Benign neoplasms of the skin and soft tissues, tumor-like skin lesions treated with laser technologies
Epithelial tumors and tumor-like lesions of the skin include: tumors of the sweat and sebaceous glands, hair follicles, epithelial tumors of unknown etiology, epithelial tumors of viral etiology, hamartomas. Also in this section, benign fibrous tissue tumors will be considered due to the similarity of their treatment.

MD, Professor, Honored Doctor of Ukraine,
President of the Ukrainian Society of Aesthetic
General Director of the Ukrainian
Institute of Plastic Surgeryand aesthetic medicine "Virtus"
The tactics of removing benign neoplasms of the skin and soft tissues is as follows: epidermal and intradermal neoplasms with a diameter of more than 5-8 mm are recommended to be surgically excised.
Benign tumors of the sweat glands
Benign tumors of the sweat glands include:
hydradenoma (syringoma);
papillary syringocystadenoma (papillary syringoadenoma, papillary adenoma of the sweat gland);
- eccrine pore;
- hydrocystoma (hydrocystoma, cystadenoma).
- The depth of these neoplasms is the dermal layer of the skin. Due to their small size, syringoma, syringoadenoma, eccrine poroma, eccrine and apocrine hydrocystomas can be easily removed with a CO2 laser (10600 nm). Continuous mode with 2-4W power is recommended.
- Benign tumors and tumor-like lesions of the sebaceous glands
This type of neoplasm includes:
nevus of sebaceous glands (Yadasson, naevus sebaceous);
Adenoma of Pringle's sebaceous glands;
- sebaceous hyperplasia (senile sebaceous hyperplasia);
- rhinophyma.
- The tactics of their treatment is determined by the depth of occurrence (dermis).
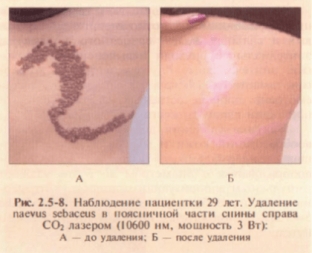
- Naevus sebaceous: surgical excision or laser vaporization may be performed (Fig. 2.5-8).
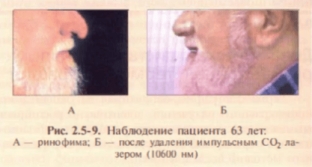
 The aim of laser ablation in the treatment of rhinophyma is to remove hypertrophic tissue while leaving an adequate glandular reserve for re-epithelialization without scarring. Ablation must be stopped immediately after reaching the level of the sebaceous glands. CO2 laser and pulse-modulated Er:YAG laser can be used to slow the development of rhinophyma (Fig. 2.5-9). Of the complications, hypopigmentation and a reduction in the number of protruding pores are often observed; scarring is unlikely but possible.
The aim of laser ablation in the treatment of rhinophyma is to remove hypertrophic tissue while leaving an adequate glandular reserve for re-epithelialization without scarring. Ablation must be stopped immediately after reaching the level of the sebaceous glands. CO2 laser and pulse-modulated Er:YAG laser can be used to slow the development of rhinophyma (Fig. 2.5-9). Of the complications, hypopigmentation and a reduction in the number of protruding pores are often observed; scarring is unlikely but possible.
 Neoplasms of the hair follicle are usually divided into three types:
Neoplasms of the hair follicle are usually divided into three types:
trichoepithelioma;
trichofolliculoma;
- Tricholemmoma.
- The depth of these neoplasms is the dermal layer of the skin.
- Trichoepithelioma, trichofolliculoma and tricholemmoma are well amenable to destruction with a CO2 laser; the prognosis is favorable.
In addition to the above neoplasms, the following occur:
senile keratoma;
keratoacanthoma;benign squamous keratosis (keratopapilloma, papilloma);
skin horn;
carcinoid skin papillomatosis Gottron.
The depth of these neoplasms is the epidermis, but they can also capture the papillary dermis.
Seborrheic keratosis is a benign hyperplastic tumor of the epidermis. Mostly destructive methods of treatment are used (for example, an erbium laser, 2940 nm) (Fig. 2.5-10). When removing such formations, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination and dermatoscopy due to the risk of malignant tumors associated with seborrheic keratosis 9 melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma).
Various methods are used to treat senile keratoma. Ablation can be performed with both pulsed CO2 and Er:YAG lasers. Laser ablation of senile keratoma is usually performed up to the papillary dermis. Prior to ablation, a biopsy of large masses is recommended to rule out squamous cell carcinoma. Re-epithelialization takes about two weeks.
For the treatment of keratopapilloma, laser destruction is used using a continuous CO2 laser; the prognosis is favorable.
To treat keratoacanthoma and cutaneous horn, both surgical excision and laser vaporization can be used.
For the treatment of Gottron's carcinoid papillomatosis, it is first advisable to eliminate acute inflammation in the lesions with the help of general and local therapy, and then laser vaporization can be applied. If this treatment is ineffective, surgical excision with subsequent plastic surgery is indicated.
Benign epithelial neoplasms of a viral nature
Common warts (vulgar, simple, palmar);flat warts (juvenile);
plantar warts;condylomas acuminata;
molluscum contagiosum.
Depth of vulgaris, flat and plantar warts - epidermis, genital warts and molluscum contagiosum - epidermis and papillary dermis.
Common warts (Verruca Vulgaris): The effectiveness of laser treatment is 50-80%. Secondary and intractable neoplasms are less susceptible to laser treatment than primary ones. One study showed that 80% of primary warts were amenable to laser therapy, while only 48% of recurrences were eliminated. Periungual warts are especially difficult to treat.
Vascular lasers (500-600nm) are also effective in the treatment of flat warts. Warts are treated to superficial blanching and after a few days become a burn eschar.
Condyloma acuminata. Ablation of clinically visible lesions is performed with a pulsed CO2 laser under local anesthesia, and additional antiviral therapy is prescribed for the final destruction of the virus.
Molluscum contagiosum. The treatment is the removal of each element with surgical tweezers, followed by treatment with a 5% iodine solution or vaporization of CO2 with a continuous action laser.
When ablating viral lesions, special safety measures must be taken: the use of filtration masks with a particle filtration threshold of 0.1 micrometers and smoke pumps connected to the treatment site at a distance of no more than a few centimeters. It should be noted that viable HIV particles have been found in smoke when treating HIV-infected tissue with a CO2 laser.
Hamartomas
Hamartomas include warty nevus (epidermal, unilateral, ichthyosiform, hyperkeratotic, hard, linear nevus) - papillomatous malformation. The warty nevus grows extremely slowly, more often due to the growth of dirty gray or brown crusts, especially after injury and infection. The depth of the lesion is the epidermis, papillary dermis.
Depending on the depth of invasion, the verrucous nevus is removed by laser ablation or by using combined laser and surgical techniques.
Benign tumors of fibrous tissue: fibroma, fibropapilloma, dermatofibroma
Depth of lesion - epidermis, papillary dermis.
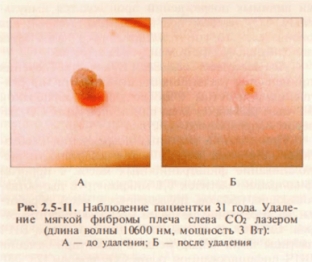
A lot of experience has been accumulated in the removal of neoplasms of fibrous tissue with a continuous CO2 laser (wavelength 10600 nm, power 2-5 W). When crossing the leg, further histological examination of the removed neoplasm is possible. These neoplasms do not recur and do not transform into a malignant tumor (Fig. 2.5-11).
 Previous parts of the article can be viewed here:
Previous parts of the article can be viewed here:
How a laser works: the physical basis of the interaction of light with tissue
Tissue damage under the influence of light and instrumental diagnostics of the condition of the skin
Source estet-portal.com






Add a comment