The problem of hair loss is one of the most frequent motives for men to visit a dermatological clinic. Androgenetic alopecia or male pattern hair loss is closely related to the hormonal characteristics of the male body. This type of alopecia is characterized by thinning of the hair of the parietal and frontal regions of the head. Timely access to a specialist helps prevent further progression of the disease.
In this article on estet-portal.com you will learn more about approaches to the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in men.
- Male Pattern Hair Loss: General details
- Non-surgical treatment of hair loss
- Hair transplantation
- Conclusion
Male Pattern Hair Loss Overview
Male pattern hair loss is the most common type of male pattern baldness. There is a gradual miniaturization of the hair, in which large pigmented terminal hairs are replaced by fine, colorless hairs. This type of baldness predominantly affects the crown, middle part of the scalp, hairline and anterior temporal areas of the scalp and is called androgenetic alopecia due to the central role of androgens and the genetic nature of inheritance.
Testosterone is converted to its metabolite 5-alpha-dihydroxytestosterone (DHT) by the second type isoenzyme of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme. Binding of DHT to androgen receptors in the hair follicle results in male pattern hair loss, although the exact molecular pathways are not fully understood. Differences in the location of these androgen receptors lead to the characteristic patterns of male pattern baldness.
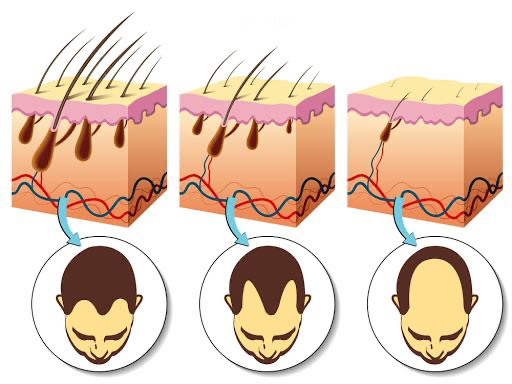
To the possible causes of alopecia also include thyroid disease, iron deficiency, diabetes, medications, chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
A common feature of various forms of scarring alopecia is irreversible damage to the hair follicles and the appearance of connective (scar) tissue in their place.
Causes of scarring alopecia in men:
Non-surgical treatment of hair loss
For those men whose hair loss is noticeable but it is too early for a hair transplant, there is an option to consider non-surgical methods.
Disease and ill health affect hair growth, so ensuring proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle and treatment of any disease is important to maintain good hair growth.
Khow drugs can affect hair growth.
Two medications can be used to treat male pattern baldness.
Topical Minoxidil is applied directly to the scalp twice daily as a liquid or foam and works by directly stimulating the growth phase of the hair follicle.
The most common side effect is contact dermatitis, which occurs less frequently with foam.
Oral finasteride, which is a type 2 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor, reduces DHT production and is taken at a dose of 1 mg per day. A possible decrease in erectile function and a decrease in libido deters some men, even if the incidence is low and is considered temporary. The incidence of prostate cancer is also thought to be declining, although men who do develop prostate cancer are associated with higher cancer rates.
Both drugs need to be taken for six to twelve months before effectiveness can be judged, and are more likely to help retain hair and delay hair loss than achieve significant growth.
Hair transplantation
Hair is removed from the donor area either by the strip method or by the Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) method. "Follicular Unit" refers to a natural group of hairs on the scalp where the follicles (from one to three, sometimes four) and their associated sebaceous glands, are surrounded by a perifollicular dermal sheath.
In the strip method, an ellipse is removed from hairy skin of various lengths and widths. Usually it is a horseshoe shape at the level of the occipital protuberance and the upper pole of the ears. Follicular units are excised from a strip of skin under magnification, ensuring minimal dissection and leaving a tissue cuff around the hair. However, when the donor wound closes and heals, a linear scar is left that is usually 1-2 mm wide (but can sometimes stretch wider).
In the follicular unit method, the hair is removed using a special instrument. A wide variety of instruments are currently in use, ranging from hand punches (identical to those used for dermatological biopsy) to automated hand punches and a robot at the most sophisticated end of the spectrum.
The benefits of the follicular unit method include less pain and faster healing of small round wounds, although the scars still remain, as on the surface, & nbsp; in the form of separate round scars, and subcutaneously.
In the future, the patient may wear a short haircut, as the ability to hide scars better than in the case of a linear scar from the strip method.
The donor area should be shaved before transplantation. In large cases, this may result in hair being collected outside the safe donor area.
Conclusion
Young men (under 30) who may be very concerned about the early onset of male pattern baldness should be treated with caution as the potential for future hair loss is not yet known at this age. The benefits of starting medication to prevent hair loss should be discussed with younger patients and a treatment plan should be developed, which may include step-by-step treatments.







Add a comment