Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) - non-scarring atrophy of hair follicles, usually observed in people with a burdened family history.
The incidence of AGA is about 80% of all cases of hair loss in men and 20-40% in women. This disease manifests itself in carriers of an autosomal dominant gene with variable penetrance and expressivity, which is activated under the influence of male sex hormones, but an increase in their concentration in men is not always fixed.
Read on our estet-portal.com the most relevant approaches to the classification of this pathology and modern methods for diagnosing hair loss.
Classification of androgenetic alopecia in men
Signs of male AGA are bald patches along the frontal hairline, mostly triangular in shape, with further hair thinning in the parietal region. Even in the most severe cases, AGA does not spread to the back of the head and the sides of the scalp.
Follow us on Instagram!
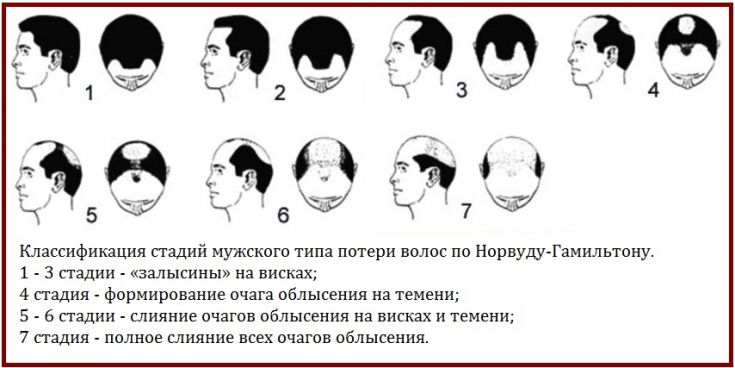
According to the classification of Hamilton (Hamilton, 1951), modified by Norwood (Norwood, 1970), in case of AGA of the male type, 7 stages of the disease are distinguished:
I – almost imperceptible signs of baldness;
II – slight shift in hair growth along the forehead;
IIA - displacement of the anterior hairline, hair thinning along the midfrontal line of the scalp;
III – pronounced displacement of the frontal hairline;
IIIA – pronounced shift of the line located along the forehead, expansion of the thinning zone;
IIIB – hair loss mainly in the parietal region, slight frontal alopecia may be recorded;
IV - thinning or absence of hair in the parietal region, frontal and frontotemporal alopecia increases towards the crown;
IVA – distribution of alopecia along the medial line and has a semicircular shape;
V - intense baldness in the frontal and parietal areas, which is separated by a narrow strip of sparse hair;
VA - continuous baldness of the frontal and parietal areas of the scalp;
VI - the entire area of alopecia extends laterally and backwards;
VII - a narrow strip of hair remains from the temporal areas to the back of the head
Almost all men with AGA have normal circulating androgen levels.
Clinical features classification of female hair loss
In women, androgenetic alopecia most often looks like diffuse thinning or thinning of hair in the central parietal region while maintaining the frontal hairline, damage to the parietal and occipital areas is observed.
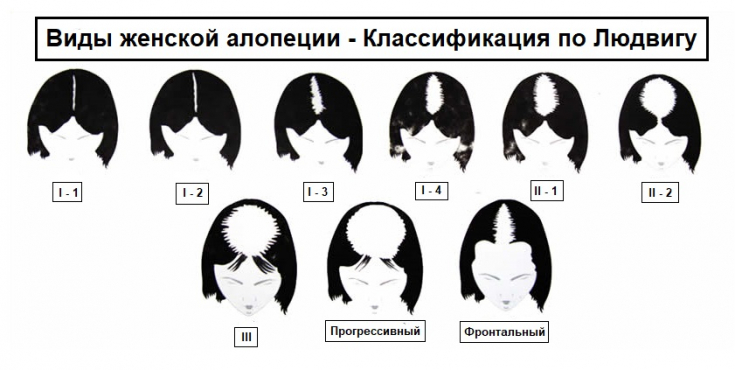
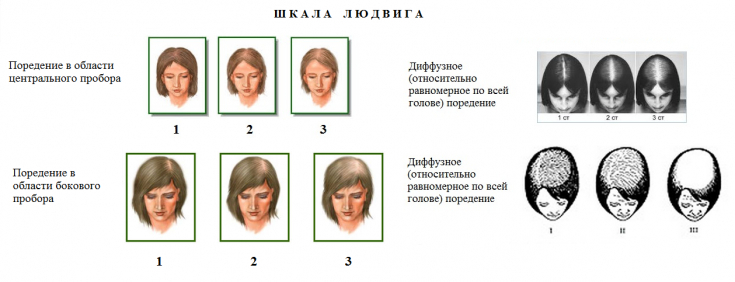
According to Ludwig's classification, there are 3 stages of the disease in case of AGA according to the female type:
I - hair thinning is observed in the parietal zone of the scalp, the frontal strip 1-3 cm wide remains unchanged;
II - a pronounced decrease in the density of hair growth in the parietal region;
III - pronounced thinning of the hair in the frontal-parietotemporal area, in the frontal area of the hair remains unchanged.
Androgenetic Alopecia: An Injectable with Proven Effectiveness
One of the types of hair loss in women is the herringbone pattern, which, like the Ludwig model, has 3 stages and is characterized by diffuse thinning of the hair of the central parietal area. At the same time, the frontal hairline is also involved in the process. Sometimes in women, hair loss can occur in male pattern baldness.
Diagnosis «Androgenetic alopecia - L64»
The diagnosis of AGA is usually established clinically by examining the hair and scalp and is based on the presence of the following clinical manifestations: progression of hair thinning and visual confirmation of the displacement of the anterior hairline, replacement of coarse hair with vellus hair in the fronto-parietal region, as well as familial history.
In patients with AGA, it is necessary to clarify the diet, the presence of bad habits (smoking), taking medications (chemotherapeutic or hormonal drugs with proandrogenic or antithyroid action, anabolic steroids, β-blockers, etc.) in women, it is necessary to tentatively collect gynecological history to rule out influence of hormonal disorders or concomitant underlying diseases.
If there is any diagnostic doubt, the following tests should be performed. In patients with AGA, the hair tension test is positive only in the active phase when there is an increase in the amount of telogen hair in the affected area. Counting the number of hairs in different growth phases - trichogram - determines the imbalance between the number of hair follicles in the growth stage and the resting stage.
An increase in the proportion of hair, is in the phellogen stage, up to 30% - the earliest sign of AGA.
The method of dermatotrichoscopy allows to assess the condition of the hair follicles and shafts, the orifices of the hair follicles, and the skin of the scalp.
In cases where at least 6% of the examined hair shows signs of miniaturization of the hair follicles, the diagnosis of AGA is not in doubt.
Additional diagnostic methods
In the case of clinical signs of AGA in the absence of a family history, manifestations of androgen excess, for example, acne, hirsutism, menstrual irregularities, galactorrhea, an endocrinological examination should be performed to identify possible diseases of the pituitary, ovaries, adrenal glands, thyroid gland. Sometimes, a biopsy of the scalp is performed to clarify the diagnosis.
To exclude any systemic disorders, complete blood count, serological testing for syphilis, antinuclear factor, antibodies to DNA, determination of serum iron concentration, ferritin, total serum iron-binding capacity are performed. Only a complete comprehensive diagnosis can provide a positive trend in the treatment of this disease.
Diagnostic algorithm: how to determine the cause of hair loss







Add a comment