This article is devoted to the study of the nature of the course of the acute-phase reaction of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus during the formation and during the conservative treatment of a neuropathic ulcer, to determine the appropriateness of its modulation in terms of increasing the effectiveness of therapeutic measures.
Theoretical generalization and solution of the scientific problem regarding the role of acute phase reactants in the pathogenesis of neuropathic ulcers in type 2 diabetes mellitus is presented.
On the website estet-portal.com you can find information on the justification for the use of methods for correcting a non-specific reaction of the body of patients for the prevention and treatment of this complication of diabetes mellitus.
Features of neuropathic ulcer development
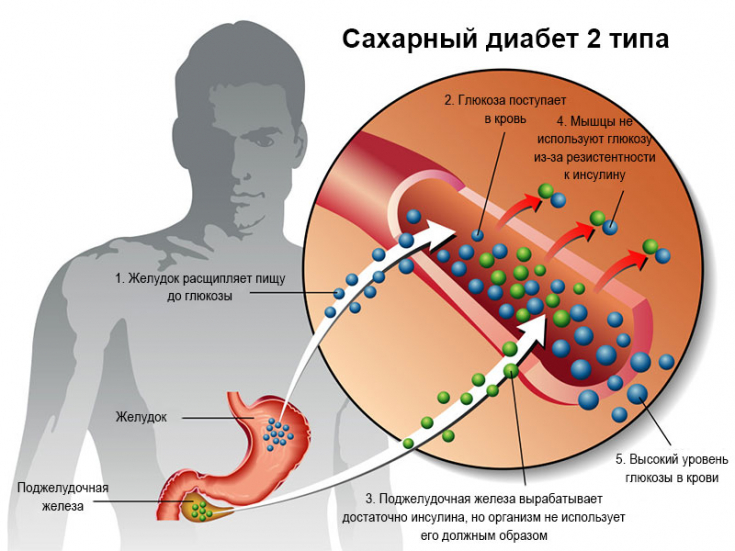
The development of diabetic neuropathic ulcer has been found to be associated with the duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus, the degree of impaired glucose metabolism, and the presence of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes is accompanied by signs of secondary immunodeficiency and chronic stress, an increase in the content of fibrinogen in the peripheral blood, inhibition of fibrinolytic activity and a decrease in the concentration of serum albumin. In individuals with a neuropathic ulcer, there is a further increase in the amount of fibrinogen without noticeable changes in fibrinolysis and albumin content.
Follow us on Instagram!
Additionally, in patients with inflammation, a significant increase in the activity of the complement system and an increase in the concentration of C-reactive protein in the blood were registered.

In cases of a positive effect of conservative treatment, a regression of the gastrophasic reaction occurs, the indicators of which are normalized already 10-15 days before the complete healing of the ulcerative process. In the absence of a therapeutic effect, the nature of the acute phase reactions in patients remains practically unchanged.
It is postulated that the activation of the synthesis of acute phase reactants, primarily fibrinogen and proteins that inhibit fibrinolysis, is to some extent responsible for the chronic course of inflammation and the impossibility of its normal repair for neuropathic ulcers in patients with type 2 diabetes.
It was concluded that it is expedient to determine these markers of the acute phase both for monitoring the course of inflammation and for timely prediction of the effectiveness of conservative therapy for diabetic neuropathic ulcers.
Links of the pathogenesis of diabetes complications
1. The course of type 2 diabetes mellitus is accompanied by an activation of a non-specific reaction & nbsp; The body is manifested by an increase in the content of fibrinogen in the peripheral blood, inhibition of the fibrinolytic activity of the blood plasma and a decrease in the concentration of serum albumin.
2. Formation of a diabetic neuropathic ulcer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus occurs in the long term after the onset of its development (12.3 ± 4.7 years) against the background of a long-term deterioration in glycemic control, progression of oxidative stress, stimulation of the complement system and subsequent activation of acute phase response, manifested by a significant increase in the content of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen in the peripheral blood.
Progressive Treatments for Diabetes Mellitus
3. The processes of activation of the synthesis of proteins of the acute phase precede the development of the inflammatory process in diabetic foot, and an increase in their content in the blood of diabetic patients can be considered as one of the indicators of an increased risk of possible formation of a neuropathic ulcer in them.
Peculiarities of treatment of complications of diabetes
Complex conservative treatment of diabetes mellitus, which includes insulin therapy, antibiotics, espa-lipon, tanakan and reopoliglyukin, contributes to a significant improvement in glucose and lipid metabolism, and a decrease in the intensity of oxidative stress.
These measures contribute to the fact that in 62.5% of cases it leads to complete healing of a neuropathic ulcer of the first and second severity.
In the case of positive results in the treatment of neuropathic ulcers, long before the complete regression of inflammation (in 10-15 days), a decrease in the acute phase response of the body is recorded. With negative consequences of therapy, the levels of C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, inhibition of fibrinolysis and activation of the complement system remain unchanged. The above indicates the feasibility of determining these indicators at the stages of treatment as prognostic markers of the possible effect of therapy for neuropathic ulcers.
Alpha-lipoic acid preparations against the background of basic therapy increase the frequency of complete regression of the inflammatory process in diabetic neuropathic ulcer by 23.2%, and this effect is accompanied by a previous decrease in the intensity of oxidative stress and suppression of the synthesis of fibrinogen and C-reactive protein with a simultaneous increase in fibrinolytic blood plasma activity.
Immunological changes in neuropathic ulcer
In patients with neuropathic ulcers with mycotic lesions of the nails, there is a lack of T-cell immunity, further inhibition of fibrinolysis processes and a decrease in the effect of conservative treatment of inflammation. The latter becomes possible only with the successful elimination of the fungal infection in patients with diabetes mellitus.
In the initial phases of the development of type 2 diabetes, activation of the formation of erythrocytes is observed, while in patients with a neuropathic ulcer, on the contrary, − depression of erythropoiesis, which is corrected by the use of insulin in complex therapy. It is postulated that such indicators as the number of erythrocytes and the content of hemoglobin in the peripheral blood of patients with type 2 diabetes in the absence of renal failure can serve as markers of the body's insulin availability.
Is it possible to achieve remission of type 2 diabetes with weight loss
The results of studies and analysis of literature data indicate that the activation of the synthesis of acute phase reactants, primarily fibrinogen and proteins that inhibit fibrinolysis, is to a certain extent responsible for the chronic course of inflammation, which determines the correction of treatment for neuropathic ulcers in patients with diabetes mellitus 2 type.
The role of a plant-based diet in the management of type 2 diabetes







Add a comment