Eyes – this is one of the organs that gives a person the opportunity to navigate in the environment. And any pathological process that directly affects the eyeball or the tissues surrounding it significantly impairs the quality of vision. Blepharitis is a disease in which the inflammatory process affects the edges of the eyelids, with a characteristic clinical picture. But this pathology can manifest itself in several forms, depending on the etiological factor. The diagnostic process is aimed at finding out the cause of the disease, which is very important for the effective treatment of blepharitis.
Correct diagnostics – key to successful treatment of blepharitis
Since blepharitis affects the tissues of the eyelids, it is quite easy to suspect this particular disease – characteristic symptoms point to it. At the same time, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods allow clarifying the etiological factor. The main danger of blepharitis is that the inflammatory process can pass to the surrounding tissues, provoking the development of keratitis, conjunctivitis, trichiasis and other eye diseases. Treatment of blepharitis should be based on the etiology of the inflammatory process and should be aimed at eliminating the cause and preventing complications of the pathology.
Blepharitis treatment:
- laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing blepharitis;
- non-drug treatment of blepharitis: modern methods;
- Drug treatment of blepharitis: what drugs are used.
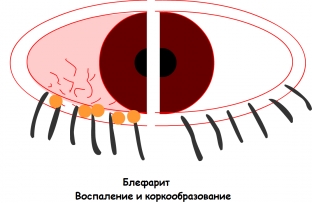
Laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing blepharitis
Diagnosis of blepharitis includes laboratory and instrumental studies, which is necessary to clarify the cause of the pathology. Among the instrumental methods, biomicroscopy of the cornea and conjunctiva using dyes is widely used. Laboratory studies are used in such cases:
- cultural methods – should be performed in patients with recurrent blepharitis, which is accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory reaction, or for those patients in whom drug therapy does not bring the desired results;
- eyelid biopsy is recommended for suspected carcinoma, drug resistance, or long-standing unilateral blepharitis;
- if a patient is suspected of having demodectic blepharitis – 5 eyelashes are removed from each eyelid and microscopy is performed. Finding larvae around the eyelash root and more than 6 motile mites confirms the suspected diagnosis.
Non-drug treatment of blepharitis: modern methods
Blepharitis often occurs in a chronic form, with periodic alternation of relapses and remissions of the disease. Non-drug treatment of blepharitis is aimed at reducing the frequency of relapses and improving the condition of the patient's eyelids. It includes the following procedures:
- moist compresses on the eyes;
- physiotherapeutic methods such as electrophoresis using solutions of antibiotics and vitamins, magnetotherapy, UHF therapy, ultraviolet irradiation and darsonvalization;
- electrolysis of hair follicles in the event of trichiasis;
- Therapeutic massage for dysfunction of the meibomian glands.
Drug treatment of blepharitis: what drugs are used
Drug treatment of blepharitis is used mainly in the period of exacerbation of the disease, to reduce its symptoms and eliminate etiological factors. Patients are advised to treat the eyelids with alkaline solutions and clean them with antiseptic preparations. Special ophthalmic solutions of antibacterial drugs, antiseptics and glucocorticosteroids are instilled into the conjunctival cavity. The edges of the eyelids, after preliminary cleaning, are treated with ointments containing corticosteroids and antibiotics. Symptoms of the "dry eye" syndrome eliminated through the use of various tear substitutes.







Add a comment