Albinism – This is a disease that is manifested not only by a change in the color of the skin and hair. The lack of melanin pigment also leads to the development of significant vision problems that begin in infancy and peak in adulthood.
First clinical studies have shown that the drug nitisinone increases melanin production in people with ocular albinism.
Read on estet-portal.com, how increasing melanin levels can help protect people with this disease from UV rays and promote normal vision.
Albinism: Pigmentation and eye damage
Oculocutaneous albinism is a rare hereditary disorder caused by mutations in the genes necessary for the production of melanin.
All types of oculocutaneous and ocular albinism present with similar ocular symptoms, including:
• various degrees of congenital nystagmus;
• hypopigmentation of the iris resulting in translucent iris;
• decreased visual acuity;
• A characteristic feature is also the incorrect passage of the optic nerves, which can lead to strabismus and reduced stereoscopic vision.
Unfortunately, no effective treatment for this disease has yet been developed. Patients are advised to avoid the sun and wear glasses. However, research is underway on how, by influencing an albino in infancy, to alleviate the course of the disease.
Read also: What metabolic disorders are accompanied by eye damage
Pathophysiology of changes in albinism
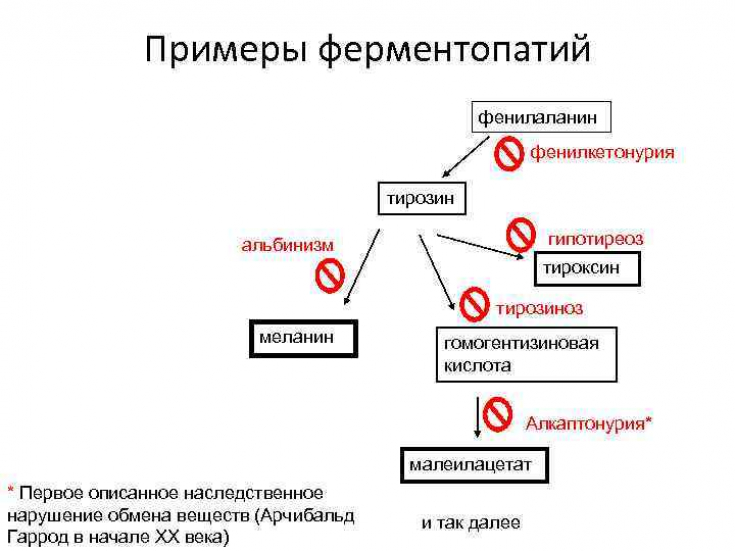
There are two types of melanin: brown-black eumelanin and yellow-red pheomelanin. Melanin is produced in specialized cells called melanocytes. Mutations in the genes responsible for the proteins that the melanocyte needs to produce melanin result in a reduction or absence of melanin pigment in a person's skin, hair, and eyes, a condition called oculocutaneous albinism.
Seven genes have been identified that are associated with different types of oculocutaneous albinism.
Depending on the degree of damage to the genetic apparatus, the clinical picture of albinism may vary. While in some patients the disease proceeds safely, in others it causes serious health problems.
Read the latest articles in Telegram!
Nitisinone: a new word in the treatment of albinism
Nitisinone — an agent for the treatment of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1, which inhibits the catabolism of the amino acid tyrosine, which leads to an increase in plasma tyrosine levels. Scientists believe that in people with albinism, higher levels of tyrosine help stabilize the mutated tyrosinase and increase the efficiency of the enzyme.
It is important to understand that treatment with nitisinone requires restriction of intake of tyrosine and phenylalanine-containing foods to prevent toxicity due to increased plasma tyrosine levels.
A recent clinical study of the effect of nitisinone showed a slight darkening of the skin and hair in patients with albinism after its use. In adult patients, the drug did not affect visual acuity, however, scientists hope that if treatment with nitisinone is started immediately after birth, pathological changes in vision can be avoided.
Children of the Moon: why does albinism manifest itself in humans







Add a comment