Ovarian cancer ranks first among all malignant processes in gynecology, which lead to death. Millions of women today suffer from various pathological processes of the ovaries, which in themselves are a factor predisposing to the occurrence of a malignant process. Considering the etiology of ovarian cancer, which has not been clarified to date, and the absence of pathognomonic symptoms of this pathology, the diagnostic process of this disease is very difficult. The treatment of ovarian cancer directly depends on at what stage of the process the tumor was diagnosed.
The main methods of diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer
To date, two main methods are used to treat ovarian cancer: surgery and chemotherapy. Radiation therapy has not shown good enough results in the treatment of ovarian cancer. An important point is the timely examination of patients at risk for developing ovarian cancer, since it is always much easier and more effective to prevent a pathology than to cure it. The risk group includes, first of all, patients with benign ovarian neoplasms, as well as women whose family history is aggravated by gynecological oncopathology.
Ovarian cancer treatment:
- instrumental and laboratory methods for diagnosing ovarian cancer;
- surgical treatment of ovarian cancer;
- The use of chemotherapy in the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Instrumental and laboratory methods for diagnosing ovarian cancer
The diagnosis of ovarian cancer is based primarily on instrumental research methods. Among laboratory studies, only the detection of ovarian cancer markers is of interest: CA-125, CA-19.9 and CA-72.4. The following instrumental methods for diagnosing ovarian cancer are used:
- ultrasound examination: on ultrasound, a malignant ovarian tumor is visualized as a large volumetric formation that does not have a clearly visualized capsule, but has many partitions and growths;
- Using Doppler ultrasound, many vessels inside the tumor can be determined, which confirms the malignant nature of the formation;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging help to clarify the structural features of ovarian tumors;
- laparoscopy is the most informative method to clarify the extent of the malignant process.
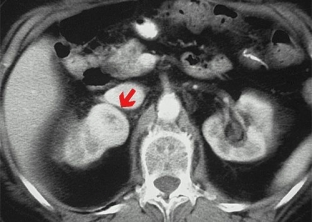
Surgical treatment of ovarian cancer
The leading treatment for ovarian cancer is surgery. Patients undergo a lower median laparotomy, which allows you to perform surgery in full. In the early stages of the disease, it is acceptable to remove the uterine appendages from the affected side with resection of the second ovary and part of the greater omentum. With a more common process, it is necessary to perform an extirpation of the uterus with appendages and resection of the omentum. For some patients, only supravaginal amputation of the uterus with appendages and subtotal resection of the greater omentum can be performed. It is important to conduct a thorough revision of the abdominal cavity to clarify the prevalence of the pathological process.
The use of chemotherapy in the treatment of ovarian cancer
Chemotherapy is now very widely used to treat ovarian cancer. Such drugs can disrupt the division of atypical cells and inhibit the growth of tumor tissues in the body. The selection of drugs depends on the nature of the malignant process, the stage of the disease, as well as the individual sensitivity of the patient to chemotherapy drugs. Several groups of cytostatics are used to treat ovarian cancer. Platinums are most effective against ovarian cancer, especially when combined with taxanes. For the treatment of advanced ovarian cancer, chlorethylamines are used, which are combined with other chemotherapy drugs. Chemotherapy can be performed before surgery, in order to reduce the tumor and stop proliferative processes, after surgery,






Add a comment