday life, while a chemical burn of the face – rarer occurrence.
The rapid development of the chemical industry in the 21st century has led to the fact that today chemical burns can also be obtained even at home.
Washing, cleaning and even cosmetics can cause a chemical burn, and this condition requires the urgent initiation of effective therapy.
Chemical burn of the face:
- Main causes of facial chemical burns;
- classification of facial chemical burns: four degrees;
- peculiarities of treatment of chemical burns of the face.
Main causes of facial chemical burns
Among the main causes of facial chemical burns are the following:
- exposure to acids: acids – dangerous substances, which, nevertheless, in certain concentrations can be useful. Acids are often used in cosmetology, as the main ingredient in chemical peels and some cosmetic products. Under certain conditions, for example, if a product with a too high concentration of acid was used, the patient may receive a chemical burn, but often not deep, since when exposed to acid, a scab forms, preventing the substance from penetrating deep;
- Alkali exposure: These substances can be found in many cleaning products. A chemical burn of the face when alkali gets on the skin is characterized by severe trauma and deep damage, since a protective barrier in the form of a scab, as when exposed to acids, is not formed in this case;
- exposure to heavy metal salts: These substances can be found in some industrial compounds, herbicides and medical preparations. With careless behavior with them, heavy metal salts can damage the skin of the face, causing a superficial chemical burn, as if damaged by acids. The most common salts of heavy metals – gold, copper, mercury, iron, lead and others.
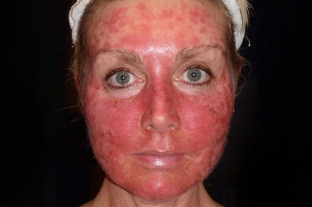
Classification of facial chemical burns: four degrees
Depending on the depth of the lesion and the characteristic clinical picture, there are 4 degrees of chemical burns of the face:
- at I degree, only upper layers of the epidermis are affected. This is accompanied by reddening of the skin, slight swelling and soreness. Dead cells, at the same time, exfoliate on their own;
- In the second degree of chemical burns, the epidermis is affected to a much greater depth, blisters with cloudy contents appear on the damaged skin. The epidermis regenerates on its own within about two weeks;
- with III degree chemical burns, all layers of the epidermis and dermis are affected. At the same time, if the dermis is partially affected – this is "A" the degree of burn, and if all layers of the skin are completely damaged – degree "B";
- IV degree chemical burn is characterized by damage to all layers of the skin, subcutaneous fat, muscles and bones. After a burn of this degree, pronounced cicatricial changes remain that persist throughout life.
Peculiarities of treatment of chemical burns of the face
Treatment of facial chemical burns depends on the degree of damage the patient is experiencing. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the pain syndrome with the help of analgesics, in especially serious cases, even narcotic ones, and also treat the burn wound. Only a doctor can remove any items or clothing from the face!
Depending on the damaging substance, it is necessary to use means that neutralize its effect.
In case of acid burns, the burnt surface is washed with 1-2% soda solution, then with 0.5% ammonia solution, and in case of alkaline burns, the wound is treated with 1-2% solution of acetic or citric acid.
In case of injuries of I and II degrees, the patient is prescribed local antibacterial drugs to prevent infection of the wound, as well as healing agents. If the damage is deeper – treatment is carried out in a hospital setting, and includes the infusion of colloid and crystalloid solutions.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read more articles on the site in the "Dermatology" section.
You may also be interested in: "Why it's important to know what caused a chemical burn".







Add a comment