Atopic dermatitis stands alone in the list of dermatological diseases, because, despite a significant history of research on this disease, there are still more questions than answers. So, it is known about the hereditary conditionality of this disease, about its many-sided manifestation, about the numerous factors that provoke an increase in its manifestation. But the methods of treatment are largely determined by the characteristics of the patient's body, as well as, of course, the timeliness of the start of therapy and scrupulous adherence to the doctor's recommendations. The patient should be aware that atopic dermatitis – it is to a large extent a way of life, following which, it is possible to increase the quality of life to an acceptable extent.
Atopic dermatitis is one of the most common dermatological diagnoses today. It is characterized by skin irritations and unbearable itching, which significantly reduces the patient's quality of life, interfering, among other things, with his social adaptation. The manifestations of atopic dermatitis can be undulating, aggravating, for example, in spring and autumn. Remission periods can range from several months to several years.
Why and who develops atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a hereditary disease. It is believed that if one of the parents or one of the next of kin suffers from atopic dermatitis, the child has a 50 percent chance of getting this disease too, if both parents are sick – the risk of transmitting dermatitis rises to 80 percent. At the same time, relatives may suffer from bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis – these are all manifestations of atopic dermatitis that should be kept in mind when taking an anamnesis.
The development of atopic dermatitis in a child can also be facilitated by a difficult pregnancy of a woman when she suffers from toxicosis and does not eat properly.
The reasons for which atopic dermatitis begins to appear may be the following:
- unfavorable ecology,
- malnutrition (including in children - lack of breastfeeding or its early termination),
- Increase in the number of industrial substances capable of causing allergies,
- stress, nervous and physical overload,
- increase in infectious diseases and decrease in immunity.
Usually, the disease manifests itself in the first five years of a child's life, and by the end of puberty, most children with atopic dermatitis recover, but in about 30 percent of them the disease passes into the adult stage.
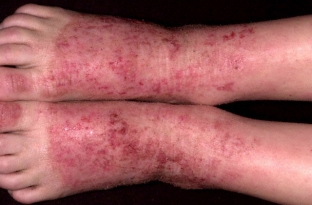
Stages, manifestations and symptoms of atopic dermatitis
Stages into which manifestations of atopic dermatitis are conditionally divided – children's and adult. The first of them manifests itself most often in the first year of a child's life, sometimes a little later, and ends by about 17 years, after which either recovery occurs or a transition to the second – adult stage. In the first stage, erythema spots on the skin are bright pink in color and are most often localized on the cheeks, buttocks and limbs. In the adult stage, erythema is pale pink, the preferred sites of inflammation – bends of the elbows and knees, face, neck, skin dry and flaky. At any stage, patients complain of severe itching of the affected areas of the skin.
In the acute stage of atopic dermatitis, a nodular rash appears on erymatous areas, the skin swells, then erosions form, which become covered with crusts and become wet. In the chronic stage, the skin thickens, pigments in places, flakes and cracks, children have wrinkles on the lower eyelids and tangled weakened hair on the back of the head.
For the chronic stage, the presence of scratching on the skin is especially characteristic, which carries the risk of complications in the form of infections.
Complications that are possible with atopic dermatitis
Complications of atopic dermatitis most often occur because the infection penetrates through scratched skin. Complications are usually of the following types:
- bacterial – when a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection joins, provoking a pustular rash all over the body, on the scalp, fever, deterioration in general well-being;
- viral – the herpes virus is most often the cause, lesions in the form of bubbles with a clear liquid appear around the lips, wings of the nose, on the eyelids, as well as in the oral cavity and on the genitals;
- fungal – the defeat is caused by yeast-like fungi, inflammation usually manifests itself in the folds of the skin, on the bends of the elbows and knees, behind the ears, on the oral mucosa.
Features of the associated infection dictate the choice of tactics for the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Principles for the choice of tactics for the treatment of atopic dermatitis
When choosing treatment tactics, all factors are taken into account – and the age of the patient, and the duration of the manifestations of the disease, and the stage and severity of manifestations, and the presence of associated or background diseases. First of all, the presence of an allergic factor that could provoke atopic dermatitis is found out, and measures are taken to eliminate it.
Further, the main task of the doctor is to eliminate itching. Antihistamines and tranquilizers, sedatives are recommended, and corticosteroids are given in severe cases.
In case of complications, therapy is supplemented with antiviral, antifungal drugs, antibiotics. If necessary, the treatment is supplemented with detoxification measures.
It is very important to explain to the patient that self-treatment of atopic dermatitis is unacceptable, since it threatens with a much more severe course with no periods of remission. In addition, the patient must remember that atopic dermatitis – it's pretty much a lifestyle that involves a specific diet, lifestyle, skin care habits – all this leads to a significant improvement in the quality of life and lengthens the periods of remission.







Add a comment