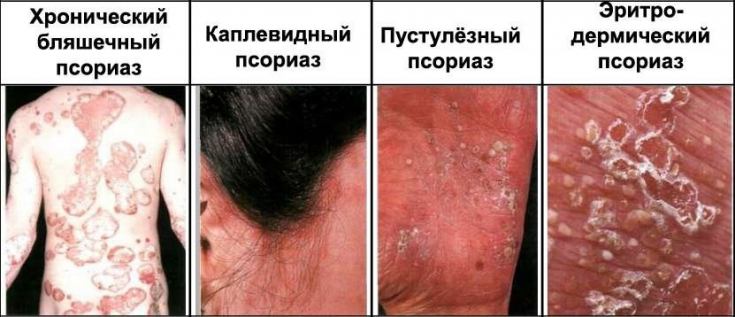
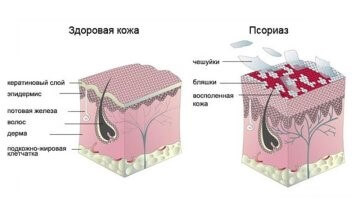
The treatment of psoriasis, especially severe forms, is not always an easy task. This is due to the fact that this disease is multifactorial and in the process of development it is possible to damage not only the skin, but also the joints, blood vessels, and kidneys. Therefore, timely therapy, evaluation of its effectiveness and, if necessary, correction is so important.
Now, the Psoriasis Research Group of the French Society of Dermatology has developed new guidelines to inform the medical society of dermatologists about new approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of psoriasis of the middle and severe degree. Read more about these developments in the article on estet-portal.com
- Diagnostic parameters for successful treatment of psoriasis
- General principles of systemic treatment of psoriasis
- Determination of the effectiveness of local and combined treatment of psoriasisa
Diagnostic parameters for successful treatment of psoriasis
Psoriasis treatment goals, both in current and previously published guidelines, set to avoid sub-optimal or unnecessary treatment. When setting goals for systemic treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis, one should take into account the severity of the disease, as well as factors that affect the progression of the disease, the presence of combined psoriatic arthritis (PSA) or any other concomitant diseases; the impact of the disease on the physical, psychological and social well-being of the patient; the risk/benefit ratio of continuous systemic treatment of psoriasis, and the patient's assessment and level of satisfaction with treatment.
Follow us on Instagram!
The European Consensus of Medical Experts defined an indicator of the effectiveness of psoriasis treatment and developed a algorithm for determining treatment tactics, which indicates that the response to the treatment of psoriatic lesions is successful if their prevalence or area has decreased to 75% ? area of active plaque inflammation (PASI 75) from baseline or 50% reduction in PASI (PASI 50) and DLQI score .
Primary psoriasis treatment failure is defined as one that does not achieve a response to a PASI 50 skin lesion level.
General principles of systemic treatment of psoriasis
Today, quite high rates of effectiveness in the treatment of moderate and severe psoriasis are observed with the use of phototherapy. It is used in the form of: low-dose narrow-spectrum ultraviolet irradiation (UVI-LUS) and psoralen photochemotherapy (PCT).
Handoplantar psoriasis: how to correctly diagnose
The use of UVA-PVA (outpatient treatment of psoriasis or self-administration at home with a device) is recommended at a frequency of 3 sessions per week (Grade A evidence), 20-30 sessions (Grade A).
When prescribing photochemotherapy for the treatment of psoriasis, the following regimens are recommended: in parallel with oral administration of psoralen (8-methoxypsoralen) at a dose of 0.6 mg / kg of body weight, followed, after 2-3 hours, UVI 2- 3 sessions per week. The total number of sessions is 20-30 (grade A).
No improvement after 20 sessions is considered ineffective for psoriasis and should be discontinued (Grade D).
Also, the updated guidelines for the treatment of psoriasis include topical psoralen baths. The following scheme for the local treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis has been developed: a bath solution is prepared by diluting a 0.75% solution of psoralen in 80-100 liters of water to obtain a concentration of 2.6 mg of psoralen per liter (grade C). The bath is taken for 15 minutes, after which, immediately after drying − UFO. The recommended doses of UVR are less than those used for oral therapy. The number of cumulative phototherapy sessions in a lifetime should not exceed 200 (Grade C).
Parapsoriasis: main varieties and their differencesi
Determination of the effectiveness of local and combined treatment of psoriasis
The beginning of the clinical effect of the treatment of psoriasis using the above regimens occurs after 1 or 2 weeks. The overall assessment of the effectiveness of therapy is carried out after 20 sessions.
Criteria for the effectiveness of local treatment of psoriasis:
- UFO-LUS: PASI 75 = 62-70%.
- Home UVI-LUS: no difference compared to stationary UVI-LUS.
- FHT: PASI 75 = 73-80%.
- FCT + bath applications: PASI 75 = 47%.
It is also possible to use combined regimens for the treatment of psoriasis using systemic drugs:
- Acitretin (10-20 mg daily, start 10-14 days before phototherapy: grade A for PCT, grade B minus; for UV-LUS, grade B for baths + PCT).
-Degree B − for methotrexate, adalimumab and eternacept + UV-LUS.
- Degree C − for ustekinumab + UFO-PVA.
Cytostatics in the treatment of arthritis as a severe complication of psoriasis
Side effects and possible complications of local and combined treatment of psoriasis: erythema, itching, skin bulosis, xerosis, hyperpigmentation, photoaging of the skin, oral administration of drugs + PCT may also cause nausea and abdominal pain.
Tocombination of local and systemic treatment of moderate and severe psoriasis not only increases the effectiveness of therapy and limits the progression of the disease, but also reduces the toxic effects of drugs with an exclusively systemic approach to the treatment of this pathology.
Updated 2019 guidelines for the treatment of psoriasis







Add a comment