The most effective sunscreens for the skin are those that block UV radiation while reducing chronic inflammation and improving the health of the stratum corneum. The skin becomes more vulnerable to damage in the presence of chronic inflammation. Such skin is more prone to developing skin cancer with prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Sunscreens were created to protect the skin from the sun's rays. What properties should sunscreens have for the skin?
Effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin
Sun damage includes immunosuppression, which is caused by ultraviolet A radiation. Immunosuppression is associated with epidermal cell dysplasia, caused by ultraviolet B radiation. Therefore, it is recommended to use sunscreens for the skin that protect against radiation.
In the absence of a sunscreen for the skin, an anti-inflammatory chain is activated on the surface of the skin, which sets the matrix metalloproteinase and gene transcription to work to produce cells that degenerate into skin cancer.
Ultraviolet damage is exacerbated by two skin anomalies that concern most adults: impaired permeability barrier of the stratum corneum
(SCPB) and overt or latent chronic inflammation of the epidermis and dermis.Skin with chronic inflammation needs to use sunscreen to prevent damage to the skin's outer barrier. In addition to inflammatory processes, external factors also destroy the skin barrier.
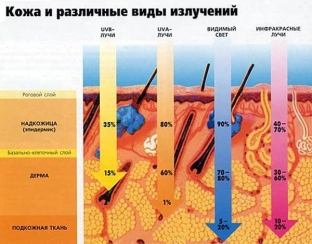
External factors that contribute to the destruction of the skin barrier:
- seasonal temperature drop;
- sudden changes in air humidity;
- exposure to pollutants;
- intensive skin cleansing and application of skin care products ;
- use of certain alcohols and derivatives of vitamins A and C;
- Hydroxy acids, which are part of the anti-age products available on the market, in concentrations that contribute to the destruction of the barrier in question;
Exposure to heavy metals such as nickel, gold, chromium, and lipid-lowering drugs also inhibit the repair of the stratum corneum barrier, damaging it like ultraviolet radiation.
Mechanism of action of skin sunscreens
Sunscreens for the skin that optimize barrier function should have anti-inflammatory, repairing and photoprotective properties
that increase the effectiveness of the sunscreen against carcinogenic ultraviolet radiation. Read more on estet-portal.com on what ingredients should be included in sunscreens for the skin. There are a large number of herbal sources that contain ingredients that create the ideal environment in the skin for maximum effectiveness of a sunscreen for the skin. They help reduce skin problems resulting from chronic inflammation.Products with sunscreen ingredients significantly slow down photoaging
and neoplasia; however, the skin cancer epidemic continues to spread. Skin sunscreen ingredients bind to corneocytes, stratum corneum lipids, and epidermal cells of the granular layer. Therefore, the damaged stratum corneum of the skin contributes to the deterioration of the bonds with the molecules of sunscreens for the skin. As a result, there is a further significant reduction in photoprotection.It is logical to assume that applying a product that restores said barrier to the skin before applying a sunscreen to the skin will enhance protection from solar radiation. The FDA recommends additional photoprotection for topical applications of hydroxy acids, retinoids, and benzoyl peroxide due to increased skin damage.
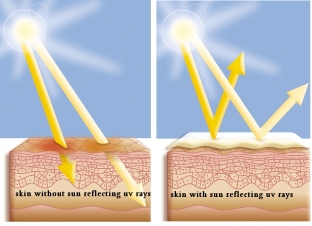
Usage rules and composition of sunscreens for skin
Hydration, or hydration, is not correlated with the function of optimizing the stratum corneum's permeability, so when using any sunscreen for the skin, which by definition is more than 50% water phase, proper repair of the damaged barrier cannot be expected. A product that truly restores the stratum corneum barrier must contain the appropriate ingredients at therapeutic concentrations.
Required Ingredients for Skin Sunscreen:
- medical vaseline;
- lanolin;
- mineral oil;
- safflower;
- olive;
- sunflower, wheat germ;
- glycerin;
- beeswax;
- mallow.
According to research, there are very few such products - only 11%.
The importance of barrier function for photoprotection has also been documented with topical application of products containing a mixture of just three protective stratum corneum lipids (cholesterol, ceramide and linoleic acid) without any specific sunscreen.
Also, products containing these lipids were statistically more effective than hydrocortisone in reducing redness and swelling of the skin caused by the use of topical tretinoin, tazarotene and exposure to ultraviolet B radiation.
Thus, the use of sunscreens with the ingredients listed above is extremely important for any skin, as it maintains its health and beauty.>






Add a comment