Erythema multiforme exudative – dermatosis, which is based on damage to the vessels of the dermis. This is an acute immune-mediated inflammatory reaction of the skin, which is characterized by rash polymorphism and a cyclic relapsing course with the appearance of a pronounced exanthema. With erythema multiforme, the mucous membranes of the mouth and genital organs are affected in the form of blisters and painful erosions.
The disease has a viral etiology and tends to resolve itself. The disease lasts 3-4 weeks, after which remission occurs with frequent relapses (up to 4-5 times a year).
Favorable factors of the occurrence of erythema can be drug allergies, gastrointestinal disorders, endocrine and visceral diseases.
Forms of erythema multiforme by etiological factor
There are two main forms of erythema multiforme – idiopathic and toxic-allergic.
The idiopathic form has an infectious-allergic genesis: most cases are provoked by the herpes simplex virus.
Other viruses are also associated with erythema multiforme: adenovirus, hepatitis B and C virus, Epstein-Barr virus.
Often this pathology accompanies such systemic diseases as autoimmune dermatitis, sarcoidosis, polyarteritis nodosa, Wegener's garnulomatosis, lymphoma and leukemia. The toxic-allergic form of the disease has an allergic origin.
This form of erythema multiforme is associated with the occurrence of immune reactions in the vessels of the upper layer of the dermis to drugs: antibiotics, sulfonamides, barbiturates, vaccines and serums.
Follow us on Facebook
Clinical picture of erythema multiforme – target papules
Very often the disease occurs in spring or autumn as a result of hypothermia or viral diseases of the respiratory tract. At the beginning, prodromal phenomena occur: malaise, fever, arthralgia, myalgia.
After the prodromal period, within 10-14 days, a polymorphic rash appears on the body - edematous spots, papules, vesicles.
Distinguish between macular, papular, maculopapular, bullous and vesicular forms of the disease.
A characteristic feature of such rashes are target-like foci (from 3 cm in diameter) with clearly defined boundaries, in the structure of which there are:
• dark disk of erythema in the center;
• ring of pale palpable edematous area;
• outer ring of erythema.
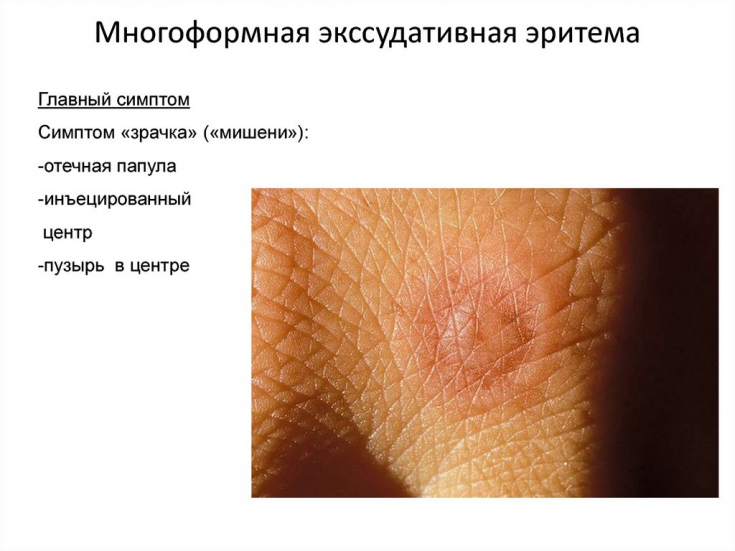
Such characteristic elements are also called the symptom of "iris", "shooting target"; or "bull's eye".
As a rule, the rash is localized on the extensor surfaces of the forearms, thighs, back of the hands and may be accompanied by itching or burning. The palms and soles, mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals are also affected.
After the formation of crusts and erosions, age spots with a yellowish-brown color remain.
The role of the herpes simplex virus in the occurrence of dermatological diseases
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis with other diseases
To make a diagnosis of erythema multiforme exudative, as a rule, the history and characteristic symptoms are sufficient. But in severe, complicated forms, as well as in doubtful cases, it is necessary to carry out the following:
• clinical examination (rash polymorphism, typical localization, subjective sensations of the patient);
• laboratory diagnostics (complete blood count – decrease in SOE, moderate leukocytosis is observed in severe form of the disease)
• Histological examination (in case of difficulty in diagnosing erythema multiforme, a skin biopsy is recommended).
The disease must be differentiated from urticarial vasculitis, Dühring's dermatitis, pemphigus acantholyticus, secondary papular syphilis, erythema annulare, Kawasaki disease and herpetic gingivostomatitis.
Treatment of erythema multiforme exudative: topical and systemic drugs
In most cases, the disease proceeds favorably, resolves on its own and does not require specific therapy.
Aniline dyes are used to treat erosions, as well as local hormonal ointments: methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% 2 times a day for 7-10 days or betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% for 2 weeks.
Systemic therapy includes antihistamines: chloropyramine 25 mg orally 2 times a day for 7-10 days or clemistine (1 mg) in the same regimen. You can also use loratadine or cetrizine hydrochloride 10 mg once a day for 7-10 days.
In severe cases, systemic glucocorticosteroids are prescribed: prednisolone 30-50 mg 0.5-1 mg per kg of body weight with a gradual dose reduction over 14 days.
If erythema is associated with herpes simplex virus, acyclovir 200 mg orally 5 times a day for a week or valaciclovir 500 mg 2 times a day for 5-10 days.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dermatology" section. You might also be interested in: How Dangerous Is Dermatitis Herpetiformis Duhring







Add a comment