Acquired pigmented skin lesions that are small in size are called blue nevus. The blue nevus is also called the blue nevus of Yadasson – Hush, it has a dark – blue coloring. Often the nevus is single. The blue nevus is a benign formation, but melanoma dangerous - in very rare cases, the nevus can become malignant. More often, a blue nevus appears during puberty. Slow growth is characteristic, which is not accompanied by any sensations. What are the forms of the blue nevus, and what symptoms do they manifest, read on.
What does a blue nevus look like? Basic forms of blue nevus
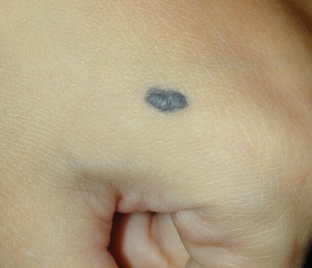
A blue nevus has the appearance of a clearly demarcated oval or spindle-shaped node located inside the skin. The size of a nevus rarely exceeds 1 centimeter in diameter. The dark blue color of the nevus is due to the accumulation of melanin in the deep layers of the skin. The nevus may rise above the skin.
Visually, looking at the nevus, it seems that there is a foreign body under the skin. Where the blue nevus is more often located, knows estet-portal.com. The nevus is localized on the back of the hands and feet, shins and forearms.
When a nevus transforms into melanoma, the clarity of its contours decreases, its growth accelerates, and unpleasant sensations appear in the area of the nevus.
Nevus growth is not accompanied by itching or pain.
Blue nevus shapes:
- Simple blue nevus – is a single nodule no more than 1 cm in diameter. It has a color from light – gray to black – blue. Most often, such a nevus is located on the neck, arms and face. May appear on the trunk, oral mucosa or cervix.
- Cellular blue nevus – education dark – blue in color, which has a size of 1.5 to 3 cm in diameter. Its surface is often uneven, so such a nevus can be perceived as a malignant neoplasm. The cellular blue nevus is located on the back surface of the feet and hands, on the lower back and buttocks.
- Combined nevus – combination of complex pigmented nevus, borderline or intradermal nevus with simple blue nevus.
Diagnosis and treatment of blue nevus
Diagnosis «blue nevus» is put on the basis of the delimitation of education, characteristic color and small size. For the purpose of more accurate diagnosis, dermatoscopy is performed, in which the boundaries, depth and structure of the nevus are visually studied with its increase. Skiascopic examination makes it possible to determine the nature of the distribution of melanin, as well as to study the structure of the nevus. Blue nevus is differentiated from dermatofibroma, melanoma, and borderline nevus.
After the removal of the blue nevus, a histological examination is performed, which reveals the accumulation of melanocytes in the middle and lower layers of the dermis. Melanin-filled cells are characteristic of a simple blue nevus.
If there is no change in the appearance of the blue nevus and its shape, the nevus does not require removal. The patient needs to be observed by a dermatologist and undergo an examination by a dermato-oncologist.







Add a comment