In the gum tissue, the inflammatory process may be accompanied by the formation of false periodontal pockets that cover the dental crown. This process is called hypertrophic gingivitis. This is a form of chronic gingivitis, which occurs with a predominance of hypertrophic processes. The disease is preceded by long-term catarrhal inflammation in the gum tissue. Hypertrophic gingivitis can be an independent pathology or accompany an exacerbation of generalized periodontitis. Read more about the causes, symptoms and treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis below.
What are the causes of hypertrophic gingivitis?
Local causes of hypertrophic gingivitis include malocclusion, dental deposits, anomalies of individual teeth, improperly installed fillings, low attachment of the frenulum, mechanical trauma to the gums, and irrationally selected dentures. Violation of oral hygiene when wearing orthodontic appliances contributes to the development of hypertrophic gingivitis.
Among the common factors that contribute to the development of hypertrophic gingivitis, there is a change in hormonal status. This reason is the main one in the development of hypertrophic gingivitis during puberty, during menopause and during pregnancy.
Also, endocrinological disorders and the use of certain medications increase the risk of developing hyperplastic gingivitis.
Main clinical manifestations of hypertrophic gingivitis
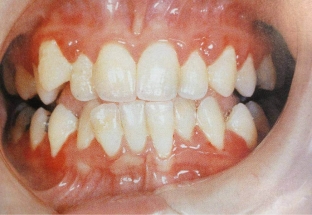
Hypertrophic gingivitis is characterized by burning sensation, bleeding gums and pain during brushing. Read about the appearance of the gums with gingivitis at estet-portal.com. The gum has a bright – red color, hypertrophy of the interdental spaces is determined. On examination, the gingival papillae are enlarged, edematous, hyperemia with a bluish tinge is determined. Gingival papillae have a glossy sheen. Gingival pockets often form and contain detritus. The dentogingival connection in hypertrophic gingivitis is not broken.
Fibrous gingivitis is manifested by the patient's complaints of gum enlargement, their pronounced density and spoiled aesthetic appearance. Such a gum can create discomfort when chewing food. At the same time, she has a pale – pink color and uneven surface. Examination reveals subgingival deposits.
Diagnostic process for hypertrophic gingivitis
When identifying suspicions of hypertrophic gingivitis, it is necessary to determine some parameters to clarify the diagnosis. This is a hygiene index, papillary – marginally – alveolar index, periodontal index, it is also necessary to conduct a Schiller test – Pisarev. Morphological examination of gum tissue and biopsy are performed as needed. No changes are found on the radiograph, so its implementation is impractical.
Differential diagnosis of hypertrophic gingivitis is carried out with the following diseases:
- epulis;
- gingival fibromatosis;
- with overgrowth of gums due to periodontal disease.
Treatment of various forms of hypertrophic gingivitis
Treatment of the edematous form of hypertrophic gingivitis consists of removing dental plaque, treating the oral mucosa with antiseptics, using periodontal applications, oral baths, rinsing with herbal decoctions and physiotherapy procedures - these are darsonvalization, ultrasound, electrophoresis, galvanization, laser therapy and gum massage.
If the above methods of treatment are ineffective, sclerosing therapy is used, which consists in injecting solutions of gluconate or calcium chloride into the gingival papilla.
Glucose and ethyl alcohol may be administered. Manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. Hormonal ointments are used to reduce swelling. Fibrous hypertrophic gingivitis is treated with cryodestruction or diathermocoagulation of hypertrophic papillae. Gingivectomy is also used, which involves the excision of an overgrown gum area.
Local treatment consists in the elimination of traumatic factors. The criteria for the effectiveness of the treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis are changes in the appearance of the gums and the absence of complaints.







Add a comment