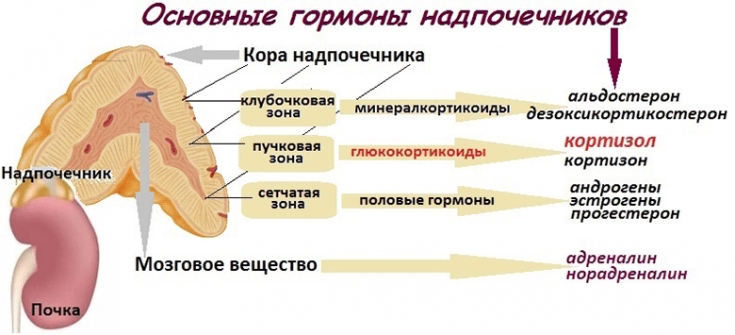
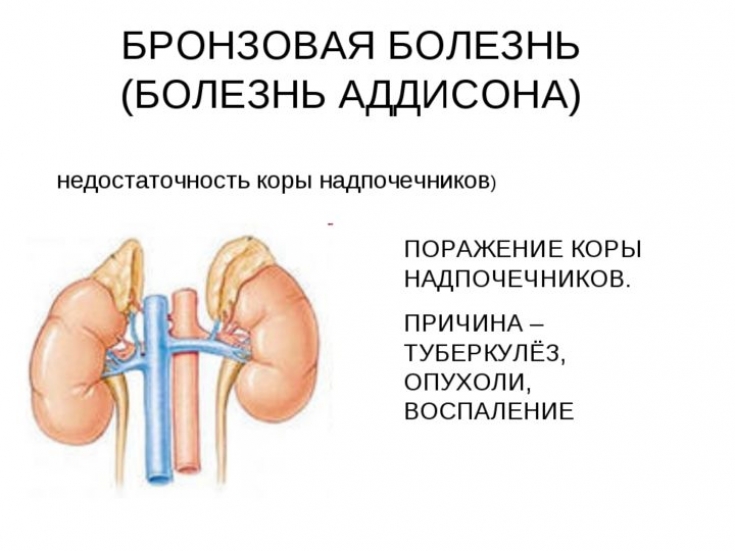
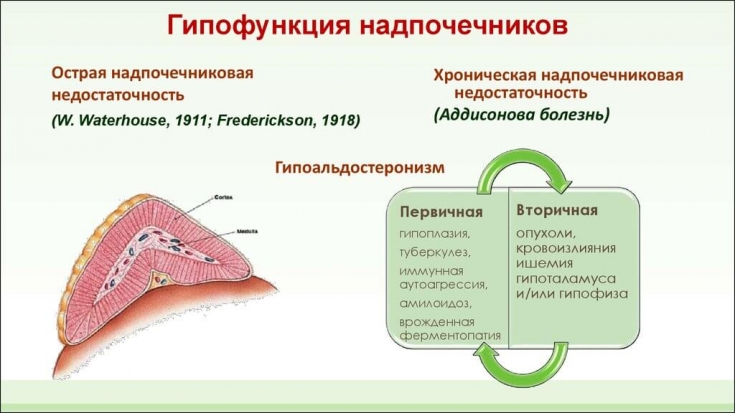
Hypocorticism – This is a pathological condition caused by hypofunction of the adrenal cortex. Among the possible causes of hypocorticism, Addison's disease (autoimmune adrenalitis, infections (tuberculosis, HIV), hemorrhages, metastases or adrenoleodystrophy) should be distinguished.
Hypocortisolism can also result from diseases of the pituitary or hypothalamus, such as neoplasms, injuries, infections, or circulatory disorders (in the elderly).
Symptoms of low cortisol levels include weight loss, fatigue, and hypotension. Possible hyperpigmentation of the skin. In some cases, hypocorticism can manifest as an acute Addisonian crisis. This condition is life-threatening and requires emergency medical care.
This article on estet-portal.com presents current approaches to the treatment of Addison's disease and other conditions that can lead to the development of hypocorticism. The scheme of emergency treatment of Addisonian crisis is also described in detail.
Life-threatening hypocorticism: emergency treatment of Addisonian crisis
If a patient is suspected of having an Addisonian crisis, the levels of the following parameters should be determined: hematocrit, plasma potassium and sodium, glycemia, plasma creatinine, plasma cortisol, ECG. Without waiting for test results, hydrocortisone replacement therapy at a dose of 100-200 mg should be started.
In the treatment of Addisonian crisis, an important point is the resumption and maintenance of adequate water and electrolyte balance: correction of hypovolemia, hyponatremia and hypoglycemia.
For more information about the medical treatment of Addisonian crisis, read further in the article.
Follow us on Telegram
Principles of Hormone Replacement Therapy for Addisonian Crisis
Hormone replacement therapy for Addisonian crisis begins with a 100-200mg hydrocortisone drug given intravenously.
Subsequently, treatment is applied according to the following scheme:
1. Day 1: Hydrocortisone 100 mg IV or IM every 6 hours;
2. Second day: Hydrocortisone 50 mg every 6 hours IV or IM;
3. Third day: hydrocortisone 25 mg every 8 hours (if possible, switch to tablets).
Subsequently, it is necessary to continue taking hydrocortisone at a dose of 40 mg intravenously / intramuscularly + 20 mg per os until the patient's condition is completely stabilized.
You may also be interested in: What are the manifestations of Cushing's syndrome in corticosteroma
Antimicrobials should be started if the patient has signs of a bacterial infection.
Hematocrit, plasma potassium, plasma sodium, and blood glucose levels should be closely monitored during the acute phase.
Addison's disease: modern principles for the treatment of hypocorticism
Treatment for Addison's disease consists of lifelong hormone replacement therapy: hydrocortisone at a dose of 10-25 mg per day (15 mg per day in a patient weighing 70 kg) and mineralocorticoids. The daily dose of hydrocortisone is divided into 2 or 3 doses to be taken between 8:00 am and 6:00 pm. In special cases, prednisolone at a dose of 2.5 mg-5 mg is taken at bedtime. Hydrocortisone at a dose of 5-10 mg can be taken in the afternoon. Reception of mineralocorticoids in a dose of 0.05-0.2 mg is carried out 1 time per day.
In the treatment of hypocorticism, the main principle is the administration of the lowest effective doses of hormones, which is associated with the development of their potential side effects.
Read also: Obesity treatment: tried and proven medicines
Features of substitution therapy for hypocorticism in special situations
Special situations where dose modification of hormone replacement therapy is necessary in a patient with hypocorticism include infection, physical activity, stress, and pregnancy.
If a patient with hypocorticism develops infections accompanied by febrile fever, the dose of hydrocortisone should be doubled.
A patient with hypocorticism may need to take an additional dose of hydrocortisone (5-10 mg) in case of intense physical activity or mental stress.
If a patient develops diarrhea for any reason or profuse sweating, hyponatremia may develop. In such cases, sodium loss can be replaced by salt intake.
In the last trimester of pregnancy, women with hypocorticism require an increase in the dose of hydrocortisone preparations by approximately 50%.
Thus, the following conclusions can be made:
1. Hypocortisolism is a condition requiring lifelong hormone replacement therapy;
2. Replacement therapy for hypocorticism consists in the use of hydrocortisone and mineralocorticoid preparations;
3. Addisonian Crisis – serious condition requiring immediate medical treatment;
4. In some situations, in particular with infections, physical stress, mental stress, and pregnancy, a modification of the doses of hormonal preparations is required.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Endocrinology" section. You may also be interested in: Cushing's syndrome: modern diagnosis and treatment of hypercortisolism.
Based on EMB Guidelines “Addison's disease and other conditions inducing hypocortisolism”







Add a comment