Botulinum toxin type A injections are among the minimally invasive procedures with a short recovery period – for this reason they are popular among men.
To achieve optimal correction results and avoid feminization in male facial rejuvenation, the practitioner must be aware of the major physiological and anatomical differences that must be considered during operation.
Dr. Aggie Zatonska talks about the important aspects of botulinum therapy for the male face.
Features to consider when rejuvenating a male face
To avoid feminization of the male face when correcting with botulinum toxin type A, it is important to take into account the following features:
• the skull of men is larger than that of women, and has a different shape;
• projection between the eyebrows in men is greater than in women;
• brow ridges in men are more pronounced;
• men's eyebrows are flatter and lower than women's;
• with androgenetic alopecia, the height of the forehead visually increases;
• in women, the forehead contour is higher, it is more rounded than in men;
• Ocular orbits in women in relation to the skull are proportionately larger;
• men's chin is wider and more massive, protrudes more;
• in women, the jaw has smoother curves.
Follow us on Instagram!
Consultation before the correction of the male face with botulinum toxin
At the examination stage, it is important to assess the patient's face: front and profile, at rest and during facial mobility, asymmetries, static and dynamic wrinkles, muscle mass.
It is imperative to warn the patient about possible side effects (swelling, bruising, redness) and discuss the results of the correction.
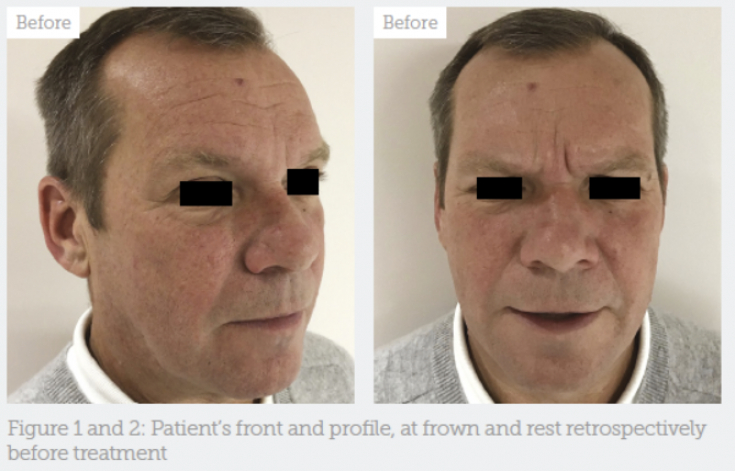
Fig. 1 and 2: face and profile of the patient at rest and during mimic activity before the procedure
The key to successful rejuvenation of both male and female faces – individual approach to the patient.
When correcting a male face with botulinum toxin type A, it is important to maintain the original position and shape of the eyebrows.
When correcting a male face with botulinum toxin type A, it is important to maintain the original position and shape of the eyebrows.
Botulinum toxin injections for forehead correction in men
Incorrect administration of botulinum toxin can lead to brow ptosis, a feeling of heaviness and unsatisfactory aesthetic results. The following are recommendations for working with the frontalis muscle, published in the journal Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery:
1. Botulinum toxin type A in the amount of 8–25 units is injected into 4–8 points.
2. The drug is injected intramuscularly along horizontal lines, lateral injection prevents the formation of an excessive bend of the eyebrow. Some experts recommend injecting smaller volumes of the toxin into the dermis of the lateral frontalis muscle to reduce the appearance of wrinkles in the lower forehead to avoid downward displacement of the eyebrow.
3. The lowest insertion points should ideally be located 1 cm above the orbital ridge.
4. Injection points in men with alopecia in the area of the frontal part of the scalp should be located higher; in such cases, an additional dose of the drug may be needed, which is injected under the bald patches.
BOTOX® in the upper part of the face: how to erase wrinkles from the forehead
Botulinum toxin type A for brow wrinkles
The brow wrinkles are usually deeper in men than in women. When botulinum toxin is injected, it is important to avoid muscle immobilization in the glabellar zone, otherwise the results of the correction will be unnatural, and the lateral part of the eyebrow will be raised, which is uncharacteristic for a male face. Because:
1. Botulinum toxin type A is injected in the amount of 12–40 units at 3–7 points.
2. When injecting into the brow pucker muscle, it is necessary to work 1 cm above the orbital ridge to avoid diffusion of the toxin into the levator eyelid muscle.
3. Too superficial mideyebrow injections can also act on the medallion frontalis muscle and lead to a lifting of the lateral brow.
4. To avoid brow lift, it is necessary to perform correction of the brow and forehead at the same time.
An angry mask on the face: everything you need to know about brow wrinkles
When correcting a male face with botulinum toxin, it is important to avoid immobilizing the muscles in the glabellar zone, otherwise the results will be unnatural.
Case study: rejuvenation of the upper third of the male face with botulinum toxin injections
A 55-year-old patient came to the author with complaints of forehead and periorbital wrinkles. 18 months earlier, forehead and eyebrow wrinkles were corrected with botulinum toxin.
During the procedure, Botox® was injected with a Becton Dickinson syringe (needle 31 gauge, 8 mm) into the central part of the interbrow and very superficially (subcutaneously) into the lateral part of the interbrow, frontalis and orbicularis muscles eyes.
In Fig. 3 shows injection points and number of units of botulinum toxin type A.
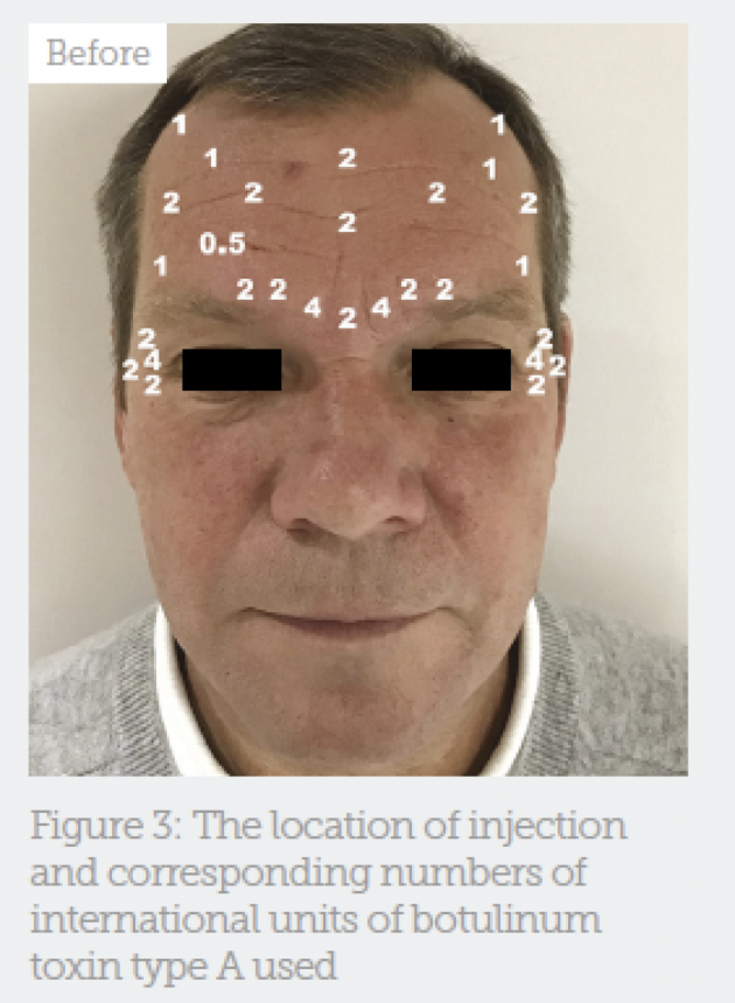
Fig. 3: Injection points and injected amount of botulinum toxin type A in international units
Note: Slight differences in injection sites and amount of drug injected on each side of the face are due to facial asymmetry.
Additional injections were made in the frontotemporal part of the hairline.
The results of the procedure are shown in photos 4 and 5.
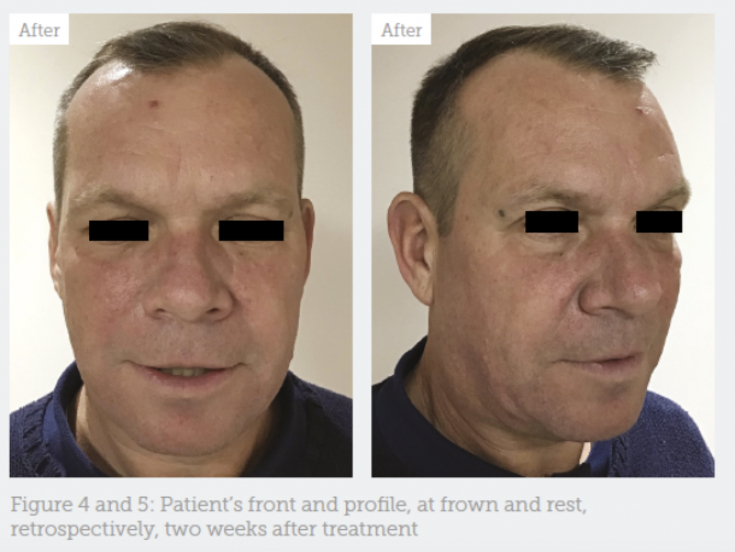
Fig. 4 and 5: face and profile of the patient at rest and during mimic activity two weeks after correction
In order to correct a slight brow lift after the initial procedure, an additional unit of neurotoxin was injected into the lateral part of the frontalis muscle on the right side of the face.
Adapted from Aesthetics







Add a comment