Today, cutaneous leishmaniasis has become an increasingly important disease due to the increasing integration of ethnic groups and opportunities to travel around the globe.
Skin leishmaniasis – transmissible protozoan disease of humans and animals, the pathogens of which are transmitted by mosquitoes. Leishmaniasis is common in Africa, Central Asia, the Americas, the Mediterranean and the Balkans.
In the CIS, the countries of Central Asia and Transcaucasia act as endemic foci of the disease. On estet-portal.com read about the pathogenesis, course, clinical picture, differential diagnosis and treatment of skin leishmaniasis.
Clinical picture of skin leishmaniasis depending on its form
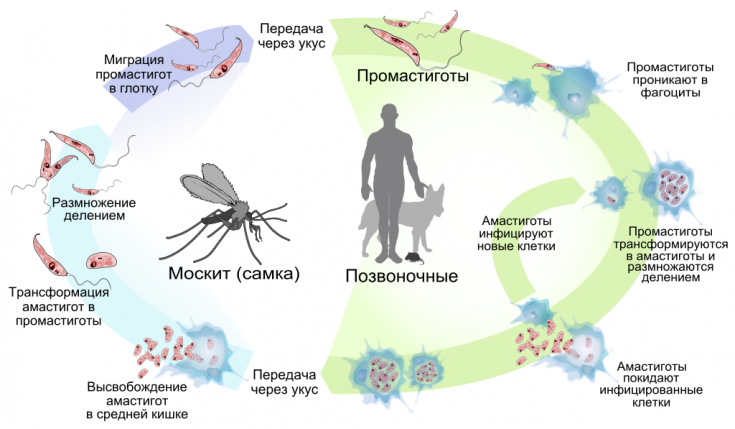
The causative agents of leishmaniasis – leishmania, live in the human or animal body as intracellular parasites.
The parasite resides in large numbers in macrophages, as well as in lesions of the skin.
The cutaneous form of leishmaniasis is represented by cutaneous leishmaniasis of the Old and New Worlds.
The clinic of cutaneous leishmaniasis of the Old World is characterized by a long incubation period: from 2-4 months to 1 year. The disease begins with the appearance of a tubercle, which slowly turns into a crater-like ulcer.
The lesion covers only the dermal layer of the skin and after about a year, scars form at the site of the tubercles.
New World leishmaniasis, which is common in America, is characterized by lesions not only of the skin, but also of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose. The pathological process can spread to neighboring areas and destroy the nasal septum, hard palate and pharynx.
Old World leishmaniasis, depending on the pathogen and the natural reservoir, is divided into urban (anthroponotic) and rural (zoonotic) types. >
Pathomorphology: characteristic histological picture of skin leishmaniasis
At the onset of the disease, when a mass reproduction of the pathogen occurs, the process begins with a banal inflammatory reaction.
Later, a granulomatous infiltrate is formed, which consists of histiocytes, neutrophil plasma cells and Langerhans cells.
For skin leishmaniasis, a decrease in the lumen of the vessels as a result of proliferation and swelling of the epithelium, as well as infiltration of the walls of the vessels.
In the lesions of the skin, specific bodies of Borovsky – bacterial cells, which are the main laboratory criterion for skin leishmaniasis.
 Cutaneous leishmaniasis must be differentiated from syphilis, skin tuberculosis, furunculosis.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis must be differentiated from syphilis, skin tuberculosis, furunculosis.
From the usual streptococcal ecthyma, such an ulcer differs in the presence of a roller-like infiltrate near its edge.
In comparison with syphilitic ecthyma, the roller in skin leishmaniasis is more pasty and less dense.
Don't scratch yourself! Ecthyma vulgaris develops after insect bites
Treatment of leishmaniasis: application of topical and general medicines
Treatment of skin leishmaniasis should be comprehensive and specific. Systemic treatment of the disease is carried out with drugs such as monomycin, glucantim, metacycline, doxycycline and antimony drugs.
Monomycin is used per os, 250 thousand units 3-6 times a day for a course of 10-12 days.
If there is a single tubercle of little age and without inflammation around it, the tubercle can be removed surgically, by diathermocoagulation, using liquid nitrogen.
Photodynamic therapy is used locally with applications of aminolevulinic acid for 3 hours and irradiation with a lamp.
Requires 5-10 treatments with a break of 10-14 days between treatments.
The lesions are dressed with ointments: 5% monomycin, 3% metacycline and 1% rivanol.Thank you, that you stay with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dermatology" section. You may also be interested in: When and what can be done with scar tissue: methods and means of correction






Add a comment