Human paranasal sinuses include the maxillary and frontal sinuses, the sphenoid sinus, and the ethmoid labyrinth. The paranasal sinuses reduce the mass of the anterior sections of the skull, insulate sensitive structures from sudden temperature fluctuations in the nasal cavity, increase the resonance of the voice, and humidify and warm the inhaled air.
Thus, a special fluid is produced in the frontal sinus, which exits the sinus through the fronto-nasal canal. If the outflow of this fluid from the canal is disturbed, the fluid accumulates and a mucocele of the frontal sinus is formed.
What are the reasons for the development of frontal sinus mucocele?
Mucocele is common among teenagers. In preschool children, the mucocele does not occur, since the development of the frontal sinus ends at 7 years. & nbsp; A deviated nasal septum, tumors, exostases, foreign bodies in the nose and nasal trauma can provoke a violation of the outflow or a complete blockage of the fronto-nasal canal, after which periostitis develops. Frontal sinusitis can also interfere with the flow of fluid from the sinus by forming adhesions or scarring. In the presence of infectious foci (sinusitis, tonsillitis, rhinitis, laryngitis, chronic tonsillitis), the mucocele can become infected and give rise to the development of a pyocele.
The main symptoms that indicate the development of a mucocele
The development of a mucocele is often prolonged and asymptomatic in the early stages. From the action of the cause to the development of signs of a mucocele, several years can pass. Mucocele of the frontal sinus manifests itself with a headache, which gradually intensifies and is localized in the area of the frontal sinus. Then the pain is felt around the eyeball, above the orbit, in the inner corner of the eye a protrusion is formed, which has a rounded shape. When pressing on this protrusion, pain appears in it, and this is accompanied by a crunch. Strong pressure can form a fistula, through which a viscous mucous liquid begins to come out.
After some time, the mucocele leads to the descent of the lower wall of the frontal sinus. In this case, the eyeball moves outward and downward. This progression of the mucocele is accompanied by impaired visual acuity, diplopia, and impaired color perception. If the mucocele compresses the lacrimal ducts, patients have lacrimation. When a large amount of fluid accumulates in the frontal sinus, the sinus can break through and form a fistula through which the mucous fluid will exit. A complication of the mucocele is suppuration of the contents and spread to neighboring structures - the brain and orbit.
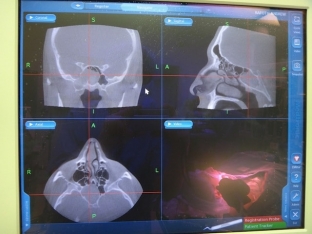
What diagnostic methods are used to detect mucocele?
It is not always possible to detect a mucocele with rhinoscopy. Only sometimes in the region of the middle nasal passage can a small, smooth protrusion be found. X-ray examination makes it possible to see an increase in the size of the sinus, a decrease in transparency and stretching of its bottom. It is possible to detect protrusion of the septum in the healthy direction. CT scan of the frontal sinus is the most accurate examination method. In order to determine the airiness, diaphanoscopy is performed. In difficult cases, a diagnostic puncture is performed. To determine the patency of the frontonasal canal, the frontal sinus is probed with a Lansberg probe. Differentiate the diagnosis of mucocele with a tumor, dermoid cyst and frontal sinusitis.
Treatment scheme for frontal sinus mucocele
Mucocele and pyocele must be subject to surgical treatment without fail. A radical operation is performed with the removal of the lower wall of the frontal sinus and the expansion of the fronto-nasal canal. After opening the sinus, its cavity is cleaned, followed by the establishment of drainage. The operation can be performed under general or local anesthesia. Postoperative drainage of the wound is carried out for 2-3 weeks after surgery until scarring. This is necessary for the stable formation of a connection between the nasal and frontal sinuses. Surgical treatment is accompanied by antibiotic therapy and, if necessary, antihistamines and decongestants.
The prognosis for frontal sinus mucocele is favorable with timely treatment. Prevention of the development of mucocele consists in the treatment of chronic infectious processes in the nasal cavity, throat and sinuses, correction of the nasal septum in case of its curvature, avoidance of injuries and hypothermia of the nose.







Add a comment