According to experts, inflammation of the gums, or gingivitis, rarely occurs today as an independent disease. Much more often it becomes a reflection of diseases of the internal organs or accompanies other diseases of the oral cavity. One of the causes of gingivitis is called a weakening of the immune system, when even a slight injury to the gums with solid food or a chemical substance leads to the activation of bacterial agents. estet-portal.com notes that cases of iatrogenic forms of gingivitis have become more frequent, when, under the pressure of an advertising and informational flow about the importance of oral care, people find themselves with gum disease, even if it is not present. Treatment of gingivitis is carried out in a complex manner, if necessary, related specialists are involved.
The most common causes of gum disease and gingivitis
Gingivitis, which is quite common in young and old people, and even in children, is based on poor dental care. With poor cleaning of the teeth, and sometimes due to a decrease in the antibacterial properties of saliva and its chemical composition, sticky plaque forms on the teeth. It usually accumulates along the edge of the gums in places where it is difficult to reach with a toothbrush. Very soon, this plaque thickens and turns into tartar, which can no longer be removed with a brush.
Accumulation of plaque promotes the multiplication of pathogens in the gum area and causes gingivitis.
One of the important reasons for the development of gingivitis is the general weakening of the body's defenses against the background of hormonal fluctuations. This version is supported by the fact that very often adolescents in the pubertal period, women during menstruation and perimenopause suffer from inflammation of the gums.
Among other causes of gingivitis:
• long-term use of oral contraceptives, immunosuppressants, certain antihypertensive drugs;
• lack of vitamin C;
• diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
• smoking;
• abuse of too hot or too cold food;
• the use of too hard products that injure the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
In children, gingivitis often develops against the background of caries and other foci of chronic infection. Gingivitis affects people with any form of diabetes, with diseases of the liver and gallbladder, rheumatism.
Gum disease: a clinical manifestation of gingivitis
Localized gingivitis is most often diagnosed when inflammation of the gums covers a small area of \u200b\u200bit, although inflammation of both jaws occurs.
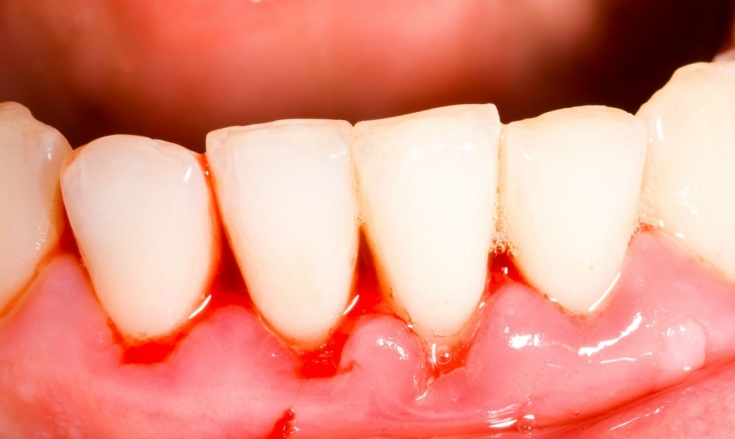
• In the acute form of gingivitis, the gum bleeds and can be ulcerated. There is swelling and hyperemia of tissues. The patient complains of pain, hypersalivation.
• In the chronic form of gingivitis, the clinical picture may be blurred, but the main manifestation of the disease is gingival hyperplasia. Sometimes almost the entire crown of the tooth is covered with gum tissue, which should not be normal.
• In the catarrhal form of gingivitis, the gums are very painful, its redness and swelling are noted. The patient notes hypersensitivity to hot and cold food, it is painful for him to chew.
• In the ulcerative-necrotic form of gingivitis, the mucous membranes of the gums have areas of necrosis. The patient's temperature may rise to febrile values, regional lymph nodes may increase, and bad breath appears. Sometimes during eating there is such severe pain that a person refuses to eat at all, and the condition is aggravated by anorexia with an increase in general weakness.
• In hypertrophic gingivitis, the gingival papillae gradually increase and cover a significant part of the tooth. At the first stages of the disease, the patient does not experience any discomfort, and only the dentist can notice hyperplasia during the examination. Over time, if left untreated, hypertrophied gums make brushing very painful, and due to poor oral care, multiple caries develops.
• In atrophic gingivitis, the level of the gums gradually decreases, exposing the neck of the tooth, and then its root. In this case, the patient can only feel discomfort when eating hot or cold food, and the dentist detects the pathology during a preventive examination.
In a separate group, some experts distinguish gingivitis in women during menopause. Inflammation of the gums here is associated with a decrease in the formation of keratin-containing epithelial cells. At the same time, the permeability of the mucous membranes increases, the gums are easily damaged and bleed even with slight touches.
Possibilities of treatment of gingivitis and troubles of its complications
Gingivitis therapy is usually started simultaneously with the treatment of the underlying disease that provoked it. They clean the teeth from plaque and tartar, prescribe rinsing with antiseptic solutions, with a strong pain syndrome, analgesics are acceptable.
For gingivitis, do not use topical preparations and rinses with an aggressive composition, including alcohol, so as not to aggravate the inflammation.
In case of hypertrophic gingivitis caused by improper filling of the tooth or an incorrectly fitted crown, the restoration of the crown or filling is carried out, after which a complete cure usually occurs. In case of persistent tissue hyperplasia, gingivectomy is indicated.
Lack of adequate and timely treatment of gingivitis is fraught with the development of periodontal disease and an increased risk of tooth loss. Therefore, if chronic forms of gingivitis are detected, even if there are no complaints from the patient, it is necessary to take measures to treat gingivitis.
Read also: When does hypertrophic gingivitis develop
Videos you might be interested in:







Add a comment